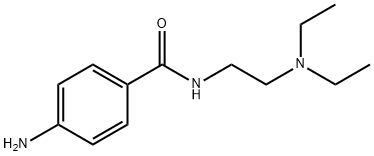
procainamide
- CAS No.
- 51-06-9
- Chemical Name:
- procainamide
- Synonyms
- C07401;Procamide;Novocamid;Procainamide;Novocainamide;PROCAINEAMIDE;Novocaine amide;procainamide USP/EP/BP;procainamide Solution, 100ppm;4-Amino-N-(2-diethylaminoethyl)
- CBNumber:
- CB5932746
- Molecular Formula:
- C13H21N3O
- Molecular Weight:
- 235.33
- MDL Number:
- MFCD00066880
- MOL File:
- 51-06-9.mol
| Melting point | 47°C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 377.72°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.060 |
| refractive index | 1.5700 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,Room temperature |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Ethyl Acetate (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | pKa 9.24±0.10 (Uncertain) |
| color | Off-White to Light Brown |
| FDA UNII | L39WTC366D |
| ATC code | C01BA02 |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| RIDADR | 2811 |
|---|---|
| HazardClass | 6.1 |
| PackingGroup | Ⅲ |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 51-06-9(Hazardous Substances Data) |
procainamide price
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Usbiological | P9005-08 | Procainamide | 51-06-9 | 200ug | $425 | 2021-12-16 | Buy |
| Matrix Scientific | 139481 | Procainamide hydrochloride 95%+ | 51-06-9 | 5g | $449 | 2021-12-16 | Buy |
| Matrix Scientific | 139481 | Procainamide hydrochloride 95%+ | 51-06-9 | 2.500g | $298 | 2021-12-16 | Buy |
| AK Scientific | 7077AB | 4-Amino-N-(2-diethylaminoethyl)benzamide | 51-06-9 | 5g | $373 | 2021-12-16 | Buy |
| Matrix Scientific | 139481 | Procainamide hydrochloride 95%+ | 51-06-9 | 1g | $139 | 2021-12-16 | Buy |
procainamide Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Procainamide and its analogs were employed by Dr Claude Beck in a series of cardiac surgeries during the early 1930s. The compound was used to alleviate arrhythmias that present during the procedures, and was selected for its favorable tissue absorption properties. Procainamide’s central amide provides it protection from inactivating esterase action and allows oral administration of the compound. Procainamide was approved for use in the United States in 1950.
Uses
Procainamide is used in the management of atrial and ventricular tachydysrhythmias.
Uses
Procainamide is intended for treating paroxysmal atrial tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, premature ventricular contraction, and ventricular tachycardia. For quickly reaching therapeutic concentrations, parenternal introduction of procainamide is preferred over cynidine.
Definition
ChEBI: 4-Aminobenzamide substituted on the amide N by a 2-(diethylamino)ethyl group. It is a pharmaceutical antiarrhythmic agent used for the medical treatment of cardiac arrhythmias.
Biological Functions
Procainamide (Pronestyl, Procan SR) is a derivative of the local anesthetic agent procaine. Procainamide has a longer half-life, does not cause CNS toxicity at therapeutic plasma concentrations, and is effective orally. Procainamide is a particularly useful antiarrhythmic drug, effective in the treatment of supraventricular, ventricular, and digitalis-induced arrhythmias.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Synthesis, p. 714, 1975 DOI: 10.1055/s-1975-23900
Mechanism of action
The chemical difference between procainamide and procaine lies in the replacement of the ester group with an amide group. The action of procainamide is qualitatively similar to the action of procaine. Its effect on the heart is identical to that of quinidine. As an antiarrhythmic, procainamide is preferred over procaine because unlike procaine, it is better absorbed when taken orally and it is more difficult for the esterases of the plasma to hydrolyze it, which results in long-lasting action.
