| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
FattyAcid | [CAS]
106168-45-0 | [Synonyms]
FattyAcid
Fatty acids, montan-wax, ethylene estersFatty acids, montan-wax, ethylene esters
Fatty acids, castor-oil, caustic-oxidized, distn. residues, compds. with amides from C18-unsatd. fatty acid dimers and polyhexamethylenepolyamines |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Industrial uses]
Fatty acids of the formula CnH2n+1 are saturated. Unsaturated fatty acids have a formula
of CnH2n-1. Typical examples of saturated fatty acids are stearic acid,
C17H35COOH, and palmitic acid, C15H31COOH. The example for an unsaturated fatty acid
is oleic acid. From the flotation point of view, unsaturated fatty acids are much more
important than saturated fatty acids. Unsaturated fatty acids are more selective than saturated fatty acids. | [Synthesis]
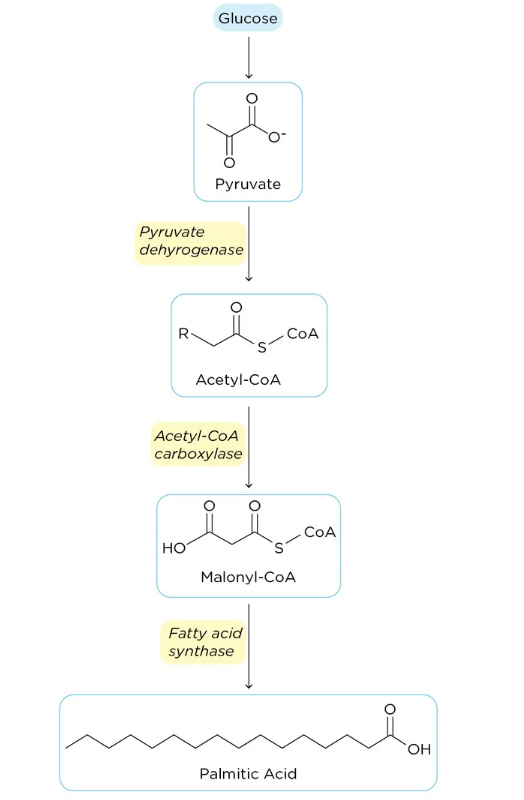
Fatty Acid synthesis occurs in the cytoplasm and endoplasmic reticulum. It is synthesised from acetyl-CoA in seven chain-extension steps, adding two carbons at a time to produce a 16-carbon fatty acid called palmitic acid; most of the synthesised fatty acid is esterified to triglycerides for storage. The synthesis pathway is mainly through the following steps:
(1) Source and transport of acetyl-CoA: Acetyl-CoA is converted from pyruvate during glycolysis. It is transported from the mitochondria to the cytoplasm in the form of citrate using.
(2) ATP citrate lyase in the cytoplasm converts citrate into acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate (which returns to the mitochondria).
(3) Acetyl-CoA in the cytoplasm is carboxylated to malonyl-CoA (three carbon atoms) in an enzymatic reaction.
(4) Fatty acid synthase, a multi-enzyme complex that mediates chain elongation, makes use of malonyl-CoA as a substrate and combines it with another acetyl-CoA molecule to form a 4-carbon fatty acid (one carbon is released as COz).
(5) The addition of the two carbons is repeated seven times in a similar process to produce a 16-carbon fatty acid called palmitate. This process must be carried out in the presence of NADPH, which acts as a reducing agent. Palmitate can then be further processed, such as using esterification.
 |
|
| Company Name: |
PVD Chemicals
|
| Tel: |
08068970178Ext 640 |
| Website: |
https://www.chemicalbook.com/ShowSupplierProductsList1738460/0.htm |
| Company Name: |
Nikunj Finechem
|
| Tel: |
08068441146Ext 349 |
| Website: |
https://www.chemicalbook.com/ShowSupplierProductsList1721611/0.htm |
| Company Name: |
SOOFI ENTERPRISES
|
| Tel: |
08048372707Ext 343 |
| Website: |
https://www.chemicalbook.com/ShowSupplierProductsList454208/0.htm |
| Company Name: |
Soofi Traders
|
| Tel: |
08048361345Ext 763 |
| Website: |
https://www.chemicalbook.com/ShowSupplierProductsList1145969/0.htm |
| Company Name: |
kemikalieimport
|
| Tel: |
+ 45 - 2034 3359 |
| Website: |
www.kemikalieimport.dk |
|