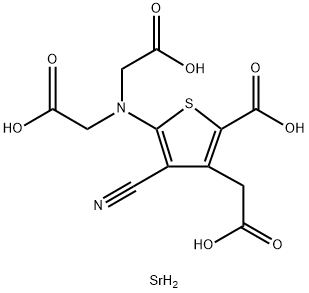
Strontium ranelate
- CAS No.
- 135459-87-9
- Chemical Name:
- Strontium ranelate
- Synonyms
- Ranelic acid strontium salt;Protos;S 12911;Protelos;S 12911-2;TrontiuMranelate;StrontiuM Ranelic;Srtontiumranelate;Ranelate StrontiuM;STRONTIUM RANELATE
- CBNumber:
- CB1838150
- Molecular Formula:
- C12H12N2O8SSr
- Molecular Weight:
- 431.91
- MDL Number:
- MFCD09038742
- MOL File:
- 135459-87-9.mol
| Melting point | >310°C (dec.) |
|---|---|
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | H2O: soluble1mg/mL, clear (warmed) |
| form | powder |
| color | white to beige |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 135459-87-9 |
| FDA UNII | 04NQ160FRU |
| NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms | strontium ranelate |
| ATC code | M05BX03 |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H302+H312+H332 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P261-P264-P280-P301+P312-P302+P352+P312-P304+P340+P312 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xn | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 20/21/22 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 36/37 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | 3077 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | XM7581000 | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29349990 | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Strontium ranelate price More Price(39)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich | SML0596 | Strontium ranelate ≥98% (HPLC) | 135459-87-9 | 10mg | $63.5 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | SML0596 | Strontium ranelate ≥98% (HPLC) | 135459-87-9 | 50mg | $248 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Cayman Chemical | 30272 | Strontium Ranelate | 135459-87-9 | 50mg | $116 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Cayman Chemical | 30272 | Strontium Ranelate | 135459-87-9 | 250mg | $397 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Cayman Chemical | 30272 | Strontium Ranelate | 135459-87-9 | 10mg | $37 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
Strontium ranelate Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Drug for the treatment of osteoporosis
Strontium ranelate is a drug for the treatment of osteoporosis with its appearance being white to light yellow powder or crystalline powder. It is odorless and slightly soluble in water but almost insoluble in ethanol and easily soluble in dilute hydrochloric acid. It was first studied and developed by the French Servier Company and had first entered into market in November 2004 in Ireland and entered into market in UK in December of same year. Japan's Fujisawa Pharmaceutical Company has owned the authorization of development, production and marketing right of this product in Japan. It is clinically mainly used for the treatment and prevention of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women with significantly reducing the risk of occurrence of vertebral fractures and hip fractures.
Strontium ranelate has dual pharmacological inhibitory effects of both inhibiting bone absorption and promoting bone formation. On the one hand, in the osteoblast-enriched cells, it can increase the synthesis of collagen and non-collagen proteins and promote the osteoblast-mediated bone formation mediated by osteoblasts through enhancing the proliferation of pre-osteoblast. On the other hand, through decreasing the osteoclast differentiation and reabsorbing activity and further reduction of bone absorption, it achieves the rebalance of bone turnover, further boosting the bone formation.
Strontium ranelate mainly exerts its pharmacological effects through its strontium atoms. Strontium is an alkaline earth metal element which is cognate with calcium and located under the calcium in the element periodic table. Its absorption, distribution, excretion is similar with calcium. After oral administration of 2g, the absolute bioavailability of strontium is 27%. Large doses of strontium cause abnormalities of bone mineral metabolism with low doses of strontium being able to the enhance the pre-osteoblast replication, increasing the number of osteoblasts to stimulate bone formation while reducing the activity of osteoclasts, reducing osteoclast quantity as well as reducing the rate of bone absorption. The results are consistent with the results found in animal and human in vivo studies.
s (OP) is a progressive skeletal disease, characterized by reduced bone mineral density (BMD) and degenerative changes in bone tissue microstructure. It is exhibited as bone fragility and fracture-prone with the latter most commonly happening in the spine, hip and wrist. For women, when after surgical removal of the ovaries or menopause, the body stops producing bone to maintain strong estrogen, thus, primary OP is particularly common in post-menopausal or menopausal women.