Clinical Use
Procainamide is an effective antiarrhythmic agent when
given in sufficient doses at relatively short (3–4 hours)
dosage intervals. Procainamide is useful in the treatment
of premature atrial contractions, paroxysmal atrial tachycardia,
and atrial fibrillation of recent onset. Procainamide
is only moderately effective in converting atrial flutter or
chronic atrial fibrillation to sinus rhythm, although it has value in preventing recurrences of these arrhythmias
once they have been terminated by direct current (DC)
cardioversion.
Procainamide can decrease the occurrence of all
types of active ventricular dysrhythmias in patients with
acute myocardial infarction who are free from A-V dissociation,
serious ventricular failure, and cardiogenic
shock. About 90% of patients with ventricular premature
contractions and 80% of patients with ventricular
tachycardia respond to procainamide administration.
Although the spectrum of action and electrophysiological
effects of quinidine and procainamide are similar,
the relatively short duration of action of procainamide
has tended to restrict its use to patients who
are intolerant of or unresponsive to quinidine.
Side effects
Acute cardiovascular reactions to procainamide administration
include hypotension, A-V block, intraventricular
block, ventricular tachyarrhythmias, and complete
heart block. The drug dosage must be reduced or even
stopped if severe depression of conduction (severe prolongation
of the QRS interval) or repolarization (severe
prolongation of the QT interval) occurs.
Long-term drug use leads to increased antinuclear
antibody titers in more than 80% of patients; more than
30% of patients receiving long-term procainamide therapy
develop a clinical lupus erythematosus–like syndrome.
The symptoms may disappear within a few days
of cessation of procainamide therapy, although the tests
for antinuclear factor and lupus erythematosus cells
may remain positive for several months.
Procainamide, unlike procaine, has little potential to
produce CNS toxicity. Rarely, patients may be confused
or have hallucinations.
Synthesis
Procainamide, 4-amino-N-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]benzamide (18.1.3), is synthesized by reacting 4-nitrobenzoic acid chloride with N,N-diethylethylendiamine and subsequent reduction of the nitro group of the resulting 4-nitro-N-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]benzamide (18.1.2) into an amino group.

Drug interactions
The inherent anticholinergic properties of procainamide may interfere with the therapeutic effect of cholinergic agents. Patients receiving cimetidine and procainamide may exhibit signs of procainamide toxicity, as cimetidine inhibits the metabolism of procainamide. Simultaneous use of alcohol will increase the hepatic clearance of procainamide. Procainamide may enhance or prolong the neuromuscular blocking activity of the aminoglycosides with the potential of producing respiratory depression. The simultaneous administration of quinidine or amiodarone may increase the plasma concentration of procainamide.
Metabolism
Metabolites of procainamide include p-aminobenzoic acid and N-acetylprocainamide. Interestingly, the acetylated metabolite is also active as an antiarrhythmic. Its formation accounts for up to one-third of the administered dose and is catalyzed by the liver enzyme N-acetyl transferase. Because acetylation is strongly influenced by an individual's genetic background, marked variability in the amounts of this active metabolite may be observed from patient to patient. Renal excretion dominates, with approximately 90% of a dose excreted as unchanged drug and metabolites. The elimination half-life is approximately 3.5 hours. A substantial percentage (60–70%) of patients on procainamide show elevated levels of antinuclear antibodies after a few months. Of these patients, between 20 and 30% develop a drug-induced lupus syndrome if therapy is continued. These adverse effects, which are attributed to the aromatic amino group, are observed more frequently and more rapidly in “slow acetylators.” Usually, the symptoms associated with procainamide-induced lupus syndrome subside fairly rapidly after the drug is discontinued. These problems, however, have discouraged long-term procainamide therapy.
