Phenylmethylsulfonyl Fluoride: A Vital Protease Inhibitor with Hazards and Toxicity Concerns
Feb 2,2024
General Description
Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride is an irreversible inhibitor of serine proteases and cysteine proteases, which are important in biological processes. It is widely used in laboratory experiments to preserve the stability and purity of protein samples during cell lysis and protein purification. However, Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride is hazardous and toxic, posing risks to human health when ingested, inhaled, or in contact with skin. Therefore, proper exposure control and personal protection measures must be taken when handling this compound. Researchers should also consider other protease inhibitors to prolong enzyme bioactivity as needed.

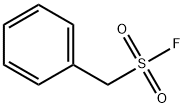
Figure 1. Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride
Overview
Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride is an irreversible serine protease inhibitor widely used in various research and laboratory processes. It appears as a white powder at room temperature, with a melting point ranging between 90-95°C. Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride exerts its action by inhibiting serine proteases such as trypsin, chymotrypsin, and thrombin, as well as cysteine proteases like papain. This process involves esterification, leading to the inactivation of enzymes containing serine at their active sites. Serine proteases naturally exist in all living organisms and are involved in diverse biological processes. For example, pancreatic proteases like trypsin and elastase function as digestive enzymes in the pancreas, while plasmin affects cell transformation. Compounds like Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride aid researchers in preserving pure cellular samples in the laboratory by preventing the enzymatic activity of proteases. Due to its limited solubility, the compound needs to be dissolved in solvents such as ethanol, methanol, or isopropanol before use. Therefore, it can serve as an alternative to water-soluble protease inhibitors like AEBSF (4-aminobenzamidine dihydrochloride). Considering its short half-life, typically lasting only between cell lysis and the first step of purification, researchers may consider applying other protease inhibitors to prolong enzyme bioactivity according to their research needs. 1
Applications in Protein Purification
Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride is widely used in protein purification to maintain protein stability during cell lysis and prevent degradation and denaturation caused by enzymatic reactions. At the cellular level, proteins are stable in their natural state or under mild environmental conditions. However, in vitro studies and experiments can disrupt the cellular mechanics of proteins, leading to degradation and denaturation. Proteinase inhibitors like Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride help researchers preserve protein stability or purity by mitigating enzyme-catalyzed reactions. During the lysis process, cells/organelles may face the disruption of regulatory mechanisms that normally inhibit protease reactions. This reaction results in the breakdown of various proteins through proteolysis. As a result, researchers may lose the protein of interest in the process, affecting the accuracy of their findings. Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride and AEBSF are commonly applied in protein purification processes because most proteases in cells and tissues belong to the serine protease group. Thus, Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride is an important component in the lysis buffer for serine-based experiments. The addition of Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride reduces sample contamination due to enzymatic reactions and provides researchers with higher concentrations of functional proteins. By adding Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride to inhibitor mixtures or protease inhibitor cocktails, researchers can provide comprehensive protection to lysate samples, safeguarding them against the catalytic actions of all four types of proteases: serine, cysteine, aspartic acid, and metalloproteases. This ensures the preservation of protein integrity and enables researchers to obtain higher yields of functional proteins. 2
Hazards and Toxicity
Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride is a chemical compound that poses various hazards to human health. Acute intraperitoneal studies on mice have shown that PMSF can cause convulsions and multiple enzyme effects. It is also toxic when ingested and can target the nerves, heart, blood, and eyes. Inhalation of Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride can cause corrosive injuries to the upper respiratory tract and lungs. To protect against Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride exposure, it is important to follow exposure control and personal protection measures. The maximum allowable concentration (MAK) for inhalable fraction of Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride is 1.0 mg/m3, while the permissible exposure limit (PEL) and threshold limit values (TLV) are both set at 2.5 mg/m3. Repeated measurements of fluorides in urine are recommended as a biological exposure index (BEI). Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride is also classified as a dermatotoxin, causing skin burns, and can induce toxic pneumonitis, which is inflammation of the lungs due to inhalation of metal fumes or toxic gases and vapours. As such, appropriate protective measures must be taken when handling Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride to minimize the risk of exposure and adverse health effects. 3
Reference
1. Ganesan S, Bashirelahi N, Young JD, Cohen SP. Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) inhibits 17 beta-estradiol binding to estrogen receptor from human prostate. Life Sci. 1987;41(25):2767-2776.
2. Mangas I, Vilanova E, Estévez J. Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, a potentiator of neuropathy, alters the interaction of organophosphorus compounds with soluble brain esterases. Chem Res Toxicol. 2012;25(11):2393-2401.
3. Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride. National Center for Biotechnology Information (2024). PubChem Compound Summary for CID 4784.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride: activities and applications Oct 20, 2023
Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride is a potent inhibitor of proteases and esterases, widely used in research for sample preservation and protein purification.
- The applications of phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride Oct 8, 2019
Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride is a serine protease inhibitor that irreversibly inhibits serine proteases by sulfonylation of the serine residue in the active site of the protease. It is widely used in protocols for the isolation of proteins
Supplementation with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate monohydrate can synthesize neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, maintaining a healthy nervous system.....
Nov 4,2025Biochemical EngineeringHexamidine diisethionate is a safe and effective antimicrobial agent, serving as a preservative and treating various skin conditions. Its recommended dosage ranges from 0.01% to 0.1%.....
Feb 2,2024APIPhenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride
329-98-6You may like
Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride manufacturers
- PMSF
-

- $48.00 / 200mg
- 2025-12-16
- CAS:329-98-6
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 99.78%
- Supply Ability: 10g
- PMSF
-

- $48.00 / 200mg
- 2025-12-16
- CAS:329-98-6
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 99.78%
- Supply Ability: 10g
- Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride
-

- $10.00 / 1KG
- 2025-12-11
- CAS:329-98-6
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 10 mt