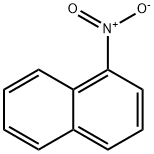
1-Nitronaphthalene
- CAS No.
- 86-57-7
- Chemical Name:
- 1-Nitronaphthalene
- Synonyms
- 1-Nitronaftalen;I-P#itronaphthalin;Nitrol (pesticide);1-Nitro-naphthaline;Naphthalene,1-nitro-;1-nitronaphthalene (alpha);NCI-C01956;1-nitronathalene;1-Nitronphthalene;nitrol(pesticide)
- CBNumber:
- CB2487528
- Molecular Formula:
- C10H7NO2
- Molecular Weight:
- 173.17
- MDL Number:
- MFCD00003913
- MOL File:
- 86-57-7.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
| Melting point | 56 °C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 304 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.223 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| refractive index | 1.5200 (estimate) |
| Flash point | 164 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: insoluble |
| color | Light Yellow To Yellow |
| Specific Gravity | 1.223 |
| Water Solubility | 0.022 g/L |
| Merck | 14,6613 |
| BRN | 1867714 |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with oxidizing agents, strong reducing agents. Mixtures with sulfuric or nitric acid are dangerous. |
| InChIKey | RJKGJBPXVHTNJL-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 86-57-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| FDA UNII | A51NP1DL2T |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 46) 1989 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Naphthalene, 1-nitro-(86-57-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1-Nitronaphthalene (86-57-7) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS02,GHS07,GHS09 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H228-H302-H411 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P210-P240-P241-P264-P273-P301+P312 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | F,T,N | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 11-25-51/53-40-36/37/38-23/24/25 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 16-45-60-61-28A-36/37/39-26 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 2538 4.1/PG 3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 2 | |||||||||
| RTECS | QJ9720000 | |||||||||
| Hazard Note | Flammable/Toxic | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 4.1 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29042000 | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
1-Nitronaphthalene Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
yellow crystalline solid
Uses
Usually used to study excited state dynamics of 1-nitropthalene in nonpolar, aprotic and protic solvents.
Uses
1-Nitronaphthalene as a nitroaromatic compound is studied for mutagenicity, as nitroaromatics are used in everyday products from polmers, dyes to drugs.
Definition
ChEBI: A mononitronaphthalene substituted by a nitro group at position 1.
Production Methods
One method to product 1-Nitronaphthalene: Naphthalene is charged to sulfuric acid alternately with mixed acid at 40 – 50 ℃ over 8 h, with the final temperature being 55 ℃. The acid strength used allows the molten product to be separated as an oil and washed. Continuous operation at 50 – 60 ℃ with mixed acid (33/48/19) gives a comparable product. The crude reaction product is obtained in 90 – 95 % yield and is purified by vacuum distillation.
General Description
1-Nitronaphthalene is a mutagenic nitroaromatic compound present in diesel exhaust and it causes acute liver and lung toxicity in rodents. 1-Nitronaphthalene is a cytochrome P450-bioactivated, nonciliated bronchiolar epithelial (Clara) cell cytotoxicant .
Biochem/physiol Actions
1-Nitronaphthalene binds covalently to protein and forms adducts in the rat airway epithelium in vivo.
Safety Profile
Poison by intraperitoneal route. Mutation data reported. A skin, eye, and mucous membrane irritant. Flammable solid and combustible liquid when exposed to heat or flame. To fight fire, use CO2, dry chemical, or water spray. Explosive reaction with nitric acid + sulfuric acid above 60°C. Forms a sensitive explosive mixture with tetranitromethane. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. See also 2-NITRONAPHTHALENE and NITRO COMPOUNDS OF AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS.
Purification Methods
Fractionally distil 1-nitronaphthalene under reduced pressure, then crystallise it from EtOH, aqueous EtOH or heptane. Chromatograph it on alumina with *benzene/pet ether as eluent. It sublimes in vacuo. The 1:1 picrate complex has m 72o (from EtOH). [Beilstein 5 H 553, 5 III 1593, 5 IV 1673.]