Valsartan
- CAS No.
- 137862-53-4
- Chemical Name:
- Valsartan
- Synonyms
- DIOVAN;Nisis;Valsratan;Varsartan;Tareg;CGP-48933;VALSARTAN;Valsatarn;Valsartane;L-Valsartan
- CBNumber:
- CB6182539
- Molecular Formula:
- C24H29N5O3
- Molecular Weight:
- 435.52
- MDL Number:
- MFCD00865840
- MOL File:
- 137862-53-4.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
| Melting point | 116-117°C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 684.9±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.212±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| vapor pressure | 0-0Pa at 20-25℃ |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: ≥20mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | 3.56±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | white to tan |
| optical activity | [α]/D -55 to -70°, c = 1 in methanol |
| Water Solubility | 84.99mg/L(25 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,9916 |
| BCS Class | 2 |
| Stability | Hygroscopic |
| InChIKey | ACWBQPMHZXGDFX-QFIPXVFZSA-N |
| LogP | 1.2-2.8 at 25℃ and pH2.5-7 |
| Surface tension | 59.6-68.1mN/m at 10-100mg/L and 20℃ |
| Dissociation constant | 3.76-4.38 at 25℃ |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 137862-53-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| FDA UNII | 80M03YXJ7I |
| NCI Drug Dictionary | Diovan |
| ATC code | C09CA03 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | L-Valine, N-(1-oxopentyl)-N-[[2'-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]- (137862-53-4) |
| UNSPSC Code | 41116107 |
| NACRES | NA.77 |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS07,GHS08 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H336-H361d | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P201-P308+P313 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xi | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 36/37/38 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-37/39 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | YV9455000 | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29339900 | |||||||||
| Hazardous Substances Data | 137862-53-4(Hazardous Substances Data) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Valsartan price More Price(51)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich | PHR1315 | Valsartan Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material | 137862-53-4 | 1g | $97.5 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | 1708762 | Valsartan United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard | 137862-53-4 | 350mg | $436 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| TCI Chemical | V0112 | Valsartan >98.0%(HPLC)(T) | 137862-53-4 | 1g | $56 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| TCI Chemical | V0112 | Valsartan >98.0%(HPLC)(T) | 137862-53-4 | 5g | $184 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Cayman Chemical | 14178 | Valsartan ≥98% | 137862-53-4 | 10mg | $44 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
Valsartan Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Indications and Usage
Valsartan (137862-53-4) is a type of specific angiotensin I (AT1) receptor antagonist and a clinical non-dermal AT1 receptor antagonist following losartan that has important effects in adjusting bodily blood pressure and maintaining electrolyte-body fluid balance. Valsartan’s antihypertensive effects are stronger than those of enalapril and is suitable for treating hypertension, mild to moderate primary hypertension, and especially secondary hypertension caused by renal damage. It can significantly reduce proteinuria for hypertension patients with diabetes or normal liver functions, and it can promote uric acid and urinary sodium to protect the kidney. Valsartan is also suitable for reducing the cardiovascular mortality for high risk patients (left ventricular failure or dysfunction) after experiencing a heart attack.
Mechanisms of Action
Valsartan (137862-53-4) selectively affects the AT1 receptor subtype and prevents AT1 from binding with AT1 receptors (its selective AT1 receptor antagonizing effect is about 20000 times greater than its effects on AT2 receptors), thus inhibiting vasoconstriction and aldosterone release, producing an antihypertensive effect, but it cannot inhibit the release of aldosterone caused by potassium ions (K+). Valsartan does not affect angiotensin-converting enzymes (ACE) or renin and its receptors, and it does not inhibit ion channels related to blood pressure regulation and sodium balance. Valsartan does not inhibit ACE and does not affect bodily bradykinin levels, thus causing less coughing side effects than ACE inhibitors. Valsartan does not affect heart rate when lowering blood pressure. Sudden ceasing in Valsartan use will not cause rebound hypertension or other side effects. Valsartan does not affect hypertension patients’ overall cholesterol, triglyceride, blood glucose, or uric acid levels.
