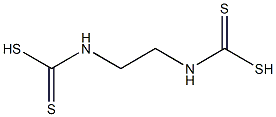
ETHYLENEBIS-(DITHIOCARBAMATE)
- CAS No.
- 34731-32-3
- Chemical Name:
- ETHYLENEBIS-(DITHIOCARBAMATE)
- Synonyms
- ETHYLENEBIS-(DITHIOCARBAMATE)
- CBNumber:
- CB81408568
- Molecular Formula:
- C4H8N2S4
- Molecular Weight:
- 212.37972
- MDL Number:
- MOL File:
- 34731-32-3.mol
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ethylenebis(dithiocarbamate) (34731-32-3) |
|---|
ETHYLENEBIS-(DITHIOCARBAMATE) Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
The presence of ethylenebisdithiocarbamate (EBCD)
fungicides in treated plants is of concern because these
fungicides can be transformed into ethylenethiourea
(ETU), a metabolite of proven oncogenic and teratogenic
effect. ETU may also occur in commercially available
formulations of EBCD fungicides, and the amount
present may increase on storage because of atmospheric
oxidation. ETU has been found in thermally treated
foods in which residues of EBCD fungicides were
detected before thermal treatment.
From the numerous compounds suggested by Hester (5),
only disodium ethylenebisdithiocarbamate and its zinc
and manganese salts are largely accepted for practical
application. Research on these dithiocarbamates led to
some promising variants.
History
The ethylenebisdithiocarbamates were rediscovered in 1945 when Dimond et al. reported a “new water soluble protectant fungicide.” The parent compound, disodium ethylenebisdithiocarbamate, was highly soluble in water and was unstable in air, and it might have been only a laboratory curiosity and remained unnoticed but for the applications developed by Heuberger and Manns (3), who stabilized it by converting it into zinc salt by the addition of zinc sulfate–lime mixture.
Uses
Ethylenebisdithiocarbamates have strong metal binding
capacity and act as inhibitors of enzymes. They
have a profound effect on biological systems, and so
they are widely used in medicine and in agriculture
as fungicides. Their residues on food and fodder are
hazardous and may potentially cause chronic damage to
health, because humans consume these items as a part
of their normal dietary intake and ethylenebisdithiocarbamates
are widely used as fungicides.
Therefore, their
residues must be closely checked because their persistent,
as well as cumulative, action may be harmful. Some of
the most-used ethylenebisdithiocarbamate fungicides are
nabam [disodium ethylenebis (dithiocarbamate)], mancozeb
[manganese/zinc ethylenebis (dithiocarbamate)],
and maneb [manganese ethylenebis (dithiocarbamate)].