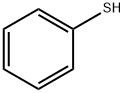
Thiophenol
- CAS No.
- 108-98-5
- Chemical Name:
- Thiophenol
- Synonyms
- BENZENETHIOL;PHENYL MERCAPTAN;Phenylthiol;Thiophenol/Benzenethiol;Thiofenol;usafxr-19;Thiohenol;FEMA 3616;thio-pheno;THIOPHENOL
- CBNumber:
- CB3852774
- Molecular Formula:
- C6H6S
- Molecular Weight:
- 110.18
- MDL Number:
- MFCD00004826
- MOL File:
- 108-98-5.mol
| Melting point | -15 °C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 169 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.078 |
| vapor density | 3.8 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 1.4 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index |
n |
| FEMA | 3616 | BENZENETHIOL |
| Flash point | 123 °F |
| storage temp. | Store at RT. |
| solubility | DMSO, Ethyl Acetate |
| pka | 6.6(at 25℃) |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Clear colorless to slightly yellow |
| Odor | Unpleasant |
| Odor Type | meaty |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| Sensitive | Stench |
| Merck | 14,9355 |
| JECFA Number | 525 |
| BRN | 506523 |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 0.5 ppm (~2.5 mg/m3 ) (ACGIH). |
| Dielectric constant | 4.4(25℃) |
| Stability | Stable. Flammable. May form explosive mixtures with air. Stench. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| LogP | 2.33 |
| Substances Added to Food (formerly EAFUS) | BENZENETHIOL |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 108-98-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EWG's Food Scores | 1 |
| FDA UNII | 7K011JR4T0 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzenethiol(108-98-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Thiophenol (108-98-5) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |     GHS02,GHS06,GHS08,GHS09 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H226-H300+H310+H330-H315-H319-H335-H361-H372-H410 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P210-P273-P280-P303+P361+P353-P304+P340+P310-P305+P351+P338 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | T+,T | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 10-24/25-26-41-36/37/38 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 23-26-28-36/37/39-45-28A-16 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 2337 6.1/PG 1 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | DC0525000 | |||||||||
| F | 10-13-23 | |||||||||
| Autoignition Temperature | 450 °C | |||||||||
| Hazard Note | Toxic/Stench | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 6.1 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | I | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29309099 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | bird - wild,LD50,oral,24mg/kg (24mg/kg),Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. Vol. 21, Pg. 315, 1972. | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Thiophenol Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
Phenyl mercaptan is a water white liquid. Repulsive, penetrating, rotten cabbage, garlic-like odor.
Chemical Properties
Benzenethiol has a repulsive, penetrating, garlic-like odor.
Chemical Properties
colorless liquid
Occurrence
Reported found in cooked/boiled beef.
Uses
In the production of pesticides, polymers, and pharmaceuticals; as a food additive
Uses
Pharmaceutical synthesis.
Uses
Thiophenol is used as a mosquito larvicideand as an intermediate in organic synthesis.It is effective in reducing peroxide formationin jet fuels (Watkins et al. 1989).
Preparation
By reduction of benzenesulfonyl chloride with zinc dust in sulfuric acid.
Definition
ChEBI: A thiol in which the sulfanyl group is attached to a phenyl group.
Aroma threshold values
Detection: 10 to 50 ppb
Synthesis Reference(s)
Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 35, p. 1770, 1987 DOI: 10.1248/cpb.35.1770
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 16, p. 946, 1951 DOI: 10.1021/jo01146a019
Tetrahedron Letters, 21, p. 1677, 1980 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)77784-7
General Description
A clear liquid with a repulsive odor. Boiling point 168.3°C. Insoluble in water and denser than water. Very toxic by ingestion, skin absorption, and by inhalation. Used as a chemical intermediate and in mosquito control.
Air & Water Reactions
Flammable. Oxidizes upon exposure to air, especially when dissolved in alcoholic ammonia, to form diphenyl disulfide, C6H5SSC6H5 [Merck 11th ed. 1989]. Is supplied under an atmosphere of nitrogen. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Thiophenol reacts with acids to generate toxic fumes of oxides of sulfur. [Lewis, 3rd ed., 1993, p. 1021]. Reacts exothermically with strong oxidizing agents.
Hazard
Skin irritant.
Health Hazard
Animal toxicity data show thiophenol to behighly toxic; the oral LD50 value in testanimals is <100 mg/kg. Its irritant actionon rabbits’ eyes and skin is severe. Thiophenol can enter the body by ingestion,absorption of the liquid through the skin,and inhalation of vapors. In humans, thetoxic symptoms include restlessness, incoordination, muscle weakness, headache, dizziness, cyanosis, lethargy, sedation, respiratorydepression, and coma. Death may result fromhigh doses. Repeated exposure to thiophenol vapors caused injury to the lung, liver,and kidneys in mice. Thiophenol did notadversely affect the growth, viability or morphological development of the offspring at adose of 40 mg/kg/day in rabbits (NTP 2005).LC50 value, inhalation (mice): 28 ppm/4 hLD50 value, oral (rats): 46 mg/kgLD50 value, skin (rats): 300 mg/kg.
Health Hazard
Marked potential for causing eye changes. May cause death
Fire Hazard
When heated to decomposition or on contact with acids, Thiophenol emits toxic fumes of sulfur oxides. May be ignited by heat, sparks or flames. Container may explode in heat of fire. Vapor explosion and poison hazard indoors, outdoors or in sewers. Unstable, oxidizes in air. Avoid contact with acids.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, inhalation, skin contact, and intraperitoneal routes. A severe eye irritant. Can cause severe dermatitis. Exposure may cause headache and dminess. When heated to decomposition or on contact with acids it emits toxic fumes of SOx. See also MERCAPTANS
Potential Exposure
Phenyl mercaptan is used as a chemical intermediate in pesticide manufacture; as a mosquito larvicide. It is used in solvent formulations for the removal of polysulfide sealants.
Shipping
UN2337 Phenyl mercaptan, Hazard class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, 3-Flammable liquid, Inhalation zone B.
Incompatibilities
At normal room temperature may vaporize forming explosive mixture with air. Violent reaction with strong oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides, calcium hypochlorite, alkali metals. Oxidizes on exposure to air; supplied under nitrogen.
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. Dissolve in flammable solvent and burn in furnace equipped with afterburner and alkaline scrubber. 100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. Dissolve in flammable solvent and burn in furnace equipped with afterburner and alkaline scrubber.