Pharmacokinetics
For most patients, a single oral dose will have antihypertensive effects that occur within 2 hours, peak at 4-6 hours, and continue for over 24 hours. 2-4 weeks of treatment will result in maximum hypertensive curative effects, which will last throughout long-term treatment. It can be used with thiazide diuretics to further strengthen antihypertensive effects.
Clinical Research
A clinical trial showed that Valsartan has very noticeable effects on mild to moderate hypertension. A daily dose of ≥80 mg can effectively control systolic and diastolic blood pressure while not affecting blood pressure’s circadian rhythm; a daily 160mg dose has more noticeable effects than a daily 100mg dose of losartan. Moderate hypertension patients with intact renal functions have a good tolerance towards Valsartan, Valsartan’s curative effects are significantly superior to those of ACE inhibitors, and there are minimal adverse reactions. Effective in treating severe hypertension when combined with other antihypertensive drugs.
Description
Diovan(Valsartan) was launched in Germany and the UK as an angiotensin Ⅱ antagonist for use as an antihypertensive agent. Biphenylbromomethyl nitrite serves as the starting material for a three step synthesis of the compound, in which the (S)- enantiomer is more active than the (R)-enantiomer. Valsartan is a nonpeptide drug which is a highly specific antagonist of the AT1 receptor and is potent and orally active. This receptor is responsible for angiotensin Ⅱ cardiovascular effects (aldosterone and catecholamine secretion, vascular constriction, positive inotropic response and renal effects). Unlike losartan, it is not a prodrug and a single daily dose is comparible in activity to the ACE drug enalapril. It also did not exhibit the coughing side effect observed with ACE inhibitors. Diovan(Valsartan) is slowly metabolized (long lasting) with its main metabolite being significantly less active. There was no evidence of rebound hypertension when drug treatment was terminated and was as effective as the dihydropyridine Ca antagonist anlodipine.
Chemical Properties
White Crystalline Powder
Originator
Norvartis (Switzerland)
Uses
Valsartan is used as a first-line drug for the treatment of uncomplicated hypertension, isolated systolic hypertension, and left ventricular hypertrophy. Valsartan is a clinically widely used antihypertensive agent with the advantages of low side effects and good tolerability, and can also be used for the treatment of hypertension in patients with diabetes and renal disease.
Definition
ChEBI: A monocarboxylic acid amide consisting of L-valine in which the amino hydrogens have been replaced by a pentanoyl and a [2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl group. It exhibits antihypertensive activity.
brand name
Diovan (Novartis).
Therapeutic Function
Antihypertensive
General Description
Valsartan, N-(1-oxopentyl)-N-[[2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]-L-valine (Diovan), likelosartan, possesses the acidic tetrazole system, which mostlikely plays a role, similar to that of the acidic groups of angiotensinII, in binding to the angiotensin II receptor. In addition,the biphenyl system that serves to separate the tetrazolefrom the aliphatic nitrogen is still present. In addition, there isa carboxylic acid side chain in the valine moiety that alsoserves to bind to the angiotensin II receptor.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Valsartan is an Angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptor antagonist and anti-hypertensive. Valsartan renders protection against heart attack and stroke resulting from abrupt increase in blood pressure. Valsartan reduces myocardial-infarction-related complications in heart attack survivors.
