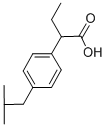
Butibufen
- CAS No.
- 55837-18-8
- Chemical Name:
- Butibufen
- Synonyms
- FF-106;DF 1903Y;Butiropan;Bitubufen;Butilopan;Butibufen;Butibufen USP/EP/BP;2-(4-Isobutylphenyl)butyric Acid;2-(p-Isobutylphenyl)butyric acid;2-(4-Isobutylphenyl)butanoic acid
- CBNumber:
- CB6875419
- Molecular Formula:
- C14H20O2
- Molecular Weight:
- 220.31
- MDL Number:
- MFCD00866068
- MOL File:
- 55837-18-8.mol
| Melting point | 51-53° |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 335.1±11.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.015±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 4.41±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| FDA UNII | JSS1TEM917 |
Butibufen price More Price(10)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRC | B689960 | Butibufen | 55837-18-8 | 250mg | $645 | 2021-12-16 | Buy |
| TRC | B689960 | Butibufen | 55837-18-8 | 500mg | $1190 | 2021-12-16 | Buy |
| American Custom Chemicals Corporation | API0015126 | BUTIBUFEN 95.00% | 55837-18-8 | 1G | $1904.7 | 2021-12-16 | Buy |
| Biosynth Carbosynth | FB19394 | Butibufen | 55837-18-8 | 5mg | $72.5 | 2021-12-16 | Buy |
| Biosynth Carbosynth | FB19394 | Butibufen | 55837-18-8 | 10mg | $102 | 2021-12-16 | Buy |
Butibufen Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Butibufen is a new phenylalkanoic antiinflammatory/analgesic useful in the treatment of rheumatologic conditions. In a study of patients with osteoarthritis, the onset of action of butibufen was faster with less frequent and milder side effects than indomethacin.
Chemical Properties
White to Off-White Solid
Originator
Juste (Spain)
Uses
Anti-inflammatory.
Definition
ChEBI: Butibufen is a monoterpenoid.
Manufacturing Process
1st method:
4-Isobutylphenylbenzyl chloride was prepared by passing a stream of
hydrogen chloride into a suspension of p-bromoaldehyde and anhydrous zinc
chloride in isobutylbenzene. A mixture of 137 g (0.75 mol) of 4-isobutylbenzyl
chloride thus prepared, 44.1 g (0.90 mol) of sodium cyanide, 216 g of 99%
ethanol, and 81.3 g of water was heated refluxed for 6 hours. The mixture
became reddish-black in color. From this mixture, 215 ml of ethanol and water was then distilled and the residue was filtered. The solids that were separated
by filtration were washed with 100 ml of diethyl ether and the ether washings
were combined with the original filtrate, to which 800 ml of water was then
added. The organic phase was then separated from the aqueous phase,
washed with five 400 ml portions of water and dried over anhydrous sodium
sulfate. The ether was evaporated from the dried organic phase by vacuum
distillation and the residue which distilled between 130°C and 132°C at a
pressure of 7 mm of mercury was collected. The yields of 4-isobutylbenzene
cyanide 100-113 g.
To a solution of 6.7 g of sodium amide in 100 ml of anhydrous diethyl ether
was added dropwise 26 g of 4-isobutylbenzene cyanide while the mixture was
stirred and heated under gentle reflux. After all of the 4-isobutylbenzene
cyanide had been added, the mixture was heated under gentle reflux for 15
min, after which 23.4 g of ethyl iodide was slowly added dropwise thereto
from the dropping funnel. After completion of the addition of the ethyl iodide,
the mixture was heated under gentle reflux for an initial period of 15 min,
after which it was diluted with an equal volume of water and shaken. The two
layers that formed were separated and the aqueous layer was then extracted
with two 50 ml portions of diethyl ether. The ether extracts were combined
and then washed with two 80 ml portions of water and dried over anhydrous
magnesium sulfate. The dried ether extract was then distilled at a
subatmospheric pressure. In this manner, 25 g of a clear transparent
uncolored liquid having a boiling point of 118-122°C at a pressure of 1mm of
mercury, which consisted of 2-(4-isobutylphenyl)butyronitrile, was collected.
This yield was equivalent to 83% of the theoretical.
A mixture of 40 g (0.2 mol) of 2-(4-isobutylphenyl)butyronitrile and 78 ml of
a freshly prepared solution of sodium hydroxide that was prepared by
dissolving 28 g of sodium hydroxide in 25 ml of distilled water and the volume
of which was brought to 100 ml by addition thereto of methanol, was heated
under gentle reflux in a flask provided with a stirrer and reflux condenser
while the mixture was stirred during a period of 9 hours. From the mixture
the methanol and a portion of the water were distilled and the mixture was
then cooled, the crystals began to separate. The mixture was then diluted
with 150 ml of water and extracted with two 25 ml portions of diethyl ether.
The remaining aqueous solution containing the sodium salt of 2-(4-
isobutylphenyl)butyric acid was then saturated with sodium chloride until the
salt started to precipitate. The solution was then cooled to 5°C and the
precipitated salt was separated by filtration, recrystallized from isopropanol,
and dried in a vacuum desiccator at a pressure of 1 mm of mercury until it
had attained a constant weight. In this manner, 32 g of sodium 2-(4-
isobutylphenyl)butyrate having a melting point of 188-191°C, which is
equivalent to a yield of 67% of the theoretical, was obtained.
Dilute hydrochloric acid (19% by weight of hydrogen chloride) was slowly
added to a cold solution of 25 g of the sodium 2-(4-isobutylphenyl)butyrate
thus prepared in 100 ml of water until the solution corresponded to pH of 1.0.
