UMiroliMus
|
- $85 - $613
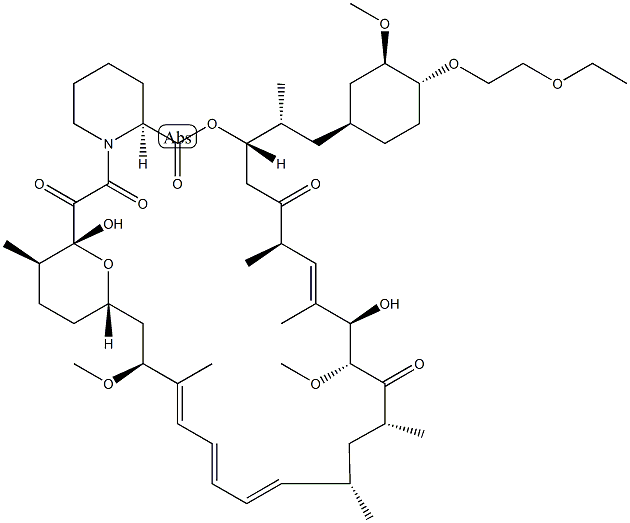
- Product name: UMiroliMus
- CAS: 851536-75-9
- MF: C55H87NO14
- MW: 986.28
- EINECS:-0
- MDL Number:MFCD22124433
- Synonyms:BioliMus;BioliMus, BioliMus A9, TRM 986;BIOLIMUS A9;UMiroliMus;Rapamycin, 42-O-(2-ethoxyethyl)-;BioliMus A9 UMiroliMus;TRM 986;TRM986
6 prices
Selected condition:
Brand
- AK Scientific
- American Custom Chemicals Corporation
- Cayman Chemical
- TRC
Package
- 1mg
- 5mg
- ManufacturerAK Scientific
- Product numberX7251
- Product descriptionUmirolimus
- Packaging5mg
- Price$613
- Updated2021-12-16
- Buy
- ManufacturerAmerican Custom Chemicals Corporation
- Product numberAPI0007715
- Product descriptionUMIROLIMUS 95.00%
- Packaging5MG
- Price$504
- Updated2021-12-16
- Buy
- ManufacturerCayman Chemical
- Product number23585
- Product descriptionUmirolimus ≥95%
- Packaging1mg
- Price$117
- Updated2024-03-01
- Buy
- ManufacturerCayman Chemical
- Product number23585
- Product descriptionUmirolimus ≥95%
- Packaging5mg
- Price$463
- Updated2024-03-01
- Buy
- ManufacturerTRC
- Product numberU710005
- Product descriptionUmirolimus
- Packaging1mg
- Price$85
- Updated2021-12-16
- Buy
- ManufacturerTRC
- Product numberU710005
- Product descriptionUmirolimus
- Packaging5mg
- Price$370
- Updated2021-12-16
- Buy
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AK Scientific | X7251 | Umirolimus | 5mg | $613 | 2021-12-16 | Buy |
| American Custom Chemicals Corporation | API0007715 | UMIROLIMUS 95.00% | 5MG | $504 | 2021-12-16 | Buy |
| Cayman Chemical | 23585 | Umirolimus ≥95% | 1mg | $117 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Cayman Chemical | 23585 | Umirolimus ≥95% | 5mg | $463 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| TRC | U710005 | Umirolimus | 1mg | $85 | 2021-12-16 | Buy |
| TRC | U710005 | Umirolimus | 5mg | $370 | 2021-12-16 | Buy |
Properties
Boiling point :991.0±75.0 °C(Predicted)
Density :1.15±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted)
storage temp. :Store at -20°C
solubility :DMF: Soluble; DMSO: Soluble; Ethanol: Soluble; Methanol: Soluble
form :A solid
pka :10.40±0.70(Predicted)
Density :1.15±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted)
storage temp. :Store at -20°C
solubility :DMF: Soluble; DMSO: Soluble; Ethanol: Soluble; Methanol: Soluble
form :A solid
pka :10.40±0.70(Predicted)
Safety Information
| Symbol(GHS): | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word: | ||||||||
| Hazard statements: |
|
|||||||
| Precautionary statements: |
|





