What is the effect of Retinoic acid on the skin?
May 8,2024
What is Retinoic acid?
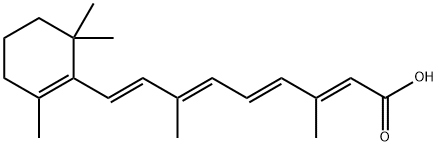
Retinoic acid, also known as all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA), tretinoin, and vitamin A acid, belongs to the group of retinoids, which are defined as synthetic or natural derivatives of vitamin A. Common retinoids include retinol, retinyl esters, retinaldehyde, and retinoic acid. Retinol and retinyl esters, of which are commonly referred to as the dietary forms of vitamin A, are not biologically active and require conversion to retinaldehyde by the enzymes cytosolic alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and microsomal retinol dehydrogenase (MDH), followed by oxidation to retinoic acid (RA) by the retinaldehyde dehydrogenase enzymes RALDH1, RALDH2 and RALDH3. The conversion of retinaldehyde to RA is irreversible, and there are several isomers of RA, the most common of which are ATRA and 9-cis retinoic acid.ATRA is also one of the major physiologically active metabolites of vitamin A. Retinoic acid is a hydrophobic compound. Retinoic acid is a hydrophobic compound and requires retinoic acid binding proteins for stabilisation in aqueous media. Retinoic acid contributes to cell growth and development, especially in the embryo.

Retinoic acid in the skin
It has been shown that retinoic acid is closely related to skin cell differentiation, value addition and epidermal barrier. Keratin-forming cells cultured in vitro in retinoic acid-deficient medium showed reduced motility, inability to form characteristic patterns, and increased adhesion. In addition, keratin production is regulated by retinoic acid concentration, and impaired epidermal barrier function can also be inhibited with the use of RA or retinol.
Retinoic acid has been reported not only for the treatment of APL (acute promyelocytic leukaemia), but is also widely used in the treatment of skin diseases such as skin cancer, psoriasis, acne, ichthyosis and even wrinkles. ATRA is also able to protect fibroblasts and other skin cells from oxidative damage induced by UV radiation. The RAR- and RXR-dependent mechanisms of the therapeutic effects of ATRA on photoaged skin in a mouse model were evaluated in a study. It was shown that ATRA and RAR agonists limited UV-induced damage to collagen fibres and increased collagen content in photoaged skin.
Moreover, modulation of retinoic acid receptors and retinoid X (or rexinoid) receptors function may affect dermal cells. The studies using complex genetic models with various combinations of retinoic acid receptors (RARs) and retinoid X (or rexinoid) receptors (RXRs) indicate that retinoic acid and its derivatives have therapeutic potential for a variety of serious dermatological disorders including some malignant conditions.
References:
[1] ŁUKASZ SZYMAŃSKI. Retinoic Acid and Its Derivatives in Skin.[J]. Cells, 2020. DOI:10.3390/cells9122660.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- The role of retinoic acid in medicine Apr 8, 2022
Retinoic acid, the molecular formula is C20H28O2, is the metabolic intermediate product of vitamin A in the body.
Olivetol, sourced from tropical plants, undergoes biotransformation, yielding three metabolites. Electrochemical detection aids cannabinoid synthesis research, highlighting its importance.....
May 8,2024APISodium ethoxide, 21% w/w in ethanol, is a strong base in organic synthesis. It finds application in various chemical reactions such as condensation, esterification, alkoxylation, and etherification.....
May 8,2024Organometallic compoundsRetinoic acid
302-79-4You may like
- Vitamin A acid Tretinoin;Retinoic Acid
-

- $150.00 / 1Kg/Bag
- 2024-05-31
- CAS:302-79-4
- Min. Order: 1Kg/Bag
- Purity: 99% up, High Density
- Supply Ability: 20 tons
- Retinoic acid
-

- $0.00 / 1kg
- 2024-05-31
- CAS:302-79-4
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 500
- Vitamin A acid / Tretinoin / Retinoic Acid
-

- $0.00/ KG
- 2024-05-29
- CAS:302-79-4
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99
- Supply Ability: 20tons