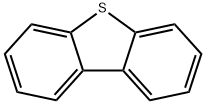
Dibenzo[b,d]thiophene---Applications and Synthesis
Jan 20,2022
Dibenzo[b,d]thiophene, commonly known as dibenzothiophene, is a tricyclic aromatic sulfur heterocycle with a 14π electron ring system formed by the fusion of two benzene rings with “b” and “d” sites of the thiophene ring. X-ray diffraction of dibenzothiophene revealed that the bond angle C-S-C is 91.5 degrees. The individual two benzene and one thiophene rings are planar but the molecules as a whole show a small but significant deviation from planarity.
Dibenzothiophene was first synthesized in 1870 by Stemhouse by heating biphenyl with iron scrap, but the as signed incorrect structure was corrected by Graebe. The natural dibenzothiophene was isolated from coal tar by Kruber. Besides this, various alkylated dibenzothiophenes have also been isolated from the crude oil, but it was difficult to desulfurize them catalytically. The presence of sulfur in the fuel produces sulfur dioxide when burnt and causes air pollution.
Dibenzothiophene is a thermally stable compound and resistant to mild oxidizing agents. Depending on the nature of the oxidizing agent it is oxidized to corresponding sulfoxide and sulfone. There are numerous protocols for the construction of dibenzothiophene but some of them are limited to the synthesis of specific compounds due to noncompatibility of functional groups. Here, only those methods that are extremely useful and have wide synthetic applications are delineated.
Physical Properties
It is a yellow-green, crystalline solid with an mp of 99.5°C and a bp of 332.5°C. It is soluble in ethanol, benzene, chloroform, and methanol but insoluble in water. Its dipole moment is 0.83 D. It is quite stable under normal temperature and pressure.
Chemical Reactivity
Dibenzothiophene is heteroaromatic in nature and undergoes electrophilic substitution reactions smoothly. Mostly, electrophilic substitution occurs at position 2 of dibenzothiophene offering 2-substituted dibenzothiophene, provided position 2 is not preoccupied.
Applications
Dibenzothiophene, particularly 3,7-diaminodibenzothiophene-5,5-dioxide, is used as a dye and fluorescent whitener. It is potentially useful as electrophilic trifluoromethylating agents. It has been used as a drug to expose the mycelia of infecting fungi or to treat corns, warts, and certain other skin diseases.
Synthesis

The parent dibenzothiophene has been synthesized by heating a mixture of biphenyl with sulfur at 120°C for 24 h in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 in 79% yields. This methodology is useful for the synthesis of substituted dibenzothiophenes.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- General Description of Dibenzo[b,d]Thiophene Jan 29, 2022
Benzothiophene is constituted by fusion of the benzene ring with the thiophene ring. There are two possible methods of fusion of the benzene ring with two different sites.
Chlorodifluoromethane was first used as an alternative to the highly ozone depleting CFC-11 and CFC-12 because of its relatively low ozone depletion potential of 0.055, among the lowest for chlorine-containing haloalkanes.....
Jan 19,2022Organic ChemistryPropionic acid (PA) is an important organic molecule of vast economic importance that includes food preservatives, flavoring agents, pharmaceutical formulations, textile and rubber auxiliaries, plasticizers, cosmetics, etc.....
Jan 20,2022Organic SolventsDibenzothiophene
132-65-0You may like
- Is sulfolane a green solvent?
May 15, 2024
- The toxicity of n-Butyl acetate
Apr 28, 2024
- Difference Between Isopropyl Alcohol and Acetone?
Mar 8, 2024
Dibenzothiophene manufacturers
- Dibenzothiophene
-

- $0.00 / 1KG
- 2024-05-24
- CAS:132-65-0
- Min. Order: 1g
- Purity: 99.90%
- Supply Ability: 10TONS
- Dibenzothiophene
-

- $0.00 / 1KG
- 2023-09-06
- CAS:132-65-0
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 500000kg
- Dibenzothiophene
-

- $0.00 / 25KG
- 2023-08-23
- CAS:132-65-0
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 50000KG/month