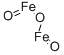Ferric oxide
- CAS No.
- 1309-37-1
- Chemical Name:
- Ferric oxide
- Synonyms
- Diiron Trioxide;Pigment red 101;Red Ferric Oxide;supra;ochre;deanox;raddle;rubigo;ferrugo;ironred
- CBNumber:
- CB3115644
- Molecular Formula:
- Fe2O3
Lewis structure

- Molecular Weight:
- 159.69
- MDL Number:
- MFCD00748135
- MOL File:
- 1309-37-1.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
| Melting point | 1538°C | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density | 5.24 | ||||||||||||||
| Flash point | >230 °F | ||||||||||||||
| storage temp. | 2-8°C | ||||||||||||||
| solubility | It is soluble In Warm Hydrochloric Acid, Slightly Soluble in Sulfuric Acid. | ||||||||||||||
| form | pieces | ||||||||||||||
| color | black | ||||||||||||||
| Specific Gravity | 5.1~5.2 | ||||||||||||||
| PH | 3.7±0.3 | ||||||||||||||
| Water Solubility | INSOLUBLE | ||||||||||||||
| Crystal Structure | Corundum type | ||||||||||||||
| crystal system | Three sides | ||||||||||||||
| Merck | 14,4028 | ||||||||||||||
| Space group | R3c | ||||||||||||||
| Lattice constant |
|
||||||||||||||
| Exposure limits |
ACGIH: TWA 5 mg/m3 OSHA: TWA 10 mg/m3; TWA 15 mg/m3; TWA 5 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 2500 mg/m3; TWA 5 mg/m3 |
||||||||||||||
| Stability | Stable. | ||||||||||||||
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1309-37-1(CAS DataBase Reference) | ||||||||||||||
| FDA 21 CFR | 186.1300; 73.1200; 73.200 | ||||||||||||||
| Substances Added to Food (formerly EAFUS) | FERRIC OXIDE | ||||||||||||||
| SCOGS (Select Committee on GRAS Substances) |
Ferric oxide Ferric oxide (packaging) |
||||||||||||||
| EWG's Food Scores | 1-2 | ||||||||||||||
| FDA UNII | 1K09F3G675 | ||||||||||||||
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 1, Sup 7) 1987 | ||||||||||||||
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Iron(iii) oxide(1309-37-1) | ||||||||||||||
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ferric oxide (1309-37-1) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS02,GHS05 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H225-H318 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P210-P280-P305+P351+P338+P310 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xi | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 36/37/38 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26 | |||||||||
| OEB | B | |||||||||
| OEL | TWA: 5 mg/m3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | - | |||||||||
| RTECS | NO7400000 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HS Code | 28211000 | |||||||||
| IDLA | 2,500 mg Fe/m3 | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Ferric oxide price More Price(50)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alfa Aesar | 010716 | Iron(III) oxide, Puratronic?, 99.998% (metals basis) | 1309-37-1 | 25g | $171 | 2023-06-20 | Buy |
| Alfa Aesar | 010716 | Iron(III) oxide, Puratronic?, 99.998% (metals basis) | 1309-37-1 | 100g | $509 | 2023-06-20 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | 747335 | Iron oxide(II,III) magnetic nanoparticles solution | 1309-37-1 | 2ml | $648 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | 720712 | Iron(III) oxide, dispersion nanoparticles, ≤110 nm particle size, 15 wt. % in ethanol | 1309-37-1 | 100g | $222 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | 544884 | Iron(III) oxide nanopowder, <50 nm particle size (BET) | 1309-37-1 | 5g | $44.9 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
Ferric oxide Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Physical Properties
Reddish-brown hexagonal crystal; refractive index 2.91; density 5.25g/cm3; Moh’s hardness 6.0; melts at 1565°C; insoluble in water; dissolves in acids.

