CATALASE
- CAS No.
- 9001-05-2
- Chemical Name:
- CATALASE
- Synonyms
- CATALASE FROM BOVINE LIVERCA. 11000 U/MG LYOPH. SALTFREE;EC 1.11.1.6;EC: 1.11.1.6;BOVINE CATALASE;CATALASE FROM BOVINE LIVER;CataL;optidase;CATALASE;caperase;equilase
- CBNumber:
- CB9273573
- Molecular Formula:
- C9H10O3
- Molecular Weight:
- 166.1739
- MDL Number:
- MFCD00081483
- MOL File:
- 9001-05-2.mol
| Density | 1.06 g/mL at 20 °C |
|---|---|
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| Flash point | 41 °C |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| form | suspension |
| color | deep brown |
| Water Solubility | 125g/L at 25℃ |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 13,1910 |
| Stability | Air and moisture sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. Refrigerate. |
| LogP | -1.3 at 20℃ |
| FDA 21 CFR | 184.1034 |
| EWG's Food Scores | 1-3 |
| FDA UNII | 27O7ZP4PVG |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Catalase (9001-05-2) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H334 |
| Precautionary statements | P261-P284-P304+P340+P312-P501 |
| Hazard Codes | B |
| Risk Statements | 10 |
| Safety Statements | 23-24/25-22 |
| RIDADR | UN 1993 3/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | FI4378000 |
| F | 10-21 |
| TSCA | Yes |
| HS Code | 35079090 |
CATALASE price More Price(48)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich | C40 | Catalase from bovine liver lyophilized powder, ≥10,000?units/mg protein | 9001-05-2 | 100mg | $77 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | C40 | Catalase from bovine liver lyophilized powder, ≥10,000?units/mg protein | 9001-05-2 | 500mg | $226 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | C40 | Catalase from bovine liver lyophilized powder, ≥10,000?units/mg protein | 9001-05-2 | 1g | $389 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | C30 | Catalase from bovine liver aqueous suspension, 10,000-40,000?units/mg protein | 9001-05-2 | 100MG | $83.3 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | C30 | Catalase from bovine liver aqueous suspension, 10,000-40,000?units/mg protein | 9001-05-2 | 500MG | $251 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
CATALASE Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Background and Overview
Catalase is an enzyme that catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. The system name of 2H2O2—→2H2O+O2 is H2O2; H2O2 is oxidoreductase (E, C, 1, 11, 1, 6). Its cofactor is heme and molecular weight is 250,000, existing in the form of tetramer. Catalase is present in almost all animal cells. In addition to the true anaerobes, this enzyme is widely used in plants and in all microbes. Animal liver, red blood cell and kidney contain a very rich catalase, which mainly exists in the microbody of the cell (also referred to as peroxidase). In the respiratory chain of the mitochondria and in the electron transfer of the enzyme reaction and other oxidation reactions, a part of the toxic redox reaction products may or may be produced. The most important are the superoxide ions O2- and H2O2, which are very active in chemical properties, which may be irreversible to damage certain biological molecules. Under the action of superoxide dismutase in cells, superoxide ions become hydrogen peroxide and oxygen. The most important role of peroxisase is to decompose hydrogen peroxide, prevent the accumulation of hydrogen peroxide, and protect cells from hydrogen peroxide. The decomposition rate of hydrogen peroxide catalyzed by catalase is very rapid. It is 104 times faster than the peroxidase, and each enzyme can catalyze the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide at 44000 molecules per second. Our country has various types of natural extreme environment in our country, and is rich in extreme microbial resources. More efforts should be made to develop catalase in various extreme microbes and increase the level of enzyme production, which is expected to change the import situation of catalase in China. With the development of modern biotechnology and bioinformatics, it will make it possible to modify and modify extreme enzymes in vitro. The development and application of CAT produced by extreme microbes will certainly show a more attractive prospect.
Overview on the Medicine
General-purpose Name: catalase
English name: CATALASE FROM MICROCOCCUS
Aliases: catalase isolated from streptococcus hemolytic streptococcus
Cas No:9001-05-2
Structural formula: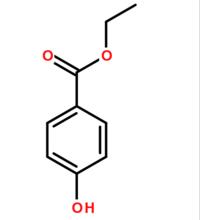
Clinical significance
CAT has various physiological functions. It can not only regulate the H2O2 level in the body, but also act as a protective agent for Hb and other sulfhydryl protein. The changes in serum CAT activity are seen in the following diseases:The increase of CAT is mainly seen in liver cirrhosis, typhoid, fever etc..
The decrease of CAT is mainly seen in all kinds of cancer, myocarditis, pneumonia, acute cholecystitis, acute pancreatitis etc..The serum CAT of starvation, rheumatic fever, trauma, local purulent infection, anemia and so on can also be reduced in varying degrees.
