674786-20-0
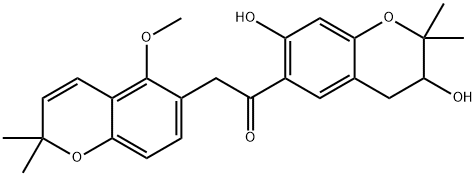 674786-20-0 结构式
674786-20-0 结构式
物理化学性质
常见问题列表
IC50: 20.9 μM (GPR56); GPR114
Assays are initiated by the addition of [
35
S]GTPγS, and the rates of aGPCR-stimulated G protein activation ([
35
S]GTPγS binding to Gα) are measured with or without the influence of added compounds. Dihydromunduletone (DHM) inhibits the kinetics of GPR56 7TM-stimulated G13 GTPγS binding to varying degrees. Dihydromunduletone is the best inhibitory compound and reduced the rate at which GPR56 7TM activated G13 >75% (from 0.18 to 0.04 minute
−1
).
At a concentration of Dihydromunduletone (DHM) that maximally inhibits GPR56 (50 μM), the rate of GPR114 7TM-stimulated Gs activity is also inhibited dramatically. When Dihydromunduletone (50 μM) is applied to the GPR110 7TM, it fails to inhibit GPR110 stimulation of Gq GTPγS binding.
Cells transfected with GPR56 A386M 7TM are incubated with increasing concentrations of Dihydromunduletone. P7 peptide agonist is added, and SRE-luciferase activity is measured. Dihydromunduletone inhibits the P7 peptide-induced luciferase activity in a concentration-dependent manner. Cells are also treated with a fixed concentration of 3 µM Dihydromunduletone and then stimulated with an increasing concentration of P7 peptide agonist. Dihydromunduletone treatment blunts P7 peptide activation at each concentration. In conclusion, Dihydromunduletone antagonizes synthetic-peptide agonist and tethered-peptide agonist-mediated aGPCR activation in isolated membranes and HEK293T cell-based assays, but it does not inhibit basal receptor signaling.