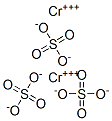Chromium sulfate
- CAS No.
- 14489-25-9
- Chemical Name:
- Chromium sulfate
- Synonyms
- Un2240;Chronisulfat;Chronisulfat [german];Chromosulfuric acid [un2240] [corrosive]
- CBNumber:
- CB81486407
- Molecular Formula:
- Cr.x(H2SO4)
- Molecular Weight:
- 0
- MDL Number:
- MOL File:
- 14489-25-9.mol
| EPA Substance Registry System | Sulfuric acid, chromium salt (14489-25-9) |
|---|
Chromium sulfate Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Chromosulfuric acid is a dark green powder.Molecular weight =724.4; Highly soluble in water(reactive)
Definition
ChEBI: Chromium(III) sulfate is a compound of chromium and sulfate in which the ratio of chromium (in the +3 oxidation state) to sulfate is 2:3 It contains a chromium(3+).
General Description
Chromium sulfate is a colorless, oily liquid. Chromium sulfate is soluble in water with the release of heat. Chromium sulfate is corrosive to skin and metals.
Air & Water Reactions
Soluble in water with the release of heat.
Reactivity Profile
Oxidizing acids are generally soluble in water with the release of hydrogen ions. The resulting solutions have pH's of less than 7.0. Materials in this group react with chemical bases (for example: amines and inorganic hydroxides) to form salts. These neutralization reactions occur as the base accepts hydrogen ions that the acid donates. Neutralizations can generate dangerously large amounts of heat in small spaces. The dissolution of acids in water or the dilution of their concentrated solutions with water may generate significant heat. The addition of water acids often generates sufficient heat in the small region of mixing to boil some of the water explosively. The resulting "bumping" spatters acid widely. These materials have significant ability as oxidizing agents. but that ability varies (for example, from high for nitric acid to low for sulfuric acid and most sulfonic acids). They can react with active metals, including iron and aluminum, and also many less active metals, to dissolve the metal and liberate hydrogen and/or toxic gases. Like other acids, materials in this group can initiate polymerization in certain classes of organic compounds. Their reactions with cyanide salts and compounds release gaseous hydrogen cyanide. Flammable and/or toxic gases are also often generated by their reactions with dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, nitriles, sulfides, and weak or strong reducing agents. Additional gas-generating reactions occur with sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates (to give H2S and SO3), dithionites (SO2), and even carbonates: the carbon dioxide gas from the last is nontoxic but the heat and spattering from the reaction can be troublesome. Acids often catalyze (increase the rate of) chemical reactions.
Health Hazard
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Non-combustible, substance itself does not burn but may decompose upon heating to produce corrosive and/or toxic fumes. Some are oxidizers and may ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated.
Potential Exposure
Chromosulfuric acid is used in chromeplating; paint, ink, and glaze manufacturing; tanning, catalyst preparation; and as a fixative in textile dyeing.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seekmedical attention immediately. If this chemical contactsthe skin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediately with soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical has been inhaled, remove fromexposure, begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing hasstopped and CPR if heart action has stopped. Transferpromptly to a medical facility. When this chemical hasbeen swallowed, get medical attention. If victim is conscious, administer water or milk. Do not induce vomiting
storage
Color Code—White: Corrosive or Contact Hazard;Store separately in a corrosion-resistant location. Prior toworking with chromosulfuric acid you should be trained onits proper handling and storage. Chromosulfuric acid mustbe stored to avoid contact with water and other incompatible materials listed above since violent reactions occur.Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilatedarea away from flammable and combustible materials.
Shipping
Chromosulfuric acid requires a “CORROSIVE”label. It falls in Hazard Class 8 and Packing Group I.
Incompatibilities
Violent reaction with water.Incompatible with caustic materials, ammonia, aliphaticamines, alkanolmines, isocyanates, epichlorohydrin.
Chromium sulfate Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molokomalapatrading Ltd. | molokomalapatrading@gmail.com | South Africa | 172 | 58 |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Molokomalapatrading Ltd. | 58 |
View Lastest Price from Chromium sulfate manufacturers
| Image | Update time | Product | Price | Min. Order | Purity | Supply Ability | Manufacturer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
2022-09-08 | Chromium sulfate
14489-25-9
|
US $50.00 / TON | 100TON | 99% | 200 | Molokomalapatrading Ltd. |
-

- Chromium sulfate
14489-25-9
- US $50.00 / TON
- 99%
- Molokomalapatrading Ltd.