Is Carbon Monoxide Polar or Nonpolar?
Dec 21,2023
Polar Covalent Bonds
A bond in which the electronegativity difference between the atoms is between 0.5 and 2.0 is called a polar covalent bond. A polar covalent bond is a covalent bond in which the atoms have an unequal attraction for electrons and so the sharing is unequal. In a polar covalent bond, sometimes simply called a polar bond, the distribution of electrons around the molecule is no longer symmetrical. The ΔEN difference of 2.0 as the upper limit between polar covalent and ionic is arbitrary rather than an absolute cut off and that the properties of the compound are the best indicator of the primary nature of the bond. The differences in electronegativity are most valuable when used to predict the relative polarity of covalent bonds.
Polarity of Carbon Monoxide
Carbon Monoxide or CO is a diatomic molecule. Carbon and Oxygen atoms share a triple bond to fill their octets. Both the atoms have lone pair of electrons and are sharing other electrons to complete their octets. It has a linear molecular geometry, given that there are only two atoms in this molecule. The arrangement of these lone pairs is symmetric, but for knowing if there is a dipole moment in the molecule, we need first to see the electronegativities of both the atoms and check if there is a difference between them.
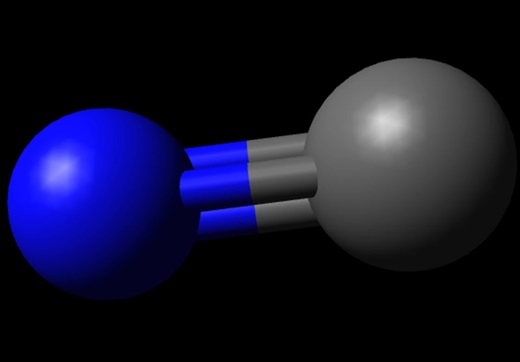
Carbon is a group 14 element on the periodic table having an electronegativity of 2.55, whereas Oxygen is a group 16 element having an electronegativity of 3.44.The oxygen atom is slightly higher in electronegativity, and hence it will try to pull the shared electrons to its side. This dipole moment in the molecule makes CO a polar molecule. The higher electronegativity if Oxygen makes it partially negatively charged and Carbon partially positively charged. And such formation of partial charges leads to the polarity in the molecule.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- How to draw the Lewis structure of CO Nov 17, 2023
The Lewis structure of CO is made up of a carbon atom (C) and an oxygen atom (O). The carbon and oxygen atoms are connected by a triple bond with a lone electron pair on each atom.
- Biological functions of Carbon monoxide Jun 24, 2022
Carbon monoxide is the second gasotransmitter that was found to have a physiological role in neurotransmission, cardiovascular regulation, and oxygen sensing.
- Mechanism of Carbon monoxide Dec 15, 2021
Carbon monoxide (CO) is historically known as a deadly gas to humans. Although produced in small amounts in the human body, toxicity occurs predominately after inhalation of preformed CO. Exposure to CO can occur in occupational settings, i
Lanolin is a complex mixture of high molecular weight esters, aliphatic alcohols, sterols, fatty acids, and hydrocarbons that has been widely used for centuries for its emollient properties.....
Dec 21,2023DrugsA century-long history in 8-aminoquinolines, the only anti-malaria drug class preventing malaria relapse, has resulted in the approval of tafenoquine by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).....
Dec 21,2023APICARBON MONOXIDE
630-08-0You may like
- The structure of Vanadium carbide
May 11, 2024
- The research on corundum-type Ti2O3
May 10, 2024
- Tungsten nitrides and W-N structures
May 10, 2024
- CARBON MONOXIDE
-

- $15.00 / 1KG
- 2021-08-12
- CAS:630-08-0
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%+ HPLC
- Supply Ability: Monthly supply of 1 ton