Source
Almost all biological organisms have catalase. It is common in breathing organisms, mainly in the plants' chloroplasts, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, animal liver and red blood cells.Its enzymatic activity provides antioxidant defense mechanism to the body.
CAT is a red blood hormone enzyme. Different sources have different structures.The level of activity is different in different tissues.Hydrogen peroxide decomposes faster in the liver than in brain or heart organs, which is due to the high levels of CAT in the liver.
Mechanism of action
Although the complete catalytic mechanism of catalase has not yet been fully understood, its catalytic process is considered to be divided into two steps:
Among them, "Fe () -E" represents the central iron atom (Fe) that combines the heme group (E) on the enzyme. Fe(IV)-E(.+) is a resonance form of Fe(V)-E . That is, the iron atom is not completely oxidized to the +V valency, but receives some "support electrons" from the heme. Therefore, the heme in the reaction stands for free radical cation (.+). Hydrogen peroxide enters the active site and interacts with the asparagine residue (Asn147) and histidine residue (His74), making a proton transfer between the oxygen atoms.The free oxygen atom coordination is combined to produce water molecules and Fe (IV) =O. Fe (IV) =O reacts with second hydrogen peroxide molecules to re-form Fe (III) -E and generates water molecules and oxygen. The reactivity of iron atoms in the active center may be enhanced by the presence of phenol based side chains ((helping Fe (III) be oxidized into Fe (IV)))in tyrosine residues (Tyr357). The efficiency of the reaction may be enhanced by the interaction of His74 and Asn147 with the reaction intermediate.The rate of the reaction is usually determined by the Michaelis equation. Catalase can also oxidize some other cytotoxic substances, such as formaldehyde, formic acid, phenol and ethanol.These processes require the use of hydrogen peroxide through the following reactions:
In the same way, the specific mechanism of the reaction is not clear.
Any heavy metal ions (such as copper ions in copper sulphate) can be used as a non competitive inhibitor of catalase. In addition, highly toxic cyanide is a competitive inhibitor of catalase, which can be bound closely to the heme of the enzyme and prevent the enzyme's catalytic reaction. The three-dimensional structure of the peroxidase intermediate, which is in the state of peroxide, has been analyzed and can be retrieved in the protein database.
Testing
Gas bubbles can be observed by the detection of catalase in the process. The catalase test is one of the three main means of detection and identification of bacteria microbiologist species, namely using hydrogen peroxide to detect the presence of catalase. If the bacteria contain catalase, a small amount of bacterial extracts in the hydrogen peroxide solution can be observed to produce oxygen bubbles. In the presence of bubbles, the bacteria are considered to be "catalase positive", such as staphylococcus and micrococcus. Without bubbles, the bacteria are considered to be "catalase negative", such as Streptococcus and Enterococcus. Although catalase detection cannot identify specific organisms, it can be effectively assisted in diagnosis by combining with other detection methods. In addition, the presence of catalase in bacteria depends on the conditions of cell growth and the medium used.
Application
Catalase is used in the food industry to remove hydrogen peroxide in milk used to make cheese. Catalase is also used in food packaging to prevent food from being oxidized. In the textile industry, catalase is used to remove hydrogen peroxide from textiles to ensure that the finished product is free from peroxide. It is also used in the cleaning of contact lenses: glasses are soaked in cleaning agents containing hydrogen peroxide, and then residual hydrogen peroxide is removed with catalase before use. The use of catalase in the beauty industry: the enzyme and hydrogen peroxide are added to some facial care to increase the amount of oxygen in the upper layer of the epidermis. Catalase is often used in the laboratory as a tool to understand the effects of enzymes on the rate of reaction.
Function Summary
Hydrogen peroxide is a waste produced during the metabolic process, which can cause damage to the body. In order to avoid this damage, hydrogen peroxide must be quickly converted into other harmless or less toxic substances. And catalase is a tool that is often used by cells to catalyze the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. But the real biological importance of catalase is not so simple: The researchers found that the mice that have been genetically engineered for the absence of catalase are still normal.This suggests that catalase is only essential to animals only under certain conditions. The level of catalase in some people is very low, but it does not show obvious pathological reaction. This is probably because the main hydrogen peroxide scavenger in normal mammalian cells is peroxiredoxin rather than catalase. Catalase is usually located in a organelle called peroxisome. Peroxisomes in plant cells are involved in photorespiration (utilizing oxygen and generating carbon dioxide) and symbiotic nitrogen fixation (the dissociation of nitrogen (N2) into activated nitrogen atoms). But when a cell is infected by a pathogen, hydrogen peroxide can be used as an effective antimicrobial agent. Some pathogens, such as mycobacterium tuberculosis, legionella pneumophila and campylobacter jejuni, can produce catalase to degrade hydrogen peroxide, so that they can survive in the host.