Synthesis
An aqueous solution (120 ml) of potassium hydroxide (0.568 mol, 31.8 g) is added in succession with 2-[(4-bromo-benzyl)-pentanoyl-amino]-3-methyl-butyric acid (0.811 mol, 30.0 g), tetrahydrofuran (120 ml), triphenylphosphine (0.0121 mol, 3.2 g) and palladium acetate (0.00405 mol, 0.91 g). The reaction mixture is refluxed and added with 2-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)-benzene-boronic acid (0.142 mol, 27.0 g) in portions in about 6 h. After completion of the addition, the mixture is left to react for 2h, then cooled to room temperature and the phases are separated. The organic phase is diluted with water (120 ml) and tetrahydrofuran is distilled off under reduced pressure. The remaining aqueous solution is acidified to pH 6.5 and washed with isopropyl acetate (60 ml). The aqueous phase is acidified to pH 2 and diluted with isopropyl acetate (60 ml), the diphasic solution is filtered to remove phenyltetrazol. Phases are separated and the organic phase is concentrated under reduced pressure, to obtain a thick oil that is crystallized from isopropyl acetate (90 ml) and heptane (150 ml). The resulting product is filtered, washed twice with a 1:1 isopropyl acetate/heptane mixture (30 ml), and dried in static dryer at 45°C to obtain 28.2 g of Valsartan.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Anaesthetics: enhanced hypotensive effect.
Analgesics: antagonism of hypotensive effect and
increased risk of renal impairment with NSAIDs;
hyperkalaemia with ketorolac and other NSAIDs.
Antihypertensives: increased risk of hyperkalaemia,
hypotension and renal impairment with ACE-Is and
aliskiren.
Ciclosporin: increased risk of hyperkalaemia and
nephrotoxicity.
Diuretics: enhanced hypotensive effect;
hyperkalaemia with potassium-sparing diuretics.
ESAs: increased risk of hyperkalaemia; antagonism
of hypotensive effect.
Lithium: reduced excretion (possibility of enhanced
lithium toxicity).
Potassium salts: increased risk of hyperkalaemia.
Tacrolimus: increased risk of hyperkalaemia and
nephrotoxicity.
Metabolism
Valsartan is not highly metabolised as only about 20% of dose is recovered as metabolites. A hydroxy metabolite has been identified in plasma at low concentrations (less than 10% of the valsartan AUC). This metabolite is pharmacologically inactive.
Valsartan is mainly eliminated by biliary excretion in faeces (about 83% of dose) and renally in urine (about 13% of dose), mainly as unchanged drug.
storage
Store at RT
References
1) Criscione?et al. (1993),?Pharmacological profile of valsartan: a potent, orally active, nonpeptide antagonist of the angiotensin II AT1-receptor subtype; Br. J. Pharmacol.,?110?761 2) Wexler?et al. (1996), Nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists: the next generation in antihypertensive therapy; J. Med. Chem.,?39?625 3) Iwashita?et al. (2013),?Valsartan restores inflammatory response by macrophages in adipose and hepatic tissues of LPS-infused mice; Adipocyte,?2?28
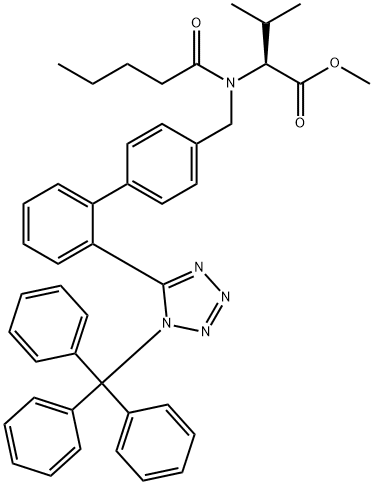
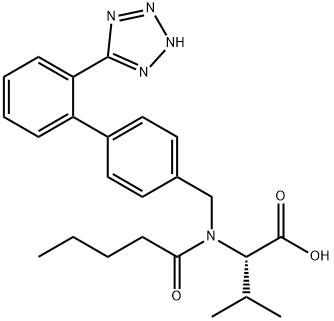
Valsartan Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of3
Preparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +86-15531157085 +86-15531157085 | abby@chuanghaibio.com | China | 8809 | 58 |
