2-Naphthol: Effects on M. incognita and Distribution in Tomato Plants
May 9,2024
General Description
2-Naphthol, a compound found in coal tar and certain plants, exhibits potent nematicidal and antioxidant effects on nematodes like M. incognita. It induces structural and biochemical changes leading to nematode death through protein synthesis inhibition, sugar metabolism disruption, and oxidative stress. When applied to tomato plants, 2-Naphthol is rapidly absorbed by roots, showing concentration-dependent uptake and localized distribution, effectively protecting against root-knot nematodes. Despite environmental concerns, methods like volatilization and biodegradation can mitigate its impact. Overall, 2-Naphthol presents a promising, low-toxicity solution for nematode control and environmental remediation.

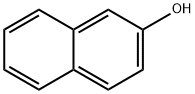
Figure 1. 2-Naphthol
Overview
2-Naphthol, also known as β-Naphthol, is a naturally occurring organic compound found primarily in coal tar, a by-product of the coal gasification process. It is also present in certain types of plants, especially those belonging to the genus of Lawsonia, which are known for their dye-producing properties. Additionally, 2-Naphthol can be extracted from certain bacteria and fungi, though in smaller quantities. 2-Naphthol, due to its unique chemical properties, has found numerous applications in various industries, including dyes, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. Its natural occurrence, coupled with its synthetic production methods, ensures a steady supply for various industrial uses. However, its handling requires caution as 2-Naphthol is a potentially harmful compound and can cause skin irritation or other health issues if not handled properly. 1
Effects on M. incognita
The impact of 2-Naphthol on M. incognita was profound and multifaceted, as evidenced by several experimental observations. Initially, the activity of nematodes treated with 2-Naphthol experienced significant reduction compared to the control group, indicating its potent nematicidal properties. Additionally, 2-Naphthol demonstrated antioxidant effects, further complicating its impact on nematodes. Microscopic analysis revealed structural alterations in nematodes following exposure to 2-Naphthol. Optical microscopy showcased a stark difference between control and treated groups, with treated nematodes appearing linear, stiff, and immobile, accompanied by the presence of vacuoles. SEM imaging highlighted substantial changes in the body wall structure of treated nematodes, with evident crinkling and blurring of body rings, suggesting damage induced by 2-Naphthol. Further biochemical analysis demonstrated significant decreases in both total protein and glycogen content in treated nematodes compared to controls. This depletion may disrupt essential physiological processes, such as protein biosynthesis and sugar metabolism, ultimately leading to nematode death. Moreover, the observed weak fluorescence of an oxidative stress marker in treated nematodes suggests a potential role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the nematicidal mechanism of 2-Naphthol. This indicates a distinct mechanism of action compared to other known nematicides. In summary, 2-Naphthol disrupts nematode activity, damages body wall structure, and induces biochemical changes, ultimately leading to nematode death through a combination of protein synthesis inhibition, disruption of sugar metabolism, and oxidative stress induction. 2
Distribution in Tomato Plants
The distribution of 2-Naphthol in tomato plants was investigated following its application, aiming to understand its efficacy against southern root-knot nematodes (RKNs). Results showed rapid absorption by roots within 4 hours post-treatment, with accumulation increasing with higher concentrations. Concentration-dependent uptake continued for 72 hours, peaking at 48 hours for both 100 μg/mL and 200 μg/mL, stabilizing thereafter. Notably, 2-Naphthol was exclusively detected in roots, indicating its fixed localization and lack of translocation to stems and leaves, crucial for preventing RKN invasion. Similar to commercial nematicide tioxazafen, this localized effect enhances plant protection. Furthermore, research revealed potent nematicidal properties of A. merrilliana leaf extract and its 2-Naphthol component against M. incognita, suggesting it as an effective natural alternative. Despite its environmental pollutant status, 2-Naphthol can be mitigated through various methods including volatilization, oxidation, and biodegradation. Notably, a combined treatment with Aspergillus niger and Bacillus subtilis achieved significant degradation within 10 days. These findings highlight 2-Naphthol's potential as a cost-effective and low-toxicity solution against nematodes, with promising avenues for environmental remediation. 2
Reference
1. 2-Naphthol. National Center for Biotechnology Information. 2024; PubChem Compound Summary for CID 8663.
2. Zhang X, Hu Z, Wang S, et al. Discovery of 2-Naphthol from the Leaves of Actephila merrilliana as a Natural Nematicide Candidate. J Agric Food Chem. 2023; 71(36): 13209-13219.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- 2-Naphthol: Polarity; Solubility and Uses Jan 4, 2024
2-Naphthol is a polar molecule. Since naphthol contains hydroxyl groups, it is a very polar molecule, and the oxygen atom attracts the electron density to itself through bonds.
- 2-Naphthol: properties and applications in synthesis of heterocyclic compounds and health risks Dec 15, 2023
2-Naphthol is valuable in organic synthesis but poses health risks, especially for children, due to its link to oxidative stress and allergic diseases.
- 2-Naphthol:Production,Human Health,Environment Feb 22, 2023
2-Naphthol is produced by sulfonation of naphthalene to 2-naphthalene sulfonic acid, and reaction with caustic soda solution to obtain the sodium salt. Reaction of the sodium salt with sodium hydroxide and treating the melt with sulfuric
Tetrahydro-4H-pyran-4-one, pivotal in drug synthesis, aids in crafting potent histamine-3 antagonists for cognitive disorders, showcasing significant medicinal potential.....
May 9,2024APID-Camphor, sourced from α-pinene and various trees, has weak antimicrobial activity but enhances other compounds' effects, vital for industrial use.....
May 9,2024API2-Naphthol
135-19-3You may like
- 2-Naphthol
-

- $2.00 / 25KG
- 2024-06-07
- CAS:135-19-3
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 1000mt/year
- 2-Naphthol
-

- $30.00 / 1kg
- 2024-06-07
- CAS:135-19-3
- Min. Order: 3kg
- Purity: 98%
- Supply Ability: 2000kg
- 2-Naphthol
-

- $50.00 / 1kg
- 2024-06-07
- CAS:135-19-3
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 20Tons