Occurrence and Uses
Ferric oxide occurs in nature as the mineral hematite. It is the principal ore of iron from which the metal and its alloys are produced. Also, this oxide occurs in the mineral, limonite, 2Fe2O3•3H2O. An important application of this compound involves producing red, orange, and yellow pigments. Other applications are in coatings for metals, steel and rubber; in ceramics; and as a catalyst for oxidation reactions.
Preparation
Ferric oxide is prepared as a reddish-brown hydrated precipitate by treating an aqueous solution of an iron(III) salt with caustic soda:
2FeCl3 + 6NaOH → Fe2O3•3H2O + 6NaCl
It also is obtained by thermal decomposition of iron(II) sulfate or the brown oxide hydroxide:
2FeSO4 → Fe2O3 + SO2 + SO3
2FeO(OH) → Fe2O3 + H2O
The oxide is prepared in industrial scale by first precipitating iron(II) hydroxide Fe(OH)2 by treating aqueous solutions of iron(II) sulfate and caustic soda. The Fe(OH)2 is then oxidized to iron(III) hydroxide by aeration. The latter is dehydrated by heating:
Fe2+ (aq) + OH¯ (aq) → Fe(OH)2(s) → 2Fe(OH)3 → Fe2O3 + 3H2O
It also is produced by ignition of iron(III) oxalate and iron carbonyls:
2Fe2(C2O4)3 +3O2 → 2Fe2O3 + 12CO
Reactions
Ferric oxide decomposes to its elements when heated at elevated temperatures:
2Fe2O3 → 4Fe + 3O2
The oxide is reduced by most reducing agents. Reaction with carbon monoxide at elevated temperatures (that occurs in the blast furnace) gives metallic iron. The overall reaction is mildly exothermic (ΔHrxn –113.4 kcal/mol):
2 Fe2O3 + 6CO → 4Fe + 6CO2
It also is reduced by powdered aluminum at elevated temperatures, forming aluminum oxide and metallic iron:
Fe2O3 + 2Al → Al2O3 + 2Fe
The reaction is highly exothermic and becomes self-sustaining after ignition.
When heated with sand in an electric furnace, iron(III) oxide forms ferrosilicon alloy. When heated in a vacuum at 1,000°C, it forms triiron tetroxide, Fe3O4.
Description
Iron oxides are produced synthetically and consist essentially of anhydrous and/or hydrated iron oxides. The range of hues includesyellows, reds, browns and blacks. Food quality iron oxides are primarily distinguished from technical grades by the comparatively low levels of contamination by other metals. This is achieved by the selection and control of the source of iron and/or by the extent of chemical purification during the manufacturing process. Iron oxides have been used to color confectionery, fillings and decorations for pastry products, cheese products, fish paste, pet foods, cosmetics and pharmaceutical products.
Chemical Properties
Hematite is a noncombustible, black to black red or brick-red mineral (iron ore) composed mainly of ferric oxide, Fe2O3. Ferric oxide
Occurrence
Iron(III) oxide occurs in nature as the mineral hematite. It is the principal ore of iron from which the metal and its alloys are produced. Also, this oxide occurs in the mineral, limonite, 2Fe2O3?3H2O. An important application of this compound involves producing red, orange, and yellow pigments. Other applications are in coatings for metals, steel and rubber; in ceramics; and as a catalyst for oxidation reactions.
Uses
Red iron oxide (Fe2O3) is an inorganic pigment of either natural or synthetic origin. It is a low chroma red with excellent durability and low cost. Synthetic pigment is made by heating iron sulfate with quicklime in a furnace. The second preparatory technique involves calcining iron sulfate in the presence of air at high temperatures. Natural and oxides of iron are mined either as the mineral hematite (Fe2O3) or as hematite in its hydrated form.
Uses
As pigment for rubber, paints, paper, linoleum, ceramics, glass; in paint for ironwork, ship hulls; as polishing agent for glass, precious metals, diamonds; in electrical resistors and semiconductors; in magnets, magnetic tapes; as catalyst; colloidal solutions as stain for polysaccharides.
Uses
Ferric Oxide is a nutrient and dietary supplement that is a source of iron.
Definition
A high-grade red pigment used as a polishing agent for glass, jewelry, etc. (2) A cosmetic prepared from dried flowers of the saf- flower.
Preparation
Iron(III) oxide is prepared as a reddish-brown hydrated precipitate by treating an aqueous solution of an iron(III) salt with caustic soda:
2FeCl3 + 6NaOH → Fe2O3?3H2O + 6NaCl
It also is obtained by thermal decomposition of iron(II) sulfate or the brown oxide hydroxide:
2FeSO4 → Fe2O3 + SO2 + SO3
2FeO(OH) → Fe2O3 + H2O
The oxide is prepared in industrial scale by first precipitating iron(II) hydroxide Fe(OH)2 by treating aqueous solutions of iron(II) sulfate and caustic soda. The Fe(OH)2 is then oxidized to iron(III) hydroxide by aeration. The latter is dehydrated by heating:
Fe2+ (aq) + OHˉ (aq) → Fe(OH)2(s) → 2Fe(OH)3 → Fe2O3 + 3H2O
It also is produced by ignition of iron(III) oxalate and iron carbonyls:
2Fe2(C2O4)3 +3O2 → 2Fe2O3 + 12CO
.
Definition
A black solid prepared by passing either steam or carbon dioxide over redhot iron. It may also be prepared by passing steam over heated iron(II) sulfide. Triiron tetroxide occurs in nature as the mineral magnetite. It is insoluble in water but will dissolve in acids to give a mixture of iron(II) and iron(III) salts in the ratio 1:2. Generally it is chemically unreactive; it is, however, a fairly good conductor of electricity.
