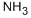How do we determine the Lewis structure for the NH3 molecule?
Nov 13,2023
Ammonia: define and importantly
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical with the chemical formula NH3. This compound is a colorless, pungent gas made of nitrogen and Hydrogen. It occurs in nature and is primarily produced by the anaerobic decay of plant and animal matter, and it has also been detected in outer space. Some plants, mainly legumes, in combination with rhizobia bacteria, “fix” atmospheric nitrogen to produce ammonia. Ammonia is directly or indirectly the precursor to most nitrogen-containing compounds. Virtually all synthetic nitrogen compounds are derived from ammonia. It is essential to understand the reaction properties of ammonia. Hence, determining the Lewis structure for the NH3 is essential.
Steps for drawing the Lewis structure for NH3
Step 1:Count total valence electrons in NH3
First, determine the valence electron available for drawing the Lewis structure of NH3 because the Lewis diagram is all about the representation of valence electrons around atoms.

As shown above, there are 5 valence electrons present in the nitrogen atom and only 1 valence electron is present in the hydrogen atom. Hence, the total number of valence electrons of NH3 is calculated by the following formula:
Total valence electrons= valence electrons given by 1 nitrogen atom + valence electrons given by 3 hydrogen atoms = 5 + 1*(3) = 8.
Step 2:Find the atom with the least electronegativity and place it in the center
In theory, the atom which is less electronegative remains at the center. Because they are more prone to share the electrons with surrounding atoms, the hydrogen atom is less electronegative than the electronegativity values of nitrogen (N). However, Hydrogen is an exception. Hydrogen is always on the outside in the Lewis diagram. Because Hydrogen atoms can form only one single bond, we can determine the approximate position of the four atoms.
Step 3: Connect outer atoms to the central atom with a single bond and place electron pairs between the atoms

In this step, join all outer atoms to the central atom with the help of a single bond. One electron pair between two atoms is equivalent to a single bond. Out of eight electrons, six will be used in pairs between atoms. The number of Lone pair electrons is 1. Hence, there is one lone electron pair to distribute. In the ammonia Lewis structure, the hydrogen atoms are the outside atoms, and each cannot keep more than two electrons in its last shell. Hence, the remaining electron pairs were drawn on the central nitrogen atom.
Step 4: Check the stability of the structure
The lesser the formal charge on atoms, the better the stability of the Lewis diagram. To calculate the formal charge on an atom. Use the formula given below:
Formal charge = Valence Electrons – Unbonded Electrons – ½ Bonded Electrons
For hydrogen atom: Formal charge=1-0-2/2=0
For nitrogen atom: Formal charge=5-2-6/2=0
Since the overall formal charge is zero, the above Lewis structure of NH3 is the most appropriate, reliable, and stable.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- What is the conjugate base of NH3?Is it amphotericital? Mar 21, 2024
The conjugate base of NH3 is NH2- which is known as the azide anion.
- What is the connection between Hydrogen peroxide and ammonia? Mar 20, 2024
The synergistic effect of hydrogen peroxide and ammonia strengthened the ammonolysis effect, whereas it weakened the oxidation effect.
- What is the formula and change of Ammonia? Feb 29, 2024
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula NH3.
Pyruvic acid has been recently used as a medium chemical peeling agent in subjects with skin diseases, such as acne melasma and photoaging. It received very limited or no discomfort in the post-stripping period.....
Nov 13,2023Flavors and fragrances1'-Acetonaphthone is a versatile and useful chemical compound, but requires careful handling to prevent harm.....
Nov 13,2023APIAmmonia
7664-41-7You may like
- Thorium dioxide: a fuel in nuclear reactors
May 20, 2024
- What is the crystal structure of Cadmium sulfide?
May 20, 2024
- Vanadium Nitride: an anode materials
May 20, 2024
- Ammonia
-

- $40.00 / 10Liters
- 2024-05-17
- CAS:7664-41-7
- Min. Order: 10Liters
- Purity: 99.99%
- Supply Ability: 100Tons
- Ammonia
-

- $2.00/ kg
- 2024-02-13
- CAS:7664-41-7
- Min. Order: 10000kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 10000000
- Ammonia
-

- $1.00 / 1KG
- 2019-12-23
- CAS:7664-41-7
- Min. Order: 1g
- Purity: 85.0-99.8%
- Supply Ability: 20ton