Dasatinib: BCR-ABL kinase inhibitor
Sep 20,2023
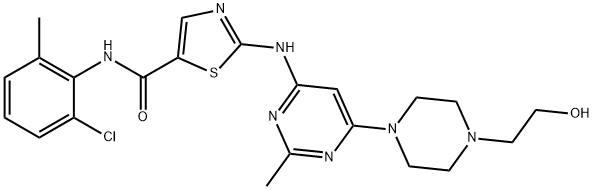
Dasatinib, chemical name: N-(2-chloro-6-methylphenyl)-2-[[6-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazinyl]-2-methyl-4-pyrimidinyl]amino]-5-thiazolecarboxamide. Trade name Sprycel, is a receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor developed by Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, in mid-2006, priority through the U.S. FDA approval, dasatinib can be a good treatment for adult chronic leukaemia and patients who have failed or are intolerant to leukaemia treatment, but also for the treatment of imatinib-resistant or intolerant adult chronic myeloid leukaemia and Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. No drug resistance has been found, and it has a very good effect on patients. Only one pharmaceutical company, Zhengda Tianqing, has been approved to produce this drug in China. Commercially available Dasatinib (SPRYCEL tablets) are white, film-coated tablets that are convex on both sides. The active ingredients include Dasatinib monohydrate, and the inactive ingredients are lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, cross-linked sodium carboxymethylcellulose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, and magnesium stearate. The tablet coating materials are hydroxypropylmethylcellulose, titanium dioxide and polyethylene glycol. In recent years, the sales of Dasatinib have increased significantly, which shows that Dasatinib has good efficacy as well as broad sales prospects.
Figure 1. Dasatinib
Pharmacological effects
Dasatinib is an oral multikinase inhibitor that can be used in all patients with treatment-failed or treatment-intolerant adult chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML), as well as for the treatment of imatinib-resistant or intolerant adult chronic myeloid leukaemia and Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia.In October 2010, the US FDA approved another indication for Dasatinib, which is for the treatment of a type of leukaemia with a high prevalence of chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML). In October 2010, the FDA approved another indication for dasatinib for the treatment of Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukaemia in the chronic phase, a rare form of leukaemia diagnosed for the first time.
Mechanism of action
The Src-family of tyrosine kinases includes at least nine non-receptor tyrosine kinases, e.g., Src, Fyn, Yes, Lyn, etc., whose related genes are involved in multiple intracellular signalling, which are related to many physiological processes, such as cell growth, differentiation, and transcription of genetic information.The Src-family of tyrosine kinases can regulate the downstream of the BCR-ABL signalling cascade reaction, and inhibition of the activity of Src-family tyrosine kinases can provide excellent synergistic effects on BCR-ABL kinases, and can even provide a block on chronic granulocytic leukaemia cells seeking other stock channels after BCR-ABL kinase inhibition. In patients possessing resistance to imatinib, although no mutations in BCR-ABL kinase were detected, intracellular Lyn (Src-family tyrosine kinase) was found to be activated or highly expressed [34-37]. If drugs can inhibit both BCR-ABL kinase and Src-kinase, the treatment of chronic granulocytic leukaemia would be more effective.Dasatinib belongs to a Src-family-derived lymphocyte cell tyrosine kinase (LCK) inhibitor, and Dasatinib not only inhibits BCR-ABL at nanomolar concentrations, but also inhibits the Src-family tyrosine kinase at nanomolar concentrations. Dasatinib not only inhibits BCR-ABL at nanomolar concentrations, but also inhibits almost all ABL mutants (excluding mutant T315I). Dasatinib has been shown to link not only to the active but also to the inactive site of the ABL tyrosine, with a more pronounced therapeutic effect than imatinib, but without lethality of the quiescent stem cell population. The pharmacokinetic properties of dasatinib and its strong in vivo activity were demonstrated in a mouse model of chronic granulocytic leukaemia.
Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Elimination
1, Absorption
Maximum plasma concentrations (Cmax) of dasatinib were observed at 0.5 and 6 hours (Tmax) after oral administration. Across the dose range of 15 mg to 240 mg/day dasatinib exhibited a proportional increase in AUC with dose and linear elimination characteristics. The mean total terminal half-life of dasatinib is 3-5 hours.
2, Distribution
In patients, dasatinib has an apparent volume of distribution of 2505 L, suggesting that the drug is widely distributed in the extravascular space. In vitro dasatinib and its active metabolite bind to human plasma proteins in approximately 96% and 93%, respectively, with no concentration dependence across the range of 100-500 ng/mL.
3, Metabolism
In humans dasatinib is extensively metabolised, mainly by cytochrome P450 enzyme 3A4.CYP3A4 is the main enzyme responsible for the formation of the active metabolite. The formation of dasatinib metabolites also involves flavin-containing plus monooxygenase [monooxygenase] 3 (FMO-3) and uridine diphosphate-glucuronide transfer (UGT) enzymes. Exposure to the active metabolite, which is equally potent as dasatinib, represents a dasatinib AUC of approximately 5%. This suggests that the active metabolite of dasatinib likely does not play a major role in the observed pharmacology of the drug. Dasatinib also has several inactive oxidative metabolites. Dasatinib is a weak time-dependent inhibitor of CYP3A4. At clinically relevant concentrations, dasatinib does not inhibit CYP1A2, 2A6, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, or 2E1. dasatinib is not an inducer of human CYP enzymes.
4, Elimination
Elimination is mainly via faeces. Following a single oral dose of [14C]-labelled dasatinib, approximately 4% and 85% of the given radioactivity was recovered in urine and faeces, respectively, within 10 days. Unchanged dasatinib in urine and faeces, 0.1% and 19% of the administered dose, respectively, with the remainder of the dose being metabolite metabolites.
Synthesis

