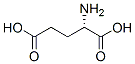
Glutamic acid
- CAS No.
- 6899-05-4
- Chemical Name:
- Glutamic acid
- Synonyms
- GLUTAMIC ACID;55695-80-2 (Mono-lithium salt);2-Aminopentanedioic acid, (S)-;19473-49-5 (Mono-potassium salt);16690-92-9 (Di-hydrochloride salt);138-15-8 (Unspecified hydrochloride);19238-49-4 (Unspecified calcium salt);24595-14-0 (Unspecified potassium salt)
- CBNumber:
- CB02130578
- Molecular Formula:
- C5H9NO4
- Molecular Weight:
- 147.13
- MOL File:
- 6899-05-4.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/8/28 13:53:20
| pka | pKa1 2.19,pKa2 4.25,pKa3 9.67(25℃) |
|---|---|
| CAS DataBase Reference | 6899-05-4 |
Glutamic acid Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Glutamic acid (abbreviated as Glu or E) is one of the 20-22 proteinogenic amino acids, and its codons are GAA and GAG. It is a non-essential amino acid. The carboxylate anions and salts of glutamic acid are known as glutamates. In neuro science, glutamate is an important neuro transmitter that plays a key role in long-term potentiation and is important for learning and memory.
Chemical Properties
The side chain carboxylic acid functional group has a pKa of 4.1 and therefore exists almost entirely in its negatively charged deprotonated carboxylate form at pH values greater than 4.1; therefore, it is negatively charged at physiological pH ranging from 7.35 to 7.45.
History
Although they occur naturally in many foods, the flavour contributions made by glutamic acid and other amino acids were only scientifically identified early in the twentieth century. The substance was discovered and identified in the year 1866, by the German chemist Karl Heinrich Leopold Ritthausen who treated wheat gluten (for which it was named) with sulfuric acid. In 1908 Japanese researcher Kikunae Ikeda of the Tokyo Imperial University identified brown crystals left behind after the evaporation of a large amount of kombu broth as glutamic acid. These crystals, when tasted, reproduced the ineffable but undeniable flavour he detected in many foods, most especially in seaweed. Professor Ikeda termed this flavour umami. He then patented a method of mass-producing a crystalline salt of glutamic acid, monosodium glutamate.
Uses
glutamic acid is a moisture binder and an anti-oxidant. glutamic acid is an amino acid manufactured by means of fermentation, generally from a vegetable protein.
Production Methods
China-based Fufeng Group Limited is the largest producer of glutamic acid in the world, with capacity increasing to 300,000 tons at the end of 2006 , Meihua is the second - largest Chinese producer. Together, the top-five producers have roughly 50 % share in China. Chinese demand is roughly 1.1 million tons per year.
Pharmacology
The drug phencyclidine (more commonly known as PCP) antagonizes glutamic acid non-competitively at the NMDA receptor. For the same reasons, dextromethorphan and ketamine also have strong dissociative and hallucinogenic effects. Glutamate does not easily pass the blood brain barrier, but , instead, is transported by a high-affinity transport system . It can also be converted into glutamine.
Glutamic acid Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panchamrut Chemicals | 08048965188 | Mumbai, India | 85 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Hebei Kingfiner Technology Development Co.Ltd | +86-15532196582 +86-15373005021 | China | 3005 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 | China | 21628 | 55 | Inquiry |
| Shanghai Yaji Biological Technology Co., Ltd. | 021-34661275 15301693058 | China | 9747 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Tianjin Yankai Scientific Co. Ltd. | 18500985499 | China | 447 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Beijing Keyi Tongda Technology Development Co., Ltd | 17743531240 | China | 1514 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Beijing Solarbio Science & Tecnology Co., Ltd. | 010-50973186 4009686088 | China | 18338 | 68 | Inquiry |
| Shanghai Kanglang Biotechnology Co., Ltd. | 021-61998208 18217752821 | China | 9618 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Beijing Anbiqi Biotechnology Co., Ltd. | 15811277462 | CHINA | 2529 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Shanghai Ziqi Biological Technology Co., Ltd. | 400-811-9081 13681619662 | CHINA | 6184 | 58 | Inquiry |
Related articles
- Biological functions and Synthesis of Glutamic acid
- Glutamic acid is the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in vertebrate nervous systems.
- Jun 23,2022





