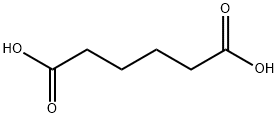
Adipic acid
- CAS No.
- 124-04-9
- Chemical Name:
- Adipic acid
- Synonyms
- adipic;adipate;Hexane diacid;Acifloctin;Hexanedioate;adipinic acid;AA, Adipic acid;Asapic;NA-9077;Adi-pure
- CBNumber:
- CB0718158
- Molecular Formula:
- C6H10O4
- Molecular Weight:
- 146.14
- MOL File:
- 124-04-9.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/9/9 19:09:56
| Melting point | 151-154 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 265 °C100 mm Hg(lit.) |
| Density | 1,36 g/cm3 |
| vapor density | 5 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 1 mm Hg ( 159.5 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.4880 |
| FEMA | 2011 | ADIPIC ACID |
| Flash point | 385 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | methanol: 0.1 g/mL, clear, colorless |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 4.43(at 25℃) |
| color | White |
| PH | 3.74(1 mM solution);3.22(10 mM solution);2.71(100 mM solution); |
| Odor | wh. monoclinic prisms, pract. odorless |
| Water Solubility | 1.44 g/100 mL (15 ºC) |
| JECFA Number | 623 |
| Merck | 14,162 |
| BRN | 1209788 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 5 mg/m3 |
| Dielectric constant | 1.8(Ambient) |
| Stability | Stable. Substances to be avoided include ammonia, strong oxidizing agents. |
| InChIKey | WNLRTRBMVRJNCN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | 0.09 at 25℃ |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 124-04-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Hexanedioic acid(124-04-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Adipic acid (124-04-9) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS05 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H318 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P280-P305+P351+P338 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xi | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 36-41 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-39-24/25 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 1 | |||||||||
| RTECS | AU8400000 | |||||||||
| Autoignition Temperature | 788 °F | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29171210 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in Rabbit: 5700 mg/kg LD50 dermal Rabbit > 7940 mg/kg | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Adipic acid price More Price(20)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | W201103 | Adipic acid ≥99.5% | 124-04-9 | 1SAMPLE | ₹4990.33 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | W201103 | Adipic acid ≥99.5% | 124-04-9 | 1KG | ₹7122.85 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | W201103 | Adipic acid ≥99.5% | 124-04-9 | 5KG | ₹15328.2 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | W201103 | Adipic acid ≥99.5% | 124-04-9 | 10KG | ₹17796.3 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | A26357 | Adipic acid 99% | 124-04-9 | 25G | ₹1861.9 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Adipic acid Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Adipic acid is a crystalline powder with practically no odor. It has the lowest acidity of any of the acids commonly used in foods and has excellent buffering capacity in the range of pH 2.5 to 3.0. Like succinic and fumaric acid, adipic acid is practically nonhygroscopic. Its addition to foods imparts a smooth, tart taste. In grape-flavored products, it adds a lingering supplementary flavor and gives an excellent set to food powders containing gelatin. As a result, adipic acid has found a wide number of uses as an accidulant in dry powdered food mixtures, especially in those products having delicate flavors and where addition of tang to the flavor is undesirable.

Its aqueous solutions have the lowest acidity of any of the common food acids. For concentrations from 0.5 to 2.4 g/100 mL, the pH of its solution varies less than half a unit. Hence, it can be used as a buffering agent to maintain acidities within the range of 2.5 to 3.0. This is highly desirable in certain foods, yet the pH is low enough to inhibit the browning of most fruits and other foodstuffs.
Chemical Properties
Adipic acid is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)4(COOH)2. From the industrial perspective, it is the most important dicarboxylic acid: About 2.5 billion kilograms of this white crystalline powder are produced annually, mainly as a precursor for the production of nylon. Adipic acid otherwise rarely occurs in nature.