| Shaanxi Dideu Medichem Co. Ltd | +86-29-81148696 +86-15536356810 | 1022@dideu.com | China | 3882 | 58 |
| Hebei Mujin Biotechnology Co.,Ltd | +86 13288715578 +8613288715578 | sales@hbmojin.com | China | 12817 | 58 |
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co,.LTD | +86-13131129325 | sales1@chuanghaibio.com | China | 5876 | 58 |
| Hebei Dangtong Import and export Co LTD | +86-86-4001020630 +8619831957301 | admin@hbdangtong.com | China | 999 | 58 |
| Henan Bao Enluo International TradeCo.,LTD | +86-17331933971 +86-17331933971 | deasea125996@gmail.com | China | 2472 | 58 |
| Hangzhou Hyper Chemicals Limited | +86-0086-57187702781 +8613675893055 | info@hyper-chem.com | China | 295 | 58 |
| Shaanxi TNJONE Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd | +8618092446649 | sarah@tnjone.com | China | 1143 | 58 |
| BEIJING SJAR TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT CO., LTD. | +86-18600796368 +86-18600796368 | sales@sjar-tech.com | China | 485 | 58 |
| HEBEI SHENGSUAN CHEMICAL INDUSTRY CO.,LTD | +8615350851019 | admin@86-ss.com | China | 1001 | 58 |
Related articles
- Valsartan: Uses, Dosage and Side Effects
- Valsartan is an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB). It widens blood vessels to act as a blood pressure reducer, making it easi....
- Jun 17,2024
- The uses and side effects of Valsartan
- Valsartan is an angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker (ARB). This drug is commonly combinated with Sacubitril.
- Nov 9,2023
Related Qustion
- Q:What are the side effects of Valsartan?
- A:ommon side effects of Valsartan include: shortness of breath, cough , dizziness and light-headedness on waking, nausea, fatigu....
- Jan 8,2024
View Lastest Price from Valsartan manufacturers
| Image | Update time | Product | Price | Min. Order | Purity | Supply Ability | Manufacturer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
2025-04-01 | Valsartan
137862-53-4
|
US $999.00-666.00 / kg | 1kg | 99% | 5000 | HEBEI SHENGSUAN CHEMICAL INDUSTRY CO.,LTD | |
 |
2025-04-01 | Valsartan
137862-53-4
|
US $0.00-0.00 / Kg/Bag | 1Kg/Bag | EP / USP / JP | 20 tons | Sinoway Industrial co., ltd. | |
 |
2025-04-01 | Valsartan
137862-53-4
|
US $1.00 / g | 1g | 99 | 2000 | Jinan Jianfeng Chemical Co., Ltd |
137862-53-4(Valsartan)Related Search:
1of4
(S)-2-(N-((2'-(1H-Tetrazol-5-yl)-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)methyl)pentanamido)-3 -methylbutanoic acid (S)-N-[p-(o-1H-Tetrazol-5-ylphenyl)benzyl]-N-valeryl-L-valine (S)-2-(N-((2'-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)methyl)pentanamido)-3-methylbutanoic acid Valsartan, 99%, a nonpeptide angiotensin II AT1 receptor antagonist Valsartan 3-Methyl-2-[pentanoyl-[[4- [2-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)phenyl]phenyl]methyl] amino]-butanoic acid Valsartan Manufacturer (S)-3-methyl-2-[N-({4-[2-(2H-1,2,3,4-tetrazol-5-yl)phenyl]phenyl}methyl)pentanamido]butanoic acid Valsatarn Valsartan Impurity 18 (S)-2-(N-((2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl) Valsartan CRS Valsartan RS Valsartan for peak identification CRS Valsartan for system suitability CRS N-Valeryl-N-[2'-(5-tetrazolyl)biphenyl-4-ylmethyl]-L-valine N-((2-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)methyl)-N-pentanoyl-L-valine Valsartan USP/EP/BP Valsartan (10mM in DMSO)





