The role of urea in skin care
Dec 14,2023
Description
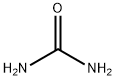
Urea is the diamide of carbonic acid with the chemical formula H2NCONH2. It is a colorless, crystalline substance that melts at 132.7° C (271° F) and decomposes before boiling. This compound has important uses as a fertilizer, feed supplement, and a starting material for manufacturing plastics and drugs[1]. Both urea and urine are different. In humans, urea is a nitrogen-containing waste substance that the kidneys clear from the blood and excrete into the urine. Human urine consists of water, urea, inorganic salts, creatinine, ammonia, and pigmented products.
Effects on the skin
Urea is a naturally occurring humectant agent that is part of the water-soluble fraction of the stratum corneum. It can both retard and promote penetration into the skin. Enhancement of skin barrier function has been frequently reported, and thus, urea is widely used to improve skin dryness. In many skin diseases characterized by dryness, such as atopic and hand eczema, urea can delay relapses in these highly chronic conditions. With this in mind, urea has been used as a well-established ingredient in various topical applications for skin care and skin diseases.

High concentrations of urea (20%-40%) dissolve atrophic nails or destroyed ones in tinea unguium. In hyperkeratotic feet, urea can improve the situation at concentrations of 10%-40%. Furthermore, urea (10%) can reduce the thickness of the stratum corneum by reducing the number of stratum corneum cell layers. Urea also improves the skin's water-holding capacity, which becomes clinically useful in ichthyotic skin. In psoriasis, urea (10%) can reduce plaque thickness but does not show effects on erythema; it is not directly anti-inflammatory in this condition. Urea also improves the skin's water-holding capacity, which becomes clinically useful in ichthyotic skin. In psoriasis, urea (10%) can reduce plaque thickness but does not show effects on erythema; thus, it is not directly anti-inflammatory in this condition[2].
Physical properties of urea, such as detachment of nails, are because of its ability to unfold proteins, thus destroying them. Urea can also replace water and increase the resistance of the stratum corneum against osmotic stress. Thymidine incorporation into DNA was observed after short-term contact with a saturated urea solution. More recently, effects of urea beyond the physical ability to be part of the natural moisturizing factor have been reported, throwing light on new aspects of action. It seems that urea can stimulate epidermal differentiation and lipid synthesis and induce the synthesis of antimicrobial peptides in the epidermis as part of the skin's immune system[3]. Various findings support the ability of urea to take effect on gene transcription: human keratinocytes react on stimulation with physiological doses of urea in the millimolar range by expression of transglutaminase, involucrin, filaggrin, and loricrin.
References
[1] Wei Xu, Prof. Shanwen Tao, Prof. Zucheng Wu. “Urea-Based Fuel Cells and Electrocatalysts for Urea Oxidation.” Energy technology 4 11 (2016): 1329–1337.
[2] Dirschka, Thomas. “Mode of action of urea.” International Journal of Clinical Practice 74 S187 (2020).
[3] I Hagemann, E Proksch. “Topical treatment by urea reduces epidermal hyperproliferation and induces differentiation in psoriasis.” Acta dermato-venereologica 76 5 (1996): 353–6.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- The Molecular Structure and Properties of Urea Dec 28, 2023
Urea is a vital organic compound used extensively in various industries due to its unique molecular structure and properties. Understanding its structure is key to comprehending its reactivity and widespread applications.
- Urea: Application, toxicity, storage, Preparation Apr 23, 2023
Urea is a key compound in the metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds in mammals and is produced naturally in the liver as a waste product of protein metabolism.
- Urea- a Versatile Nitrogenous Compound Nov 18, 2019
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula CO(NH2)2. This amide has two –NH2 groups joined by a carbonyl (C=O) functional group. It is also a carbonyl group with two C-bound amine groups.
Bromelain, from pineapples, is a proteolytic enzyme with anti-inflammatory benefits, widely used in medicine, cosmetics, and food industries.....
Dec 14,2023Food AdditivesThe poor water solubility of terbinafine hydrochloride leads to reduced oral bioavailability, so attempts were made to improve the solubility of terbinafine hydrochloride by using hydrotropic solubilisation technique.....
Dec 14,2023APIUrea
57-13-6You may like
- The toxicity of Triethylene glycol
May 14, 2024
- Is 1,4-benzoquinone a toxicity compound?
May 11, 2024
- The Synthesis method and Toxicity of 18-Crown-6
May 10, 2024
- Urea
-

- $400.00 / 1Tons
- 2024-05-24
- CAS:57-13-6
- Min. Order: 1Tons
- Purity: 99.99%
- Supply Ability: 200tons
- Urea
-

- $63.00 / 1ton
- 2024-05-24
- CAS:57-13-6
- Min. Order: 10ton
- Purity: 46%
- Supply Ability: 5000tons
- Urea
-

- $440.00 / 100tons
- 2024-05-24
- CAS:57-13-6
- Min. Order: 20tons
- Purity: 99.9%
- Supply Ability: 10000tons