Physical properties
Adipic acid is a straight-chain dicarboxylic acid that exists as a white crystalline compound at standard temperature and pressure. Adipic acid is one of the most important industrial chemicals and typically ranks in the top 10 in terms of volume used annually by the chemical industry.
Occurrence
Reported found as a minor constituent in butter, and has been found in other fats as a product of oxidative rancidity. It also occurs in beet juice, pork fat, guava fruit (Psidium guajava L.), papaya (Carica papaya L.) and raspberry (Rubus idaeus L.).
Uses
Adipic Acid is primarily used in the synthesis of nylon. It has been used as a reagent in the solid-state polymerization of nylon analogs.
Production Methods
Adipic acid is prepared by nitric acid oxidation of cyclohexanol or cyclohexanone or a mixture of the two compounds. Recently, oxidation of cyclohexene with 30% aqueous hydrogen peroxide under organic solvent- and halide-free conditions has been proposed as an environmentally friendly alternative for obtaining colorless crystalline adipic acid.
Definition
ChEBI: An alpha,omega-dicarboxylic acid that is the 1,4-dicarboxy derivative of butane.
Preparation
Adipic acid is produced from a mixture of cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone called "KA oil", the abbreviation of "ketone-alcohol oil." The KA oil is oxidized with nitric acid to give adipic acid, via a multistep pathway. Early in the reaction the cyclohexanol is converted to the ketone, releasing nitrous acid:
HOC6H11 + HNO3 → OC6H10 + HNO2 + H2O
Among its many reactions, the cyclohexanone is nitrosated, setting the stage for the scission of the C- C bond:
HNO2 + HNO3 → NO+NO3- + H2O
OC6H10 + NO+→ OC6H9-2 - NO + H+
Side products of the method include glutaric and succinic acids.
Related processes start from cyclohexanol, which is obtained from the hydrogenation of phenol.
Reactions
Adipic acid is a dibasic acid (can be deprotonated twice). Its pKa's are 4.41 and 5.41.
With the carboxylate groups separated by four methylene groups, adipic acid is suited for intramolecular condensation reactions. Upon treatment with barium hydroxide at elevated temperatures, it undergoes ketonization to give cyclopentanone.
General Description
Adipic acid is a white crystalline solid. Adipic acid is insoluble in water. The primary hazard is the threat to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit its spread to the environment. Adipic acid is used to make plastics and foams and for other uses.
Air & Water Reactions
Dust may form explosive mixture with air [USCG, 1999]. Insoluble in water.
Health Hazard
Exposures to adipic acid cause pain, redness of the skin and eyes, tearing or lacrimation. Adipic acid has been reported as a non-toxic chemical. Excessive concentrations of adipic acid dust are known to cause moderate eye irritation, irritation to the skin, and dermatitis.It may be harmful if swallowed or inhaled. It causes respiratory tract irritation with symptoms of coughing, sneezing, and blood-tinged mucous.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Adipic acid is used as an acidifying and buffering agent in
intramuscular, intravenous and vaginal formulations. It is also
used in food products as a leavening, pH-controlling, or flavoring
agent.
Adipic acid has been incorporated into controlled-release
formulation matrix tablets to obtain pH-independent release for
both weakly basicand weakly acidic drugs.It has also been
incorporated into the polymeric coating of hydrophilic monolithic
systems to modulate the intragel pH, resulting in zero-order release
of a hydrophilic drug.The disintegration at intestinal pH of the
enteric polymer shellac has been reported to improve when adipic
acid was used as a pore-forming agent without affecting release in
the acidic media.Other controlled-release formulations have
included adipic acid with the intention of obtaining a late-burst
release profile.
Safety Profile
Poison by intraperitoneal route. Moderately toxic by other routes. A severe eye irritant. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame; can react with oxidzing materials. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and fumes.
Safety
Adipic acid is used in pharmaceutical formulations and food
products. The pure form of adipic acid is toxic by the IP route, and
moderately toxic by other routes. It is a severe eye irritant, and may
cause occupational asthma.