Figure 2. Synthesis of Dasatinib
In 2000, Das, Jagabandhu et al. of Bristol-MyersSquibb developed a synthetic route as shown in the figure. This synthetic route was obtained by Boc protection of 2-amino-5-thiazolecarboxylic acid ethyl ester (2) with amino group, hydrolysis, acidification, followed by chlorination to amide, deprotection of protecting group, reaction with 4,6-dichloro-2-methylpyrimidine and finally nucleophilic substitution reaction with 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazine. The reaction conditions are mild and the raw materials are easy to obtain, but the catalyst DMAP used in the reaction is expensive and the reaction steps are complicated, which reduces the total yield of the reaction. Zhang Shaoning et al. from Southeast University optimised the synthetic route by combining the third and fourth steps of the reaction and using THF as the reaction solvent, which increased the total yield to 46.0%.
References
[1]Dasatinib. In:Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed). Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; July 19, 2021.
[2]Hoínková J, íma M, Slana O. Pharmacokinetics of Dasatinib.Prague Med Rep. 2019;120(2-3):52-63. doi:10.14712/23362936.2019.10.
[3]Cortes JE, Jimenez CA, Mauro MJ, Geyer A, Pinilla-Ibarz J, Smith BD. Pleural Effusion in Dasatinib-Treated Patients With Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Chronic Phase: Identification and Management.Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2017;17(2):78-82. doi:10.1016/j.clml.2016.09.012.
[4]Levêque D, Becker G, Bilger K, Natarajan-Amé S. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Dasatinib.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2020;59(7):849-856. doi:10.1007/s40262-020-00872-4.
[5]Korashy HM, Rahman AF, Kassem MG. Dasatinib.Profiles Drug Subst Excip Relat Methodol. 2014;39:205-237. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-800173-8.00004-0.
[6]Lindauer M, Hochhaus A. Dasatinib.Recent Results Cancer Res. 2014;201:27-65. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-54490-3_2.
[7]Alqattan Y, Ali S, Almohammad R, Kayali N, Alhuraiji A. Dasatinib-induced Chylothorax in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia.Gulf J Oncolog. 2022;1(40):74-77.
[8]zgür Yurtta N, E?kazan AE. Dasatinib-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension.;ampBr J Clin Pharmacol. 2018;84(5):835-845. doi:10.1111/bcp.13508.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Dasatinib: Mechanism of action and Safety Mar 29, 2024
Dasatinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, primarily treats chronic myeloid leukemia and Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
- Dasatinib: A second-generation BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitor Sep 18, 2023
Dasatinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia, but side effects may occur during use
- What is Dasatinib? Aug 27, 2021
Dasatinib Anhydrous is an orally bioavailable synthetic small molecule-inhibitor of SRC-family protein-tyrosine kinases. Dasatinib binds to and inhibits the growth-promoting activities of these kinases.
Distearyl thiodipropionate is a versatile antioxidant and UV stabilizer used in cosmetics. It protects against free radicals and UV damage and preserves moisture.....
Sep 20,2023APIClomiphene citrate is an orally administered, non-steroidal anti-estrogen with ovulation-stimulating properties.The drug was approved by the FDA for marketing in the United States in 1967.....
Sep 20,2023APIDasatinib
302962-49-8You may like
- Dasatinib
-

- $5.00 / 1kg
- 2024-05-17
- CAS:302962-49-8
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 300tons
- BMS-354825;Dasatinib
-

- $0.00 / 1kg
- 2024-05-13
- CAS:302962-49-8
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 10000kg
- Dasatinib
-

- $0.00 / 1kg
- 2024-05-09
- CAS:302962-49-8
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%, Single impurity<0.1
- Supply Ability: 1 ton