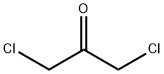
1,3-Dichloroacetone
- CAS No.
- 534-07-6
- Chemical Name:
- 1,3-Dichloroacetone
- Synonyms
- DCA;1,3-DICHLORO-2-PROPANONE;SYM-DICHLOROACETONE;1,3-dichloropropanone;1,3-dichloro-propan-2-one;1,3-DCA;NSC 8745;dichloroacetone;s-Dichloroacetone;,-Dichloroacetone
- CBNumber:
- CB3853746
- Molecular Formula:
- C3H4Cl2O
- Molecular Weight:
- 126.97
- MDL Number:
- MFCD00000937
- MOL File:
- 534-07-6.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
| Melting point | 43 °C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 73 °C733.4 mm Hg(lit.) |
| Density | 1.383 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 4.38 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | <0.1 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.4400 |
| Flash point | 193 °F |
| storage temp. | Refrigerator (+4°C) + Poison room |
| solubility | alcohol: very soluble |
| form | Crystals |
| Specific Gravity | 1.383 |
| color | White or colorless |
| PH | 4.2 (10g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Water Solubility | 27.9 g/L (20 º C) |
| Merck | 14,3052 |
| BRN | 605456 |
| Dielectric constant | 14.0(20℃) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 534-07-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EWG's Food Scores | 1 |
| FDA UNII | UFH8559WS5 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 1,3-Dichloro-2-propanone(534-07-6) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Bis(chloromethyl) ketone (534-07-6) |
| UNSPSC Code | 12352100 |
| NACRES | NA.22 |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS05,GHS06,GHS08 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H300+H310+H330-H314-H341 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P202-P260-P280-P303+P361+P353-P304+P340+P310-P305+P351+P338 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | T+,F | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 24-26/28-34-68-36/37/38-11 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-36/37/39-45-28A-1-28-16 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 3286 3/PG 2 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | UC1430000 | |||||||||
| F | 19 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 6.1 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | II | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29147090 | |||||||||
| Hazardous Substances Data | 534-07-6(Hazardous Substances Data) | |||||||||
| Toxicity | mmo-sat 1250 ng/plate MUREAV 157,111,85 | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
1,3-Dichloroacetone Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
1,3-Dichloroacetone is a chemical substance with the molecular formula C3H4Cl2O. TLC has discovered that it is a metabolite of 1,3-dichloropropanol. The crystalline solid is denser than water and is not water-soluble.
Applications
1,3-Dichloroacetone is employed in the synthesis of citric acid. Additionally, it is used as an intermediate and a solvent in organic synthesis. Furthermore, 1,3-Dichloroacetone is utilized as an acceptor substrate in the cross-aldol reaction with donor substrates such as clyclohexanone, cyclopentanone, and acetone. 1,3-Dichloroacetone is also employed in the preparation of famotidine which is an active pharmaceutical ingredient.
Safety
When exposed or inhaled, 1,3-Dichloroacetone can result in damage or irritation to eyes, lungs, throat, kidney, and kidneys. It can also lead to fainting and headaches. The substance has been classified as extremely hazardous in America.
Description
Bis(chloromethyl)ketone is a crystalline solid.Molecular weight=127.02; Freezing/Melting point=45℃;Boiling point=173℃. Hazard Identification (based onNFPA-704 M Rating System): Health 3, Flammability 1,Reactivity 0. Soluble in water.
Chemical Properties
Bis(chhloromethyl)ketone is a crystalline solid.
Chemical Properties
White or colorless crystals
Uses
1,3-Dichloroacetone was used as acceptor substrate in the cross-aldol reaction with donor substrates such as acetone, cyclopentanone and cyclohexanon
Definition
ChEBI: 1,3-dichloroacetone is a ketone that is propan-2-one in which a hydrogen at positions 1 and 3 have been replaced by chloro groups. It is used in the synthesis of citric acid. Also used as a solvent and as an intermediate in organic synthesis. It is an organochlorine compound and a ketone. It is functionally related to a 1,3-dichloropropan-2-ol.
General Description
A crystalline solid. Denser than water and insoluble in water. Inhalation of dust or powder may cause adverse health reactions.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
A halogenated ketone. Ketones are reactive with many acids and bases liberating heat and flammable gases (e.g., H2). The amount of heat may be sufficient to start a fire in the unreacted portion of the ketone. Ketones react with reducing agents such as hydrides, alkali metals, and nitrides to produce flammable gas (H2) and heat. Ketones are incompatible with isocyanates, aldehydes, cyanides, peroxides, and anhydrides. They react violently with aldehydes, HNO3, HNO3 + H2O2, and HClO4.
Health Hazard
1,3-Dichloroacetone may be fatal if inhaled, swallowed or absorbed through skin. Contact may cause burns to skin and eyes. Fire may produce irritating or poisonous gases. Runoff from fire control water may give off poisonous gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
When heated to decomposition, 1,3-Dichloroacetone emits highly toxic fumes of chlorides. 1,3-Dichloroacetone may burn but does not ignite readily. Container may explode in heat of fire.
Safety Profile
Poison by inhalation. Mutationdata reported. A systemic irritant by ingestion andinhalation routes. Dangerous; whenheated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes ofCl-.
Potential Exposure
Formerly extensively used in textiles (especially polyester fabrics) and still employed in polyurethane foams, textile backcoating and adhesives.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPRif heart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit. Keepvictim quiet and maintain normal body temperature. Effectsmay be delayed; keep victim under observation.
storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Store in asecure poison location. Keep away from sources of ignition.Store in a refrigerator, in a tightly closed container. Storebelow 4℃. Keep away from oxidizers, heat, flame, and sparks.Shipping: The DOT label requirement for 1,3-Dichloroacetone is “POISONOUS/TOXIC MATERIALS.” TheHazard Class is 6.1 and the Packing Group is II.[19, 20]
Shipping
UN2649 1,3-Dichloroacetone, Hazard class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1—Poisonous materials.
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from CCl4, CHCl3 or *benzene and/or distil under vacuum [Conant & Quayle Org Synth Coll Vol I 211 1941, Hall & Sirel J Am Chem Soc 74 836 1952]. It is dimorphic [Daasch & Kagarise J Am Chem Soc 77 6156 1955]. The oxime has m 130-131o, b 106o/25mm [Arzneimittel-Forsch 8 638 1958]. [Beilstein 1 IV 3219.]
1,3-Dichloroacetone Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
1of3
534-07-6(1,3-Dichloroacetone)Related Search:
1of4