LD50 (mouse, IP): 0.28 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, IV): 0.68 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, oral): 1.9 g/kg
LD50 (rat, IP): 0.28 g/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): >11 g/kg
Potential Exposure
Workers in manufacture of nylon, plasticizers, urethanes, adhesives, and food additives
storage
Adipic acid is normally stable but decomposes above boiling point. It should be stored in a tightly closed container in a cool, dry place, and should be kept away from heat, sparks, and open flame.
Shipping
UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required
Purification Methods
For use as a volumetric standard, adipic acid is crystallised once from hot water with the addition of a little animal charcoal, dried at 120o for 2hours, then recrystallised from acetone and again dried at 120o for 2hours. Other purification procedures include crystallisation from ethyl acetate and from acetone/petroleum ether, fusion followed by filtration and crystallisation from the melt, and preliminary distillation under vacuum. [Beilstein 2 IV 1956.]
Incompatibilities
Adipic acid is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents as well as strong bases and reducing agents. Contact with alcohols, glycols, aldehydes, epoxides, or other polymerizing compounds can result in violent reactions.
Waste Disposal
Dissolve or mix the material with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be observed
Precautions
Occupational workers should avoid contact of the adipic acid with the eyes, avoid breathing dust, and keep the container closed. Workers should use adipic acid only with adequate ventilation. Workers should wash thoroughly after handling adipic acid and keep away from heat, sparks, and flame. Also, workers should use rubber gloves and laboratory coats, aprons, or coveralls, and avoid creating a dust cloud when handling, transferring, and cleaning up.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (IM, IV, and vaginal preparations). Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in an oral pastille formulation available in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Adipic acid Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of3
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1of6
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sudarshan Pharma Industries Limited | +91-2242221111 +91-9320932107 | Maharashtra, India | 37 | 58 | Inquiry |
| ADVENT CHEMBIO PRIVATE LIMITED | +91-9821524116 +91-9821524116 | Mumbai, India | 353 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Soham Chemical Industries | +91-7016081644 +91-7016081644 | Mumbai, India | 83 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Royal Chemicals | +91-9221503305 +91-9221503305 | Maharashtra, India | 28 | 58 | Inquiry |
| PERFECT CHEMICAL | +91-9820465461 +91-9820465461 | Mumbai, India | 391 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Evans Fine Chem | +91-9821340302 +91-9821340302 | Maharashtra, India | 286 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Chem stride | +91-8169461298 +91-8169461298 | Maharashtra, India | 27 | 58 | Inquiry |
| LANXESS India Pvt. Ltd. | +91-8356878763 +91-8356878763 | Maharashtra, India | 190 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Merck Ltd | +91-2262109800 +91-2262109000 | Maharashtra, India | 272 | 58 | Inquiry |
| UNILOSA INTERNATINAL PRIVATE LIMITED | +91-9999069917 +91-9999069917 | New Delhi, India | 152 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Sudarshan Pharma Industries Limited | 58 |
| ADVENT CHEMBIO PRIVATE LIMITED | 58 |
| Soham Chemical Industries | 58 |
| Royal Chemicals | 58 |
| PERFECT CHEMICAL | 58 |
| Evans Fine Chem | 58 |
| Chem stride | 58 |
| LANXESS India Pvt. Ltd. | 58 |
| Merck Ltd | 58 |
| UNILOSA INTERNATINAL PRIVATE LIMITED | 58 |
Related articles
- Adipic Acid: A Versatile Industrial Compound
- Adipic acid, a vital organic compound in the industrial chemistry realm, is primarily known for its role in the production of ....
- Jul 8,2024
- Adipic acid: Physicochemical properties, production host screening and toxicity
- Adipic acid is an odourless, white crystalline powder with a wide range of roles in chemical generation and manufacture.
- May 20,2024
- Adipic acid: Uses and Synthesis
- This passage describes that Adipic acid is used in medicine and foods, and also introduces the laboratory and industrial synth....
- Nov 16,2022





