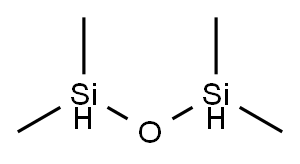
1,1,3,3-Tetramethyldisiloxane: A Versatile Compound for Efficient Chemical Transformations and Synthesis
Dec 26,2023
General Description
1,1,3,3-Tetramethyldisiloxane is a compound synthesized through hydrosilylation reactions using the Karstedt's catalyst. It is a versatile compound widely used in various chemical reactions. It can be synthesized through hydrosilylation reactions of allyl derivatives with hydrosilanes in the presence of the Karstedt's catalyst. The conversion and selectivity of the reaction can be improved by adding a phosphine ligand to the catalyst. 1,1,3,3-Tetramethyldisiloxane serves as a reactant in the hydrosilylation reaction with 1-octene, forming silicon-containing compounds used in industries such as pharmaceuticals, electronics, coatings, and elastomers. It is also used as a reagent in catalytic hydrosilylation reactions, enabling efficient and cost-effective transformation of tertiary and secondary amides to amines. The use of cationic IrIII metallacycles as catalysts and 1,1,3,3-Tetramethyldisiloxane as the silane reagent facilitates fast reactions with high yields, selectivities, and turnover numbers. Insights from mass spectrometry and DFT calculations provide a foundation for optimizing these catalysts and improving their catalytic performance in various chemical transformations.
Synthesis by Hydrosilylation Reactions
1,1,3,3-Tetramethyldisiloxane is a compound that can be synthesized through hydrosilylation reactions of allyl derivatives with hydrosilanes in the presence of the Karstedt's catalyst. In a study conducted by Igarashi et al. (2014), different allyl derivatives such as allyl acetate, N,N-dimethylallylamine, and allyl Et ether were reacted with hydrosilanes including octahydridosilsesquioxane, 2,4,6,8-tetramethylcyclotetrasiloxane, and tetramethyldisiloxane, using the Karstedt's catalyst. The conversion and selectivity of the reaction were also studied with the addition of a phosphine ligand, PPh3, to the catalyst. The hydrosilylation of allyl derivatives with T, D, and M type hydrosilanes using Bis(1,3-divinyl-1,1,3,3-tetramethyldisiloxane)platinum as the catalyst and solvents such as xylene and toluene-d8 at temperatures ranging from room temperature to 60°C for 3 hours resulted in a 100% yield of 1,1,3,3-tetramethyldisiloxane. This synthetic method can be useful in the production of 1,1,3,3-tetramethyldisiloxane for various industrial applications. 1

Figure 1. Synthesis of 1,1,3,3-tetramethyldisiloxane
Applications in organic synthesis
Reactant
1,1,3,3-Tetramethyldisiloxane is a versatile reactant widely used in various chemical reactions. In the context mentioned, it serves as a reactant in the hydrosilylation reaction with 1-octene. The invention describes a fixed-bed catalyst complex, which consists of a platinum-based metal carbene catalyst and a catalyst support containing silica, alumina, and/or glass. The N-Methyl-N'-(3-trimethoxysilylpropyl)imidazolecarbene divinyltetramethyldisiloxane platinum complex is specifically prepared for this purpose. During the hydrosilylation reaction, 1,1,3,3-Tetramethyldisiloxane reacts with 1-octene in the presence of the catalyst complex. The reaction results in the addition of silicon atoms from 1,1,3,3-Tetramethyldisiloxane to the carbon-carbon double bond of 1-octene, forming a new silicon-carbon bond. This process is known as hydrosilylation and is widely utilized in the synthesis of silicon-containing compounds. 1,1,3,3-Tetramethyldisiloxane's use as a reactant in hydrosilylation reactions enables the synthesis of various organosilicon compounds with diverse applications. These compounds find use in industries such as pharmaceuticals, electronics, coatings, and elastomers. 2
Reagent
1,1,3,3-Tetramethyldisiloxane finds significant application as a reagent in the catalytic hydrosilylation reaction described in the given context. The reaction utilizes readily accessible cationic IrIII metallacycles as catalysts, along with 1,1,3,3-Tetramethyldisiloxane as the inexpensive silane reagent. The hydrosilylation of tertiary and secondary amides to amines is efficiently catalyzed by these IrIII metallacycles at low loadings. The use of 1,1,3,3-Tetramethyldisiloxane enables fast reactions with high yields, selectivities, and turnover numbers. Through the employment of mass spectrometry, a transient iminium intermediate has been observed for the first time, shedding light on the reaction mechanism. Furthermore, density functional theory (DFT) calculations have been employed to study the activation of the catalyst and 1,1,3,3-Tetramethyldisiloxane. These insights provide a foundation for optimizing IrIII metallacycles through ligand modifications, thereby improving their catalytic performance. Ultimately, this advancement facilitates the broad application of catalysts based on metallacycles in various chemical transformations beyond the scope of the present reaction. 3
Reference
1. Hydrosilylation of allyl derivatives with T, D and M type hydrosilanes. Journal of Organometallic Chemistry, 2014, 749: 421-427.
2. Fixed-bed platinum carbene hydrosilylation catalyst complexes and related methods. 2010, Patent Number: US20100280266.
3. Efficient and Selective Hydrosilylation of Secondary and Tertiary Amides Catalyzed by an Iridium(III) Metallacycle: Development and Mechanistic Investigation. ChemCatChem, 2017, 9(11): 2009-2017.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- 1,1,3,3-Tetramethyldisiloxane: A Versatile Organosilane for Safe and Selective Organic Synthesis Processes Apr 28, 2024
1,1,3,3-Tetramethyldisiloxane is a versatile organosilane with reactivity, and safety in organic synthesis, notably as a reducing agent for selective transformations, like phosphine oxides.
- 1,1,3,3-Tetramethyldisiloxane: properties, applications in battery production and safety Jul 12, 2023
1,1,3,3-Tetramethyldisiloxane enhances battery performance and is compatible with various materials. Follow safety precautions when using it.
- Application of 1,1,3,3-Tetramethyldisiloxane Oct 24, 2019
1,1,3,3-Tetramethyldisiloxane is soluble in many organic solvents, such as aromatic hydrocarbon and petroleum hydrocarbons, and so on.
Bakuchiol (BAK), a meroterpene phenol abundant in the plant Psoralea corylifolia, is an emerging cosmeceutical agent with promising anti-aging, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial properties.....
Dec 26,2023Natural ProductsThe method for the synthesis of berotralstat dihydrochloride relies on two fragments, berotralstat carboxylic acidFragment and chiral dibenzylamine.....
Dec 26,2023Inhibitors1,1,3,3-Tetramethyldisiloxane
3277-26-7You may like
1,1,3,3-Tetramethyldisiloxane manufacturers
- 1,1,3,3-Tetramethyldisiloxane
-

- $50.00 / 1kg
- 2023-11-16
- CAS:3277-26-7
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 0.99
- Supply Ability: 20 tons
- 1,1,3,3-Tetramethyldisiloxane
-
- $0.00 / 1kg
- 2023-11-01
- CAS:3277-26-7
- Min. Order: 0.1kg
- Purity: 99.0%min
- Supply Ability: 20000kg
- 1,1,3,3-Tetramethyldisiloxane
-

- $0.00 / 25KG
- 2023-09-08
- CAS:3277-26-7
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 50000KG/month