There are currently two major kinds of drugs used in the treatment of osteoporosis: one kind includes those drugs that inhibits osteoclast activity and therefore inhibiting bone absorption such as bisphosphonates, estrogen and calcitonin; the second category includes those drugs which promote the osteoblast activity, and thereby stimulating bone formation and there are currently only a product, human recombinant parathyroid hormone 1-34, that has entered into market. It however requires injection with high drug prices.
The above information is edited by the chemicalbook of Dai Xiongfeng.
Uses
It is mainly used for the treatment and prevention of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and significantly reduces the risk of occurrence of vertebral fractures and hip fractures.
Description
Strontium ranelate, a divalent strontium salt of ranelic acid, has been developed and launched for the treatment of osteoporosis. As early as 1910, investigations suggested that strontium stimulates the formation of osteoid tissues while simultaneously repressing the resorptive process in bones. Specifically, strontium enhances pre-osteoblastic cell replication, inhibits pre-osteoclast differentiation, and suppresses the bone-resorbng activity of osteoclasts. From the evaluation of 26 strontium salts, ranelic acid was selected as the ideal strontium carrier due to its physicochemical and pharmacokinetic properties. The thiophene core of ranelic acid is constructed by the condensation of dialkyl 3-oxoglutarate, malononitrile, and sulfur in a suitable alcohol in the presence of morpholine or diethylamine. The resultant diester of 5-amino-3-carboxymethyl-4-cyano-2-thiophenecarboxylic acid is subsequently dialkylated with an alkyl bromoacetate to provide the tetraester precursor to strontium ranelate. Strontium ranelate is supplied in a 2 g sachet, and the drug is evenly suspended in water prior to consumption. Since the simultaneous ingestion of either calcium or food has a negative influence on the bioavailability of strontium ranelate, it is recommended that strontium ranelate be administered once a day at bedtime. Following this regimen, the absolute bioavailability of strontium is 27% while that of ranelic acid is 2.5%. Because strontium ranelate dissociates after intake, and ranelic acid has negligible absorption, the effects of the drug on bone metabolism are dependent on the pharmacokinetics of strontium. In postmenopausal women, the half-life of strontium is 6.3±2.3 days, and renal clearance accounts for 57%of the total clearance of 12mL/min. After a 25-day treatment, the maximum plasma concentration of strontium is 20±2.3 mg/L. In addition, not only is perfect stability of strontium plasma concentration achieved within 3 to 24 months of chronic administration so is stabilization of strontium incorporation into bones. Strontium is incorporated into bone by two mechanisms. The predominant mode involves the rapid, saturable surface exchange with calcium. A slower mechanism embodies the incorporation of strontium into the crystal lattice of the bone mineral; however, only a small amount of calcium in the apatite is substituted by strontium at pharmacological doses. A phase II clinical trial assessed the effect of various strontium ranelate doses in postmenopausal women with established osteoporosis. The primary efficacy endpoint for this double-blind, randomized, placebo- controlled trial was the measure of mean lumbar bone mineral density (BMD) by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. A statistically significant dose-dependent increase in lumbar BMD was observed; increases of 1.3, 5.9, 8.3, and 13.6% were recorded for placebo, 500-, 1000-, and 2000-mg doses of strontium ranelate, respectively. In a phase III trial encompassing 1,649 osteoporotic postmenopausal women from 12 countries, the efficacy of a 2 g/day dose in preventing new vertebral fractures was evaluated. The mean lumbar BMD was 0.73 g/cm2 while the mean age at baseline was 70 years. All of the enrolled patients had at least one prior vertebral fracture. The primary end point for this study was a reduction in the incidence of patients experiencing fractures. While 222 women in the placebo group experienced a new vertebral fracture, only 139 patients treated with strontium ranelate presented with new fractures. Furthermore, the risk of fracture was reduced by 51% in the third year alone, implicating the sustained efficacy of the drug. For both the phase II and phase III studies, strontium ranelate was well tolerated with most of the adverse events being mild-to-moderate in severity. The most commonly reported events in all treatment groups were musculoskeletal disorders (back pain, arthralgia, and lumbar pain). As for laboratory measurements, only creatine phosphokinase, the musculoskeletal isoenzyme, was significantly elevated in the 1000-mg and 2000-mg strontium ranelate groups; however, this did not translate into any particular clinical or biological abnormality. Without relevant data regarding bone safety in patients with renal impairment, strontium ranelate is currently contraindicated in patients with creatine clearance below 30mL/min.
