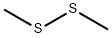Dimethyl disulfide: Toxicity, Applications, storage, Preparation
Apr 24,2023
Introduction
Dimethyl disulfide (DMDS) is a colorless to pale yellow liquid with a strong, unpleasant odor. It is an organic compound composed of two methyl groups and two sulfur atoms. DMDS is commonly used as a sulfiding agent for catalysts in the petroleum industry, as well as for soil fumigation in agriculture. It also has applications as a flavoring agent in food and beverage production, and as a precursor for the synthesis of various chemicals. DMDS is flammable and can be hazardous if not handled properly[1].

Figure 1 Appearance of Dimethyl disulfide
Toxicity
Dimethyl disulfide (DMDS) is a corrosive and flammable compound that can pose various risks to human health if exposure occurs. The degree of toxicity of DMDS primarily depends on the extent and duration of exposure to the compound, as well as the concentration and route of exposure. Acute exposure to DMDS can result in skin, eye, and respiratory irritation, gastrointestinal disturbances, and headache. Inhalation of high concentrations of DMDS can cause shortness of breath, coughing, and chest pain. Chronic exposure to DMDS can lead to liver and kidney damage, anemia, and neurological effects such as depression, insomnia, and disorientation. DMDS is classified as a Group D carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), indicating that it is not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans due to lack of sufficient evidence. However, some studies have suggested that DMDS may potentially have carcinogenic effects. Therefore, it is essential to follow proper safety measures and guidelines when handling DMDS, such as wearing appropriate personal protective equipment and working in a well-ventilated area. It is also important to use DMDS only in accordance with all relevant safety regulations and guidelines[2].
Applications
Dimethyl disulfide (DMDS) is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3SSCH3. DMDS has a wide range of applications, including its use as a sulfiding agent in petrochemical refining and as a soil fumigant in agriculture.
In petrochemical refining, DMDS is used to convert metal oxides and sulfur compounds in catalysts and adsorbents into their corresponding sulfides. This process helps to maintain the activity and selectivity of these materials, which are crucial for the production of high-quality fuels and chemicals.
As a soil fumigant, DMDS is used to control pests, weeds, and pathogens in agricultural soils. It is particularly effective against nematodes, fungi, and weed seeds, making it a valuable tool for crop protection. DMDS is also biodegradable, which means that it breaks down into harmless byproducts over time, reducing its impact on the environment.
Overall, DMDS is a versatile chemical with a variety of important applications in both the petrochemical and agricultural industries[3,4].
Storage
Dimethyl disulfide is a colorless liquid organic compound with an unpleasant odor, commonly used as a solvent and in the production of thiochemicals. When storing dimethyl disulfide, it is important to follow certain guidelines to ensure safe handling and storage. The compound should be stored in cool, dry, well-ventilated areas away from heat sources and oxidizing materials. It should also be kept in tightly closed containers made of non-reactive materials such as stainless steel or glass. Additionally, proper labeling and segregation from incompatible substances is recommended to prevent accidental mixing and potential chemical reactions. As with all chemicals, it is important to adhere to proper safety protocols and consult material safety data sheets for specific information on handling and storage requirements.
Preparation
Dimethyl disulfide is an organic compound with the chemical formula (CH3)2S2. It is a colorless liquid with a strong odor that is commonly used in the food, pharmaceutical, and petroleum industries. The synthesis of dimethyl disulfide involves the reaction of methanol with sulfur in the presence of zinc oxide or activated carbon as a catalyst. The reaction occurs at high temperatures and pressures, typically around 300-400°C and 20-30 atmospheres. The resulting product is then purified through distillation or other separation techniques to obtain the final dimethyl disulfide product. This synthesis method is widely used due to its efficiency and high yield of product. Dimethyl disulfide has many applications, including use as a flavoring agent in foods, a solvent in industrial processes, and a feedstock for the production of various chemicals[5-7].
References
[1] Wang, D., Liu, D. Use of Dimethyl Disulfide (DMDS) as a Soil Fumigant in the United States. [J] Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2013, 61(39), 9382–9390
[2] Zhou, X., Zhang, Y., Zhou, D., et al. Dimethyl Disulfide (DMDS) for Pest Control: Toxicity and Modes of Action against Soil Pests.[J] Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2017, 65(20), 4076–4082.
[3] Wang, L., Jiang, Y., Lu, Y.,et al. Effect of Dimethyl Disulfide (DMDS) on Odor Control in Sewer Systems.[J] Water Science and Technology. 2020, 81(9), 1891-1899.
[4] Bicchi, C., Cordero, C., Rubiolo, P. Use of Dimethyl Disulfide (DMDS) in Flavor and Fragrance Applications. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. 2018, 58(16), 2794-2804.
[5] Hua, W. et al. Synthesis of dimethyl disulfide by catalytic reaction of methanol with hydrogen sulfide over γ-Al2O3 supported nano Ni catalysts.[J] Chemical Engineering Journal. 2012, 183, 355-359.
[6] Qi, Y. et al. Preparation of dimethyl disulfide from sulfur and methanol.[J] Advanced Materials Research. 2013, 781-784, 2046-2049.
[7] Prasad, R. Sharma, M.M. Studies on the synthesis of dimethyl disulfide from dimethyl sulfate and sodium sulfide.[J] Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research. 1987, 26(2), 346-350.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Applications of Dimethyl disulfide Nov 22, 2019
Dimethyl disulfide(MDMS) appears as a colorless oily liquid with a garlic-like odor. Dimethyl disulfide is denser than water and slightly soluble in water,and vapors heavier than air.
Sodium nitrite is a salt and an inorganic compound with the chemical formula NaNO2. Sodium nitrite is commonly used as a food preservative, particularly for cured meats.....
Apr 24,2023APIFluorescein sodium, also called uranine, has been commonly used as a quantitative fluorophore for studying different tissues of the eye.....
Apr 24,2023APIDimethyl disulfide
624-92-0You may like
Dimethyl disulfide manufacturers
- Dimethyl disulfide
-

- $0.00 / 25kg
- 2024-05-23
- CAS:624-92-0
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 50000KG/month
- Dimethyl disulfide
-

- $0.00 / 200KG
- 2023-09-06
- CAS:624-92-0
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 500000kg
- Dimethyl disulfide
-

- $0.00 / 25KG
- 2023-08-24
- CAS:624-92-0
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 50000KG/month