Hazard
Pneumoconiosis. Questionable carcinogen.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Potential Exposure
Hematite; as an iron ore composed mainly of ferric oxide, is a major source of iron and is used as a pigment for rubber, paints, paper, linoleum, ceramics, dental restoratives; and as a polishing agent for glass and pre cious metals. It is also used in electrical resistors, semiconduc tors, magnets, and as a catalyst. Human exposure to hematite from underground hematite mining is principally through inhalation and/or ingestion of dusts. No estimates are available concerning the number of underground miners exposed.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irri gate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek med-ical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, includ-ing resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medi-cal attention. Give large quantities of water and induce :vomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.Note to physician: For severepoisoning,do not useBAL .[British Anti-Lewisite, dimercaprol, dithiopropanol (C3HgOS2)] as it is contraindicated or ineffective in poisoningfrom iron.
Carcinogenicity
Welders are typically exposed to a complex mixture of dust and fume of metallic oxides, as well as irritant gases, and are subject to mixeddust pneumoconiosis with possible loss of pulmonary function; this should not be confused with benign pneumoconiosis caused by iron oxide.1 Although an increased incidence of lung cancer has been observed among hematite miners exposed to iron oxide, presumably owing to concomitant radon gas exposure, there is no evidence that iron oxide alone is carcinogenic to man or animals.6
storage
Color Code- Green: General storage may be used.Prior to working with this chemical you should be trainedonits proper handling and storage. Store in tightly closedcontainers in a cool, well-ventilatedarea. .Where possible,automatically transfer material from other storage contain-ers to process containers A regulated, marked area shouldbe established where this chemical is handled, used, orstored in compliance with OSHA Standard 1910.1045.
Properties and Applications
|
TEST ITEMS |
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE |
DARK RED POWDER |
|
SHADE |
CLOSE TO STANDARD |
|
CONTENT OF Fe 2 O 3 |
96% min |
|
pH VALUE |
3-7 |
|
OIL ABSORPTION |
15-25% |
|
RESIDUE ON 320 MESH |
0.3% max |
|
WATER SOLUBLE |
0.3% max |
|
VOLATITE 105 °C |
1.0% max |
|
TINTING STRENGTH |
98-102 % |
Incompatibilities
Contact with hydrogen peroxide, ethyl ene oxide, calcium hypochlorite will cause explosion. Violent reaction with powdered aluminum; hydrazine, hydrogen trisulfide.
Ferric oxide Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of5
Preparation Products
1of2
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hebei Andu Technology Com.,Ltd | +86-86-17798073498 +8617798073498 | admin@hbandu.com | China | 299 | 58 |
| Shaanxi Dideu Medichem Co. Ltd | +86-29-81148696 +86-15536356810 | 1022@dideu.com | China | 3882 | 58 |
| Hebei Dangtong Import and export Co LTD | +86-13910575315 +86-13910575315 | admin@hbdangtong.com | China | 1000 | 58 |
| Hebei Weibang Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8617732866630 | bess@weibangbio.com | China | 18153 | 58 |
| Henan Bao Enluo International TradeCo.,LTD | +86-17331933971 +86-17331933971 | deasea125996@gmail.com | China | 2472 | 58 |
| Hebei Kingfiner Technology Development Co.Ltd | +86-15532196582 +86-15373005021 | lisa@kingfinertech.com | China | 3010 | 58 |
| Yujiang Chemical (Shandong) Co.,Ltd. | +86-17736087130 +86-18633844644 | catherine@yjchem.com.cn | China | 985 | 58 |
| Hebei Zhuanglai Chemical Trading Co.,Ltd | +8613343047651 | admin@zlchemi.com | China | 3002 | 58 |
| Hebei Shengyang Water Conservancy Engineering Co., Ltd. | +8615373025980 | clara@hbshengyang.com | China | 874 | 58 |
| Shandong Deshang Chemical Co., Ltd. | +86-0531-8875-2665 +8613153039501 | info@deshangchem.com | China | 662 | 58 |
Related articles
- Ferric oxide: Polarity and Application
- Fe2O3 is an ionic compound. The electronegativity difference between iron and oxygen atoms is 1.6, which corresponds to the el....
- Jan 4,2024
View Lastest Price from Ferric oxide manufacturers
| Image | Update time | Product | Price | Min. Order | Purity | Supply Ability | Manufacturer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
2024-11-25 | Ferric oxide
1309-37-1
|
US $100.00-75.00 / kg | 1kg | 99% | 5000 | HEBEI SHENGSUAN CHEMICAL INDUSTRY CO.,LTD | |
 |
2024-11-25 | Ferric oxide
1309-37-1
|
US $3.50 / kg | 1kg | 0.99 | 3000tons/month | Hebei Andu Technology Com.,Ltd | |
 |
2024-11-22 | Ferric oxide
1309-37-1
|
US $50.00-30.00 / kg | 1kg | 99% | 5000kg/Month | Hebei Zhuanglai Chemical Trading Co.,Ltd |
-

- Ferric oxide
1309-37-1
- US $100.00-75.00 / kg
- 99%
- HEBEI SHENGSUAN CHEMICAL INDUSTRY CO.,LTD
-

- Ferric oxide
1309-37-1
- US $3.50 / kg
- 0.99
- Hebei Andu Technology Com.,Ltd
-

- Ferric oxide
1309-37-1
- US $50.00-30.00 / kg
- 99%
- Hebei Zhuanglai Chemical Trading Co.,Ltd