Bleaching action
It should be explained that the enzyme can be used to promote bleaching.Wool is bleached in hydrogen peroxide bleaching solution containing protease Bactosol ST, which can significantly improve the whiteness and hydrophilicity of wool. This is because the enzyme can promote the initial rapid erosion of wool fiber, making its easier to carry out the wool bleach. From this principle, protease can pretreat wool first, expose the fiber surface and bleach. The result is obviously better and fiber damage is easy to control.
Distribution
Catalase is present in all tissues of all known animals, especially in the liver at high concentrations.In the bombardier beetle, catalase has a unique purpose. The beetle has two sets of chemicals stored separately in the gland. The large glands store hydroquinone and hydrogen peroxide. The small glands store catalase and horseradish peroxidase. When the beetle mixes the chemicals in the two glands, it releases oxygen. Oxygen can oxidize hydroquinone can act as a booster. Catalase is also ubiquitous in plants and does not include fungi, although some fungi have been found to be able to produce this enzyme in low pH and warm conditions. The vast majority of aerobic microorganisms contain catalase, except for streptococcus, an aerobic bacteria without catalase. Some anaerobic microbes, such as methanosarcina barkeri, also contain catalase.
Chemical Properties
brown crystalline solid
Uses
Catalase from Sigma has been used as a positive control during the functional characterization of Clostridium difficile spore coat proteins.
Uses
Catalase agarose has been used in a study to advance the treatment of oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Catalase agarose has also been used in a study to investigate the growth of cyanobacterium on agar media in the presence of heterotrophic bacteria.
Uses
In combination with glucose oxidase, for treatment of food wrappers to prevent oxidative deterioration of food: Sarett, Scott, US 2765233 (1956 to Ben L. Sarett). In the removal of traces of peroxide in the process of cold sterilization (preservation of milk and cheese by treatment with hydrogen peroxide). With glucose oxidase, q.v., in food preservation.
Definition
ChEBI: Ethylparaben is an ethyl ester resulting from the formal condensation of the carboxy group of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid with ethanol, It has a role as an antimicrobial food preservative, an antifungal agent, a plant metabolite and a phytoestrogen. It is a paraben and an ethyl ester.
General Description
CAT (catalase) is an endogenous antioxidant enzyme, thus conferring protection to cells against damage by ROS (reactive oxygen species). In humans, this gene is localized to chromosome 11p13, which is composed of 12 introns and 13 exons.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Catalase has an ability to convert solar radiation into reactive oxidant species (ROS). It is involved in regulation of tissue peroxide levels. Mutation in catalase gene result in the progress of essential hypertension (EH).
CATALASE Preparation Products And Raw materials
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hebei Mojin Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +86 13288715578 +8613288715578 | sales@hbmojin.com | China | 12835 | 58 |
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co,.LTD | +86-13131129325 | sales1@chuanghaibio.com | China | 5893 | 58 |
| Hebei Kingfiner Technology Development Co.Ltd | +86-15532196582 +86-15373005021 | lisa@kingfinertech.com | China | 2990 | 58 |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 | info@tianfuchem.com | China | 21637 | 55 |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 | sales@coreychem.com | China | 29885 | 58 |
| Hebei Weibang Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8615531157085 | abby@weibangbio.com | China | 8816 | 58 |
| Shandong chuangyingchemical Co., Ltd. | 18853181302 | sale@chuangyingchem.com | CHINA | 5906 | 58 |
| Chongqing Chemdad Co., Ltd | +86-023-6139-8061 +86-86-13650506873 | sales@chemdad.com | China | 39894 | 58 |
| Shaanxi Dideu Medichem Co. Ltd | +86-029-81138252 +86-18789408387 | 1057@dideu.com | China | 3958 | 58 |
| Creative Enzymes | 1-516-855-7709 | info@creative-enzymes.com | United States | 8748 | 58 |
View Lastest Price from CATALASE manufacturers
| Image | Update time | Product | Price | Min. Order | Purity | Supply Ability | Manufacturer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
2024-11-04 | Catalase
9001-05-2
|
US $0.00-0.00 / g | 1g | 98.0% | 1kg/month | WUHAN FORTUNA CHEMICAL CO., LTD | |
 |
2024-10-28 | Catalase
9001-05-2
|
US $41.00-59.00 / mg | 10g | TargetMol Chemicals Inc. | |||
 |
2024-10-11 | CATALASE
9001-05-2
|
US $19.60 / KG | 1KG | 99% | 5000kg | Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co,.LTD |
9001-05-2(CATALASE)Related Search:
1of4