The oil which precipitated was then allowed to solidify to a white solid by
standing in a refrigerator. The white solid was then separated by filtration,
dried, and recrystallized from petroleum ether. It had a melting point of 50-
52°C, and its elementary analysis corresponded to the 2-(4-
isobutylphenyl)butyric acid.
2nd method:
5.0 g of small pellets of sodium metal were added slowly with stirring to 150
ml of absolute ethanol, while a current of nitrogen gas was passed there
through so as to blanket the solution from the atmosphere. After all of the
sodium metal had been dissolved and while the solution was maintained at a
temperature of 50°C, a solution of 52 g of ethyl 2-(4-
isobutylphenyl)cyanoacetate in 50 ml of absolute ethanol was added dropwise
while the mixture was stirred. Subsequently, 81 g of ethyl iodide was
gradually added to the mixture with stirring, after which the introduction of
nitrogen gas into the mixture was discontinued and the mixture was heated
for a period of 2.5 hours under gentle reflux. Thereafter, the ethanol and
excess ethyl iodide were distilled from the mixture and the residue was then
diluted with three times its volume of water and shaken therewith. The 2-(4-
isobutylphenyl)-2-(ethoxycarbonyl)butyronitrile was then extracted from the
mixture with three 50 ml portions of diethyl ether, the extracts were
combined, washed with a 20% aqueous solution of sodium bisulfate and dried
over anhydrous magnesium sulfate. The ether was then expelled from the
extract by distillation and the residue was distilled at a subatmospheric
pressure, yielding 45 g of a fraction containing 2-(4-isobutylphenyl)-2-
(ethoxycarbonyl)butyronitrile having a boiling point of 150-155°C/3 mm of
mercury (78% of the theoretical yield).
In a 2-liter flask provided with a stirrer and reflux condenser a solution of 129
g of 2-(4-isobutylphenyl)-2-(ethyoxycarbonyl)butyronitrile in 980 ml of a 20%
solution of potassium hydroxide in methanol was heated with stirring at 40°C
for a period of 1 hour. The mixture was then heated under gentle reflux with
stirring for an additional period of 3 hours, during which a white solid
precipitated. This mixture was then poured into 1.5 liters of water and
acidified with an aqueous solution of hydrochloric acid (concentrated
hydrochloric acid diluted with an equal volume of water) to a hydrogen ion
concentration corresponding to a pH of 2.5, while carbon dioxide was evolved
therefrom. The aqueous mixture was then extracted with diethyl ether. The
extracts were washed successively with a saturated solution of sodium
bicarbonate and water, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and distilled
at a subatmospheric pressure, to yield 86.5 g of a fraction consisting of 2-(4-
isobutylphenyl)butyronitrile having a boiling point of 124-128°C at a pressure
of 1.5 mm of mercury, which is equivalent to approximately 0.43 mol and a
yield of 91% of the theoretical based on the original 2-(4-isobutylphenyl)-2-
(ethoxycarbonyl)butyronitrile.
The 2-(4-isobutylphenyl)butyronitrile was converted to sodium 2-(4-
isobutylphenyl)butyrate and subsequently to 2-(4-isobutylphenyl)butyric acid
in the same manner as described in Method 1 hereinbefore.
brand name
Butilopan
Therapeutic Function
Antiinflammatory, Analgesic
Butibufen Preparation Products And Raw materials
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jinan Carbotang Biotech Co.,Ltd. | +8615866703830 | figo.gao@foxmail.com | China | 8497 | 58 |
| Alchem Pharmtech,Inc. | 8485655694 | sales@alchempharmtech.com | United States | 63687 | 58 |
| TargetMol Chemicals Inc. | +1-781-999-5354 +1-00000000000 | marketing@targetmol.com | United States | 32165 | 58 |
| Dideu Industries Group Limited | +86-29-89586680 +86-15129568250 | 1026@dideu.com | China | 22783 | 58 |
| Zhejiang J&C Biological Technology Co.,Limited | +1-2135480471 +1-2135480471 | sales@sarms4muscle.com | China | 10473 | 58 |
| Aladdin Scientific | +1-+1(833)-552-7181 | sales@aladdinsci.com | United States | 57505 | 58 |
| Guangzhou CATO Research Chemicals Inc. | +86-020-81960175-617 +8615602392859 | Intermediate@cato-chem.com | China | 8056 | 58 |
| Amadis Chemical Company Limited | 571-89925085 | sales@amadischem.com | China | 131957 | 58 |
| J & K SCIENTIFIC LTD. | 010-82848833 400-666-7788 | jkinfo@jkchemical.com | China | 96815 | 76 |
| Chembest Research Laboratories Limited | +86-21-20908456 | sales@BioChemBest.com | China | 6005 | 61 |
View Lastest Price from Butibufen manufacturers
| Image | Update time | Product | Price | Min. Order | Purity | Supply Ability | Manufacturer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
2024-11-20 | Butibufen
55837-18-8
|
US $35.00-109.00 / mg | 99.29% | 10g | TargetMol Chemicals Inc. | ||
 |
2021-06-10 | Butibufen USP/EP/BP
55837-18-8
|
US $1.10 / g | 1g | 99.9% | 100 Tons Min | Dideu Industries Group Limited |
-

- Butibufen
55837-18-8
- US $35.00-109.00 / mg
- 99.29%
- TargetMol Chemicals Inc.
-

- Butibufen USP/EP/BP
55837-18-8
- US $1.10 / g
- 99.9%
- Dideu Industries Group Limited