Toxicity of Potassium nonafluoro-1-butanesulfonate
Jan 14,2020

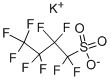
Potassium nonafluoro-1-butanesulfonate (K+PFBS) is a four-carbon, fully fluorinated alkane members of a large and diverse class of linear and branched compounds known as polyfluoroalkyl substance. K+PFBS, also known as 1-butanesulfonic acid, 1,1,2,2,3,3,4,4,4-nonafluoro-, potassium salt; 1,1,2,2,3,3,4,4,4-nonafluorobutane-1-sulfonic acid, potassium salt; and potassium 1,1,2,2,3,3,4,4,4-nonafluorobutane-1-sulphonate, is a simple salt of a PFAS chemical and is listed on the Australian Inventory of Chemical Substances(AICS).
As a man-made substance, K+PFBS does not occur naturally in the environment. Potential applications for K+PFBS chemical, which has unique physical and surfactant properties and hence potentially a range of speciality applications, may include heat, chemical and abrasion resistance and as dispersion, wetting and surface treatments [1].
K+PFBS has low acute toxicity via the oral route with an oral median lethal dose (LD50) > 2,000 mg/kg bw in rats. A single oral dose was administered by gavage to fasted animals. No treatment-related adverse clinical observations, mortality, changes in body weight or gross pathology were found. K+PFBS has low acute toxicity via the dermal route with dermal LD50s > 2,000 mg/kg bw. A single dose of each chemical was administered under semi-occlusive conditions for 24 hours. There were no clinical signs of reaction to treatment, nor dermal response to treatment observed in any animal throughout the studies. Potassium nonafluoro-1-butanesulfonate (K+PFBS) has in one study been assessed for developmental and reproductive effects in rats at maternal doses until 1g/kg/day. No adverse effect on embryo/fetal development was noted, and no significant alterations were observed in a two-generation study [2].
Human studies have examined possible associations between K+PFBS exposure and potential health outcomes such as alteration of menstruation, reproductive hormones or semen parameters, kidney function (uric acid production), lung function (induction of asthma), and lipid profile. Of the examined outcomes, only asthma, serum cholesterol, and high-density lipoprotein levels were found to exhibit a statistically significant positive association with K+PFBS exposure. No studies have been identified that evaluate the association between K+PFBS exposure and potential cancer outcomes [3].
Reference
[1]Existing Chemical Hazard Assessment Report: Potassium Perfluorobutane Sulfonate, Nov. 2005, Australian Government, Department of Health and Ageing NICNAS.
[2]Draft EHS Summary of Perfluorobutanesulfonic acid for the MATURA Science Advisory Board Meeting – April 11, 2018
[3]Human Health Toxicity Values for Perfluorobutane Sulfonic Acid (CASRN 375-73-5) and Related Compound Potassium Perfluorobutane Sulfonate (CASRN 29420-49-3), EPA-823-R-18-307 Public Comment Draft
[4]https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/23675274
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Potassium nonafluoro-1-butanesulfonate: properties, applications and safety Nov 27, 2023
Potassium nonafluoro-1-butanesulfonate, a stable fluorinating reagent, is widely used in organic synthesis and material production, offering low health risk with proper handling.
Hydrazine Sulfate is a salt of the cation hydrazinium and the anion bisulfate (hydrogen sulfate), with the formula [N2H5+] [HSO4?] or N2H6SO4. It is a white, water-soluble solid at room temperature.....
Jan 14,2020Inorganic saltsThymosin-β4 acetate (Tβ4) is a 43 amino acid peptide which is regarded as the main intracellular G-actin sequestering peptide. Extracellular thymosin β4 may contribute to physiological processes.....
Jan 14,2020Biochemical EngineeringPotassium nonafluoro-1-butanesulfonate
29420-49-3You may like
- Is oxalyl chloride toxic?
Nov 6, 2024
- 1-Pentanol:Preparation,Uses,Hazards and Incompatibility
Nov 2, 2024
- What is 4-Methylmorpholine Used for?
Nov 2, 2024
Potassium nonafluoro-1-butanesulfonate manufacturers
- Potassium nonafluoro-1-butanesulfonate
-

- $2.00 / 200KG
- 2024-11-06
- CAS:29420-49-3
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 500mt/year
- Potassium nonafluoro-1-butanesulfonate
-

- $6.00 / 1kg
- 2024-11-06
- CAS:29420-49-3
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: More than 99%
- Supply Ability: 2000KG/Month
- Potassium nonafluoro-1-butanesulfonate
-

- $99.00 / 1kg
- 2024-11-06
- CAS:29420-49-3
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 20ton