PERCHLORATE
- CAS No.
- 14797-73-0
- Chemical Name:
- PERCHLORATE
- Synonyms
- Perchlorate ion;Perchlorate ion(1-);Hyperchloric acid ion;Hyperchloric acid anion
- CBNumber:
- CB81413485
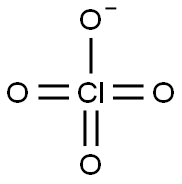
- Molecular Formula:
- ClO4
- Molecular Weight:
- 99.45
- MOL File:
- 14797-73-0.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2023/5/4 17:34:33
| Melting point | 262-263 °C |
|---|---|
| EPA Substance Registry System | Perchlorate (14797-73-0) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS03,GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H271-H302 |
| Precautionary statements | P210-P220-P221-P280-P283-P306+P360-P371+P380+P375-P370+P378-P501-P264-P270-P301+P312-P330-P501 |
PERCHLORATE Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Concern about environmental perchlorate exposure centers on its inhibition of iodide uptake into the thyroid. Decreased iodine intake may decrease thyroid hormone production. In the last few years, perchlorate has become a major inorganic contaminant in drinking water and has been detected in a number of public drinking water systems throughout the Unites States. In 1998, the US EPA added perchlorate to the Drinking Water Candidate Contaminant List.
Uses
Perchlorate is a soluble oxychloro anion most commonly used as a solid salt in the form of ammonium perchlorate, potassium perchlorate, lithium perchlorate, or sodium per- chlorate, all of which are highly soluble. Ammonium perchlorate is the most widely used perchlorate compound. In their pure forms, these salts are white or colorless crystals or powders. Perchlorate salts dissolve in water and readily move from surface to groundwater. Perchlorate is known to originate from both natural and man-made sources.
The most common uses for ammonium perchlorate are in explosives, military munitions, and rocket propellants. In addition, perchlorate salts are used in a wide range of nonmilitary applications, including pyrotechnics and fireworks, blasting agents, solid rocket fuel, matches, lubricating oils, nuclear reactors, air bags, and certain types of fertilizers. Improper storage and disposal related to these uses is the most typical route for perchlorate to enter into the environment. Monitoring data show that more than 4% of public water systems, serving between 5 million and 17 million people, have detected perchlorate in their finished water.
General Description
Crystalline or powdered solids. May explode under exposure to heat or fire. If available, obtain the technical name from the shipping papers and contact CHEMTREC, 800-424-9300 for specific response information.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
PERCHLORATE is a strong oxidizing agents. May be self-reactive (e.g., ammonium perchlorate, glycol perchlorate) and liable to violent decomposition. The violence of decomposition of some perchlorates exceeds that of nitroglycerine. Noncombustible but able to accelerate the burning of combustible materials. If large quantities are involved in a fire or the combustible material is finely divided, then an explosion may result.
Health Hazard
Inhalation, ingestion or contact (skin, eyes) with vapors or substance may cause severe injury, burns or death. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
These substances will accelerate burning when involved in a fire. Some may decompose explosively when heated or involved in a fire. May explode from heat or contamination. Some will react explosively with hydrocarbons (fuels). May ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may create fire or explosion hazard.
Environmental Fate
Environmental Persistency (Degradation and Speciation):
Perchlorate salts such as ammonium perchlorate are
expected to exist as a solid aerosol or be absorbed to suspended
particulate matter. Therefore, removal from the
atmosphere is expected to occur by both wet and dry
depositions. Perchlorates are not expected to undergo direct
photolysis in air. If released in soil, the perchlorate ion is
only weakly absorbed to mineral surfaces of moderate ionic
strength. The ion exhibits high aqueous solubility, and
together these properties contribute to its ability to readily
migrate in groundwater systems. The ion is not expected to
volatilize from soil to the atmosphere because perchlorates
exhibit very low vapor pressures. If released to water,
ammonium perchlorate readily dissolves and dissociates to
the perchlorate ion. Perchlorate is an ion; therefore, volatilization
from water surfaces is not expected to be an
important fate process. Hydrolysis does not occur for
inorganic salts such as ammonium perchlorate, which
ionizes in aqueous solution.
Handling and storage: Keep the container tightly closed. Keep
the container in a cool, well-ventilated area, separate from
acids, alkalies, reducing agents, and combustibles.
Bioaccumulation and biomagnifications: Significant decomposition
of perchlorate does not occur in nature, making
human interventions necessary for efficient environmental
cleanup.
PERCHLORATE Preparation Products And Raw materials
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | +91-22-45045900 | Hyderabad, India | 6257 | 58 | Inquiry |
| ShangHai Anpel Co, Ltd. | 18501792038; 18501792038 | China | 9611 | 58 | Inquiry |
| AccuStandard Inc | (800) 442-5290 | United States | 5300 | 76 | Inquiry |
| Portail Substances Chimiques | 10 20 0000 | France | 6024 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | 58 |
| ShangHai Anpel Co, Ltd. | 58 |
| AccuStandard Inc | 76 |
| Portail Substances Chimiques | 58 |





