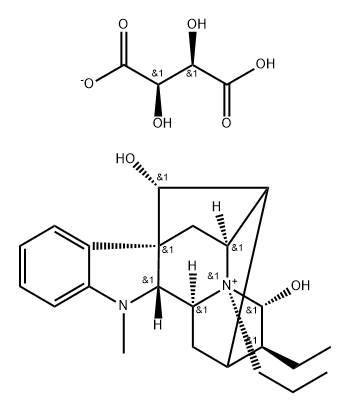
prajmalium bitartrate
- CAS No.
- 2589-47-1
- Chemical Name:
- prajmalium bitartrate
- Synonyms
- NPAP;Neo-gilurytmal;prajmalium bitartrate
- CBNumber:
- CB5902101
- Molecular Formula:
- C23H33N2O2.C4H5O6
- Molecular Weight:
- 518.61
- MDL Number:
- MFCD28388247
- MOL File:
- 2589-47-1.mol
| Melting point | 149-152° |
|---|---|
| FDA UNII | H671L9190Z |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS08,GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H301-H361 |
| Precautionary statements | P264-P270-P301+P310-P321-P330-P405-P501-P201-P202-P281-P308+P313-P405-P501 |
| Toxicity | LD50 in mice (mg/kg): 43 orally; 1.7 i.v. (Von Philipsborn, Stalder) |
prajmalium bitartrate Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Originator
Neo-Gilurtymal, Giulini ,W. Germany,1973
Manufacturing Process
1 g of ajmaline was dissolved in 4 cc of chloroform, and 1 cc of allyl bromidewas added to the resulting solution. The reaction mixture thus obtained was allowed to stand for 24 hours at room temperature. Thereafter, the clear reaction solution was briefly cooled to a temperature below 0°C, whereby crystallization set in. The crystals were filtered off and were then recrystallized from a mixture of absolute methanol and absolute ether. The purified colorless crystalline product was identified to be N-(b)-allyl-ajmalinium-bromide having a melting point of 252°C to 254°C.
75 g of N-(b)-n-propyl-ajmalinium-bromide were suspended in 3 liters of an aqueous saturated solution of sodium bicarbonate, and the suspension was admixed with 3 liters of chloroform. The resulting mixture was vigorously stirred for six to eight hours. Thereafter, the chloroform phase was separated and evaporated to dryness. 68 g of a yellow syrup remained as a residue. The aldehyde base was dissolved in about 150 cc of acetone and, while stirring and cooling on an ice bath, the solution was slowly admixed with a solution of 25 g of tartaric acid in 2 liters of acetone. The fine white precipitate formed thereby was separated by vacuum filtration, washed with ether and dried. The raw product, weighing 80 g, was recrystallized once from a mixture of ethanol and ether, yielding 50 g of N-(b)-n-propyl-ajmalinium hydrogen tartrate having a melting point of 149°C to 152°C (decomposition).
Therapeutic Function
Antiarrhythmic
Mechanism of action
The activity profile of prajmalium is very similar to that of ajmaline, although the sodium channels are blocked much longer by it than by any other class I antiarrhythmic .
Clinical Use
With at least five times the potency of ajmaline, prajmalium is a most effective antiarrhythmic, and it is superior to ajmaline in its reliable oral effect and sustained action .
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and intravenous routes. An experimental teratogen. Human systemic effects by ingestion: hallucinations and distorted perceptions. Experimental reproductive effects. An antiarrhythmic agent. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx
prajmalium bitartrate Preparation Products And Raw materials
prajmalium bitartrate Suppliers
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TargetMol Chemicals Inc. | +1-781-999-5354 +1-00000000000 | marketing@targetmol.com | United States | 19892 | 58 |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| TargetMol Chemicals Inc. | 58 |