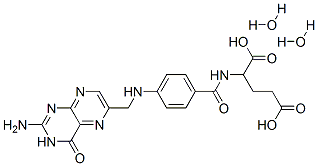
FOLIC ACID DIHYDRATE
- CAS No.
- 75708-92-8
- Chemical Name:
- FOLIC ACID DIHYDRATE
- Synonyms
- FolicAcidB.P.;PGA DIHYDRATE;FOLIC ACID pure;FOLIC ACID DIHYDRATE;PTEROYLGLUTAMIC ACID;FOLIC ACID, 500MG, NEAT;VitaMin M or VitaMin Bc;FOLIC ACID DIHYDRATE 97%;PGA, Pteroylglutamic acid;PTEROYLGLUTAMIC ACID DIHYDRATE
- CBNumber:
- CB3453412
- Molecular Formula:
- C19H23N7O8
- Molecular Weight:
- 477.43
- MOL File:
- 75708-92-8.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2023/4/23 13:52:06
| Melting point | 250°C |
|---|---|
| storage temp. | Store at RT. |
| solubility | Aqueous Acid (Slightly), Aqueous Base (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly) |
| pka | pK1:8.26 (25°C) |
| form | Solid |
| color | Yellow to Dark Yellow |
| Water Solubility | Miscible with water. |
| Merck | 14,4221 |
| BRN | 100781 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 75708-92-8 |
FOLIC ACID DIHYDRATE price More Price(2)
FOLIC ACID DIHYDRATE Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
Yellow to yellow-orange crystalline powd
Uses
Vitamin B9. A B-complex vitamin necessary for the body to produce red blood cellsFolic acid dehydrate is used to form non-covalent complexes with polyethylenimine. It is used for the delivery of genes, which finds application in gene therapy. It is a B-complex vitamin, which is necessary for the body to produce red blood cells.
Purification Methods
If paper chromatography indicates impurities, then recrystallise it from hot H2O or from dilute acid [Walker et al. J Am Chem Soc 70 19 1948]. Impurities may be removed by repeated extraction with n-BuOH of a neutral aqueous solution of folic acid (by suspending in H2O and adding N NaOH dropwise till the solid dissolves, then adjusting the pH to ~7.0-7.5) followed by precipitation with acid, filtration, or better collected by centrifugation and recrystallised form hot H2O. [Blakley Biochem J 65 331 1975, Kalifa et al. Helv Chim Acta 6 1 2739 1978.] Chromatography on cellulose followed by filtration through charcoal has also been used to obtain pure acid. [Sakami & Knowles Science 129 274 1959.] UV: max 247 and 296nm ( 12,800 and 18,700) in H2O pH 1.0; 282 and 346nm ( 27.600 and 7,200) in H2O pH 7.0; 256, 284 and 366nm ( 24600, 24,500 and 86,00) in H2O pH 13 [Rabinowitz in The Enzymes (Boyer et al. Eds), 2 185 1960]. [Beilstein 26 III/IV 3944.]
FOLIC ACID DIHYDRATE Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHEMSWORTH | +91-261-2397244 | New Delhi, India | 6707 | 30 | Inquiry |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | +91-22-45045900 | Hyderabad, India | 6351 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Alfa Aesar | 1 800 209 7001 | Maharashtra, India | 6913 | 58 | Inquiry |
| A.J Chemicals | 91-9810153283 | New Delhi, India | 6124 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Alfa Chemistry | United States | 2344 | 58 | Inquiry | |
| Nextpeptide Inc | +86-0571-81612335 +8613336028439 | China | 19915 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Hangzhou MolCore BioPharmatech Co.,Ltd. | +86-057181025280; +8617767106207 | China | 49739 | 58 | Inquiry |
| SUZHOU SENFEIDA CHEMICAL CO.,LTD | +86-0512-83500002 +8615195660023 | China | 10814 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Aladdin Scientific | +1-+1(833)-552-7181 | United States | 57511 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co.,Ltd. | +86-18521732826 | China | 48467 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| CHEMSWORTH | 30 |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | 58 |
| Alfa Aesar | 58 |
| A.J Chemicals | 58 |
| Alfa Chemistry | 58 |
| Nextpeptide Inc | 58 |
| Hangzhou MolCore BioPharmatech Co.,Ltd. | 58 |
| SUZHOU SENFEIDA CHEMICAL CO.,LTD | 58 |
| Aladdin Scientific | 58 |
| Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co.,Ltd. | 58 |