Toxicity evaluation
Procainamide is a class 1a antiarrhythmic that has a mechanism
that resembles quinidine by binding to the transmembrane
Nat channels and decreasing the number available
for depolarization. This creates a delay of Nat entry into the
cardiac myocyte during phase 0 of depolarization. As a result,
the upslope of depolarization is slowed and the QRS complex
widens. Procainamide may also affect phase 3 of the action
potential, resulting in prolongation of repolarization and
manifesting as QTc prolongation on the electrocardiogram
(EKG). Unlike quinine, however, procainamide lacks alphablocking
activity and quinidine’s vagolytic ability.
Vasodilation associated with procainamide toxicity
(>10 mg ml°1) is due to interference with ganglionic transmission
of catecholamine neurotransmitters and/or central
nervous system (CNS) sympathetic inhibition. A reflex tachycardia
may occur in response to this vasodilation. Rapid
intravenous dosing of procainamide can be dangerous as its
initial Vd is less than its final; thus adverse myocardial effects
can often be seen as the initial ‘compartment’ and includes the
cardiovascular system. Myocardial complications can initially
be more pronounced. Procainamide may also have weak
anticholinergic effects that produce tachycardia. Negative
inotropic effects may occur in toxicity. The NAPA metabolite of
procainamide lacks Nat channel blocking activity but still
retains blockade of the Kt rectifier currents. It is therefore
pharmacologic, similar to a type III antidysrhythmic.
Precautions
Contraindications to procainamide are similar to those for quinidine. Because of its effects on A-V nodal and His-Purkinje conduction, procainamide should be administered with caution to patients with second-degree A-V block and bundle branch block. Procainamide should not be administered to patients who have shown procaine or procainamide hypersensitivity and should be used with caution in patients with bronchial asthma. Prolonged administration should be accompanied by hematological studies, since agranulocytosis may occur.
procainamide Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hubei Jusheng Technology Co.,Ltd. | 18871490254 | linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 28172 | 58 |
| Alchem Pharmtech,Inc. | 8485655694 | sales@alchempharmtech.com | United States | 63687 | 58 |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 | factory@coreychem.com | China | 29810 | 58 |
| TargetMol Chemicals Inc. | +1-781-999-5354 +1-00000000000 | marketing@targetmol.com | United States | 32161 | 58 |
| Dideu Industries Group Limited | +86-29-89586680 +86-15129568250 | 1026@dideu.com | China | 22787 | 58 |
| Finetech Industry Limited | +86-27-87465837 +8618971612321 | info@finetechnology-ind.com | China | 9639 | 58 |
| LEAPCHEM CO., LTD. | +86-852-30606658 | market18@leapchem.com | China | 43340 | 58 |
| Aladdin Scientific | +1-+1(833)-552-7181 | sales@aladdinsci.com | United States | 57505 | 58 |
| Energy Chemical | 021-021-58432009 400-005-6266 | sales8178@energy-chemical.com | China | 44689 | 61 |
| Beijing HuaMeiHuLiBiological Chemical | 010-56205725 | waley188@sohu.com | China | 12335 | 58 |
View Lastest Price from procainamide manufacturers
| Image | Update time | Product | Price | Min. Order | Purity | Supply Ability | Manufacturer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
2024-11-19 | Procainamide
51-06-9
|
US $33.00 / mg | 98.86% | 10g | TargetMol Chemicals Inc. | ||
 |
2021-08-12 | procainamide USP/EP/BP
51-06-9
|
US $1.10 / g | 1g | 99.9% | 100 Tons min | Dideu Industries Group Limited | |
 |
2020-02-05 | procainamide
51-06-9
|
US $1.00 / KG | 1KG | 98-99.9% | 100kg | Career Henan Chemical Co |
-

- Procainamide
51-06-9
- US $33.00 / mg
- 98.86%
- TargetMol Chemicals Inc.
-

- procainamide USP/EP/BP
51-06-9
- US $1.10 / g
- 99.9%
- Dideu Industries Group Limited
-

- procainamide
51-06-9
- US $1.00 / KG
- 98-99.9%
- Career Henan Chemical Co
51-06-9(procainamide)Related Search:
1of4