Chemical Properties
Crystalline Solid
Originator
Fujisawa (Japan)
Uses
Strontium ranelate (Protelos) is a strontium(II) salt of ranelic acid for (-)-desmethoxyverapamil binding to calcium channel with IC50 of 0.5 mM.
Uses
Bone metabolism modulator; inhibits bone resorption while maintaining bone formation. Antiosteoporotic.
brand name
Protelos
Clinical Use
Treatment of post menopausal osteoporosis and men at high risk of fractures
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Calcium-containing compounds: separate
administration by at least 2 hours.
Antacids: separate administration by at least 2 hours.
Antibiotics: strontium can reduce absorption of oral
tetracycline and quinolones - suspend strontium
therapy during treatment.
Metabolism
Strontium ranelate has a high affinity for bone tissue. It is not metabolised, and excretion occurs via the kidneys and gastrointestinal tract.
Strontium ranelate Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wuhan Fortuna Chemical Co., Ltd | +86-027-59207850 | info@fortunachem.com | China | 5975 | 58 |
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co,.LTD | +86-13131129325 | sales1@chuanghaibio.com | China | 5889 | 58 |
| Shaanxi Haibo Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +undefined18602966907 | qinhe02@xaltbio.com | China | 997 | 58 |
| Shaanxi TNJONE Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd | +8618092446649 | sarah@tnjone.com | China | 1143 | 58 |
| Hebei Zhuanglai Chemical Trading Co.,Ltd | +8613343047651 | admin@zlchemi.com | China | 3002 | 58 |
| BEIJING SJAR TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT CO., LTD. | +86-18600796368 +86-18600796368 | sales@sjar-tech.com | China | 484 | 58 |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 | info@tianfuchem.com | China | 21634 | 55 |
| Nanjing Finetech Chemical Co., Ltd. | 025-85710122 17714198479 | sales@fine-chemtech.com | CHINA | 885 | 55 |
| ATK CHEMICAL COMPANY LIMITED | +undefined-21-51877795 | ivan@atkchemical.com | China | 32956 | 60 |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 | sales@coreychem.com | China | 29880 | 58 |
View Lastest Price from Strontium ranelate manufacturers
| Image | Update time | Product | Price | Min. Order | Purity | Supply Ability | Manufacturer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
2025-01-03 | Strontium ranelate
135459-87-9
|
US $70.00 / kg | 1kg | 99 | 5000 | Hebei Zhuanglai Chemical Trading Co.,Ltd | |
 |
2024-12-30 | Strontium Ranelate
135459-87-9
|
US $0.00 / g | 1g | More Than 99% | 50kg/Month | BEIJING SJAR TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT CO., LTD. | |
 |
2024-12-27 | Strontium ranelate
135459-87-9
|
US $0.00-0.00 / Kg/Drum | 1KG | 99%min | 1000kg | WUHAN FORTUNA CHEMICAL CO., LTD |
-

- Strontium ranelate
135459-87-9
- US $70.00 / kg
- 99
- Hebei Zhuanglai Chemical Trading Co.,Ltd
-

- Strontium Ranelate
135459-87-9
- US $0.00 / g
- More Than 99%
- BEIJING SJAR TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT CO., LTD.
-

- Strontium ranelate
135459-87-9
- US $0.00-0.00 / Kg/Drum
- 99%min
- WUHAN FORTUNA CHEMICAL CO., LTD