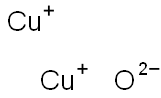Cuprous oxide nanoparticles
Mar 17,2023
CuO nanoparticles (CuO-NPs) serve several important functions in human life, particularly in the fields of medicine, engineering, and technology. These nanoparticles have been utilized as catalysts, semiconductors, sensors, gaseous and solid ceramic pigments, and magnet rotatable devices.
CuO engineered nanoparticles (ENPs) are used in industrial applications as a catalyst for carbon monoxide oxidation and a component of heat transfer fluids. Their antimicrobial and antifouling properties make CuO ENPs useful in soaps and antifouling paints and coatings for boat hulls and other submerged surfaces, suggesting that release into the environment is likely. Increased production and use will lead to greater environmental release of CuO ENPs, which is of concern because of the lack of information regarding their environmental safety.

Although Cu is an essential metal, it is extremely toxic at elevated concentrations and negatively impacts mussels, fish , and crustaceans at concentrations as low as 4 μg L−1. Mechanisms of toxicity include interference with osmoregulation due to enzyme inhibition, decreased immune function, and decreased respiration. Addition of CuO ENPs to the environment may have negative impacts on marine organisms and ecosystems. However, little is known about the toxicity of CuO ENPs in the aquatic environment. CuO ENPs do not readily dissolve in aqueous media, suggesting that they may be less bioavailable than Cu salts but more bioavailable than micro-sized CuO.
Further use for CuO-NPs has been employed in the pharmaceutical industry especially in the production of anti-microbial fabric treatments or prevention of infections caused by Escherichia coli and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Two key potential routes of exposure to CuO-NPs exist through inhalation and skin exposure. Toxicity of these nanoparticles has been reported in various studies; however, no study as of yet has investigated the complete cellular mechanisms involved in CuO-NPs toxicity on human cells.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Uses and properties of Cuprous oxide Jun 15, 2022
Cuprous oxide is a narrow bandgap (1.8–2.2 eV) p-type semiconductor that is abundant and cheap. Because of this, it can also absorb a substantial portion of the solar spectrum.
Copper pyrithione is Pyridinethione derivative, and it belong to a class of cyclic sulfur organo products containing sulfur atom (S) and often oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), hydrogen (H), as well as other elements, can find application for maki....
Mar 17,2023Pharmaceutical intermediatesN-Bromosuccinimide (NBS) is a convenient source of bromine for both radical substitution and electrophilic addition reactions.....
Mar 20,2023Chemical ReagentsCuprous oxide
1317-39-1You may like
- The research on corundum-type Ti2O3
May 10, 2024
- Tungsten nitrides and W-N structures
May 10, 2024
- The structure of Mg2Sn
May 9, 2024
- Cuprous oxide
-

- $40.00 / 1kg
- 2023-09-26
- CAS:1317-39-1
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 0.99
- Supply Ability: 10 tons
- Cuprous oxide
-

- $0.00 / 25KG
- 2023-09-20
- CAS:1317-39-1
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 50000KG/month
- Cuprous oxide
-

- $0.00 / 25KG
- 2023-09-12
- CAS:1317-39-1
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 50000KG/month