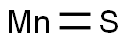Applications and Crystal Structure of Manganese Sulfide
Apr 15,2024
Manganese sulfide (MnS) is a p-type semiconductor with a wide bandgap (Eg = ~3 eV) that undergoes a transition to an antiferromagnetically (AFM) ordered phase below room temperature. These features attracted interest for the potential applications of nanosized manganese sulfide in the field of short wavelength optoelectronics, or as a photoluminescent component, photoreduction catalysts, and contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Properties and Applications
The optical properties of manganese sulfide have also raised considerable interest in protobiology since it is deemed to have played a key role (along with ZnS in mixed haloes formed around primeval sub-aerial hot springs) in the prebiotic photosynthesis development, thanks to its ability to photoreduce CO2. More recently, interesting energy-related applications have been demonstrated, where manganese sulfide was employed as an electrode material in Li-ion batteries and as a supercapacitor material.
α, β, and γ Structures
Naturally occurring manganese sulfide minerals with α, β, and γ structures are known, but they have curiously been discovered in a large time interval. Natural α-MnS has been known as alabandite since the beginning of the nineteenth century and is a widespread manganese ore. MnS minerals with β and γ structures have been much more recently reported upon: rambergite (γ-MnS) has been discovered in 1996 in Sweden whereas browneite (β-MnS) was found in a meteorite collected in Poland in 2012.
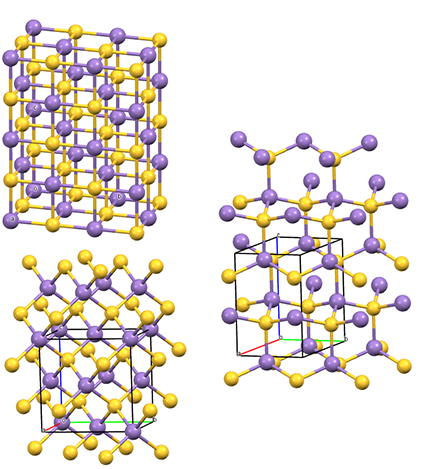
The figure above shows the three polymorphs of manganese sulfide. Upper left: cubic α-MnS (rock salt); lower left: cubic β-MnS (zincblende); right: hexagonal γ-MnS (wurtzite). The primitive cell is also shown. Color code: Mn, violet; S, yellow.
In the cubic rock-salt α-MnS structure, sulfide anions an expanded fcc lattice, and the manganese cations occupy all octahedral sites. The metastable form β-MnS has the cubic zincblende structure. Similarly to α-MnS, β-MnS comprises an expanded fcc lattice of S2−anions, but in this polymorph, the Mn2+ cations reside on half of the tetrahedral sites. Finally, γ-MnS has the hexagonal wurtzite structure, based on a slightly compressed (c/a = 1.618) hcp lattice of sulfide anions with manganese cations occupying half of the tetrahedral sites.
Reference
[1] M. Ferretti, Anna, Sara Mondini, and Alessandro Ponti. 2016. 'Manganese Sulfide (MnS) Nanocrystals: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications'. Advances in Colloid Science. IntechOpen. doi:10.5772/65092.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
Supplementation with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate monohydrate can synthesize neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, maintaining a healthy nervous system.....
Nov 4,2025Biochemical EngineeringAluminum hydroxide treats heartburn, upset stomach, sour stomach, or acid indigestion.....
Apr 15,2024Inorganic chemistryManganese sulfide
18820-29-6You may like
Manganese sulfide manufacturers
- Manganese sulfide
-

- $8.00 / 1KG
- 2025-09-25
- CAS:18820-29-6
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: g-kg-tons, free sample is available
- Manganese sulfide
-

- $15.00 / 1KG
- 2021-07-13
- CAS:18820-29-6
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%+ HPLC
- Supply Ability: Monthly supply of 1 ton
- Manganese sulfide
-

- $15.00 / 1KG
- 2021-07-10
- CAS:18820-29-6
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%+ HPLC
- Supply Ability: Monthly supply of 1 ton