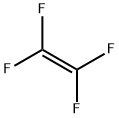
Tetrafluoroethylene
- CAS No.
- 116-14-3
- Chemical Name:
- Tetrafluoroethylene
- Synonyms
- C2F4;Perfluoroethene;R1114;MS-122;PFC-1114;fluoroplast4;Fluoroplast 4;Tetrafluorethen;Tetrafluorethene;Perfluoroethylene
- CBNumber:
- CB6225793
- Molecular Formula:
- C2F4
- Molecular Weight:
- 100.01
- MOL File:
- 116-14-3.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2025/6/13 14:48:16
| Melting point | -142°C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | -76.3°C |
| Density | 1.1507 |
| refractive index | 1.2420 (estimate) |
| Water Solubility | 110mg/L at 28℃ |
| Dielectric constant | 1.9(Ambient) |
| Stability | Stable. Reactive when heated. |
| LogP | 1.21 at 20℃ |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 116-14-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2A (Vol. 19, Sup 7, 71, 110) 2017 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Ethene, tetrafluoro-(116-14-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Tetrafluoroethene (116-14-3) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS08 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H350 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | C,F | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 11 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 16-36/37/39-45 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | 1081 | |||||||||
| Hazard Note | Corrosive/Flammable | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 2.1 | |||||||||
| Hazardous Substances Data | 116-14-3(Hazardous Substances Data) | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LC50 (4 hr) in rats, mice, hamsters, guinea pigs (ppm): 37500-45000, 35000, 28500, 28000 (Kennedy) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Tetrafluoroethylene Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Tetrafluoroethylene is a synthetic, colorless, flammable gas that is insoluble in water. Tetrafluoroethylene is used primarily in the synthesis of polytetrafluoroethylene resins. It is also used as a monomer in the synthesis of copolymers and as a propellant for food product aerosols. When heated to decomposition, tetrafluoroethylene emits highly toxic fluorocarbon fumes. The primary route of human exposure to this compound is inhalation. Acute inhalation exposure to tetrafluoroethylene may result in irritation of the respiratory tract and buildup of fluid in the lungs (pulmonary edema). Contact with this gas can cause eye irritation. This chemical is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen. (NCI05)
Chemical Properties
Tetrafluoroethylene is a colorless, flammable gas. Heavier than air. insoluble in water. soluble in acetone.
Uses
In manufacture of polymers and synthesis of fluorinated refrigerants, dielectric media and solvents. In vinyl polymerization, cycloalkylation and addition reactions.
Definition
Tetrafluoroethene is a fluorocarbon. It is a gaseous organic compound (a fluorocarbon and a haloalkene) used to make the plastic polytetrafluoroethene (PTFE).
Preparation
Tetrafluoroethylene (TFE) is manufactured from chloroform. Chloroform is fluorinated by reaction with hydrogen fluoride to produce chlorodifluoromethane (R-22). Pyrolysis of chlorodifluoromethane then yields TFE.
CHCl3 + 2 HF → CHClF2 + 2 HCl
2CHClF2 → C2F4 + 2 HCl
A laboratory synthesis entails pyrolysis of a PTFE under a vacuum. The PTFE polymer "cracks" and depending on the pressure, produces mainly C2F4.
Application
The main use of tetrafluoroethylene is in the manufacture of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) that is used as nonstick coatings on cookware, membranes for clothing that are both waterproof and breathable, electrical-wire casing, fire- and chemical-resistant tubing, and plumbing thread seal tape.The most widely known PTFE formulation is sold under the brand name of Teflon®. PTFE was discovered by DuPont Co. in 1938.
General Description
Tetrafluoroethylene, stabilized appears as a colorless odorless gas. Easily ignited. Vapors are heavier than air. May asphyxiate by the displacement of air. May violently polymerize under prolonged exposure to fire or heat, violently rupturing the container. Under prolonged exposure to fire or heat the containers may rupture violently and rocket. Water insoluble.
Air & Water Reactions
Flammable. Forms polymeric peroxides that are explosive [Bretherick 1979 p. 164].
Reactivity Profile
Tetrafluoroethylene reacts with air (oxygen) to form polymeric peroxides that are explosive [Bretherick 1979 p. 164]. Probably susceptible to similar reactions with a number of oxidizing agents.May polymerize violently (inhibitor tends to prevent this reaction). May react violently with aluminum. Contamination of a tetrafluoroethylene gas supply system led to a reaction between the inhibitor, limonene, and the contaminant, iodine pentafluoride. This initiated an explosive polymerization event [MCA Case History No. 1520].
Hazard
Flammable, dangerous fire risk. Kidney and liver damage; kidney and liver cancer. Possible carcinogen.
Health Hazard
Inhalation causes irritation of respiratory system. Contact with eyes causes slight irritation.
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen. Mildly toxic by inhalation. Can act as an asphyxiant and may have other toxic properties. The gas is flammable when exposed to heat or flame. The inhibited monomer will explode if igntted. Explosive in the form of vapor when exposed to heat or flame. Will explode at pressures above 2.7 bar if limonene inhbitor is not added. Iodine pentafluoride depletes the limonene inhbitor and then causes explosive polymerization of the monomer. Mixtures with hexafluoropropene and air form an explosive peroxide. Reacts violently with SO3; air; dfluoromethylene dihypofluorite; loxygen difluoride; iodine pentafluoride; oxygen. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of F-. See also FLUORIDES.
Potential Exposure
A potential danger to those involved in the production of TFE and the manufacture of fluorocarbon polymers.
Carcinogenicity
Tetrafluoroethylene is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in experimental animals (NTP 1997).
Incompatibilities
Reacts with air. Hazardous polymerization may occur unless inhibited. Will explode at pressures above 2.7 bar if terpene inhibitor is not added. Inhibited monomer can decompose explosively in fire, under pressure, or upon contact with materials with which it can react exothermically. Violent reaction with oxygen, oxidizers, sulfur trioxide; halogen compounds.
Waste Disposal
Return refillable compressed gas cylinders to supplier. Nonrefillable cylinders should be disposed of in accordance with local, state and federal regulations. Allow remaining gas to vent slowly into atmosphere in an unconfined area or exhaust hood. Refillable-type cylinders should be returned to original supplier with any valve caps and outlet plugs secured and valve protection caps in place.
Tetrafluoroethylene Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1of3
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diamond Polymers | 08048372277Ext 767 | Maharashtra, India | 1 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Ami Polymers | 08048371900Ext 629 | Gujarat, India | 1 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 | China | 21622 | 55 | Inquiry |
| CONIER CHEM AND PHARMA LIMITED | +8618523575427 | China | 49732 | 58 | Inquiry |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 | China | 29806 | 58 | Inquiry |
| LEAP CHEM CO., LTD. | +86-852-30606658 | China | 24727 | 58 | Inquiry |
| PT CHEM GROUP LIMITED | +86-85511178; +86-85511178; | China | 35425 | 58 | Inquiry |
| SUZHOU SENFEIDA CHEMICAL CO.,LTD | +86-0512-83500002 +8618662433356 | China | 26362 | 58 | Inquiry |
| XIAMEN AMITY INDUSTRY AND TRADE CO., LTD. | +8618950047208 | China | 43416 | 58 | Inquiry |
| DAYANG CHEM (HANGZHOU) CO.,LTD | +86-88938639 +86-17705817739 | China | 53900 | 58 | Inquiry |
116-14-3(Tetrafluoroethylene)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




