葉酸水和物 化学特性,用途語,生産方法
外観
黄色~赤みの黄色, 粉末
性質
C19H19N7O6(441.40).略称PGA.ビタミンM,ビタミン Bc ともいわれたビタミンB複合体の一つ.1941年,H.A. Mitchellらによって,ホウレンソウの葉の抽出濃縮物から単離され,乳酸菌の生育に必要な因子に対して“folium”(葉)にちなんで名づけられた.化学的には,2,4,5-トリアミノ-6-ヒドロキシピリミジン,ジブロモプロヒオンアルデヒド,p-アミノベンゾイルグルタミン酸を酢酸緩衝液中で順次反応させて合成する.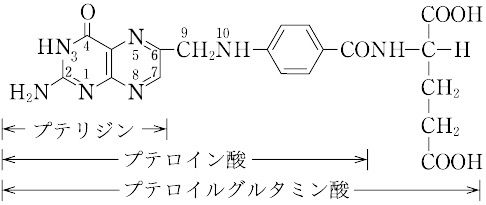 橙黄色の針状晶.明確な融点を示さず,約250 ℃ から炭化する.[α]<sup>25</sup>D+23°(0.1 mol L-1 水酸化ナトリウム).水,有機溶媒に難溶,熱湯,フェノール,酢酸,ピリジン,アルカリに可溶.酸性では熱や光に不安定である.λmax 247,296 nm(pH 1),282,346 nm(pH 7.2),256,284,366 nm(pH 13),(log ε :12.8,19.7,27.6,7.2,24.6,24.5,8.6).葉酸のグルタミン酸残基に,さらに2個あるいは5個のグルタミン酸がγ-ペプチド結合したものも知られている.いずれも細胞の増殖促進,造血作用をもつ.補酵素として活性をもつのは葉酸の還元型,5,6,7,8-テトラヒドロ葉酸で,N5,N10 の位置に C1 基,すなわち,ホルミル(-CHO),メチル(-CH3),ヒドロキシメチル(-CH2OH),メチレン(
橙黄色の針状晶.明確な融点を示さず,約250 ℃ から炭化する.[α]<sup>25</sup>D+23°(0.1 mol L-1 水酸化ナトリウム).水,有機溶媒に難溶,熱湯,フェノール,酢酸,ピリジン,アルカリに可溶.酸性では熱や光に不安定である.λmax 247,296 nm(pH 1),282,346 nm(pH 7.2),256,284,366 nm(pH 13),(log ε :12.8,19.7,27.6,7.2,24.6,24.5,8.6).葉酸のグルタミン酸残基に,さらに2個あるいは5個のグルタミン酸がγ-ペプチド結合したものも知られている.いずれも細胞の増殖促進,造血作用をもつ.補酵素として活性をもつのは葉酸の還元型,5,6,7,8-テトラヒドロ葉酸で,N5,N10 の位置に C1 基,すなわち,ホルミル(-CHO),メチル(-CH3),ヒドロキシメチル(-CH2OH),メチレン(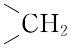 ),メチリジン(
),メチリジン(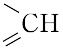 )およびホルムイミノ(-CH=NH)基などを結合して運搬し,プリン,ピリミジンの生合成,したがってRNA,DNAの生合成に関与している.葉酸は,酵母,肝臓,アスパラガス,レタス,ホウレンソウなどに豊富に含まれており,野菜類では主としてホルミル誘導体,酵母や肝臓などではメチル誘導体を含む.ほ乳動物の抗貧血因子である.
)およびホルムイミノ(-CH=NH)基などを結合して運搬し,プリン,ピリミジンの生合成,したがってRNA,DNAの生合成に関与している.葉酸は,酵母,肝臓,アスパラガス,レタス,ホウレンソウなどに豊富に含まれており,野菜類では主としてホルミル誘導体,酵母や肝臓などではメチル誘導体を含む.ほ乳動物の抗貧血因子である.
定義
本品は、グルタミン酸誘導体であり、次の化学式で表される。
溶解性
うすい水酸化ナトリウム溶液、うすい塩酸及びうすい硫酸に溶け、水及びエタノールにほとんど溶けない。
生理機能
ビタミンB群の一つ。かつてビタミンMやビタミンBCともよばれていた。分子式C19H19N7O6、分子量441.40。融点250℃。黄橙(おうとう)色針状結晶。酢酸、アルカリ、ピリジンに易溶。プテリジンとp(パラ)-アミノ安息香酸からなるプテロイン酸に、グルタミン酸が結合したプテロイルグルタミン酸で、おもにトリまたはヘプタグルタミルペプチドの形で存在する。1941年ミッチェルHerschel K. Mitchell(1913―2000)らによりホウレンソウなどの緑葉中からある種の乳酸菌生育因子として抽出され、ラテン語の葉foliumにちなんで命名され、ホラシンfolacinともよばれていた。酵母や肝臓などからも抽出され、造血に有効な因子で、微生物の増殖を促進する。生化学的に活性な型はテトラヒドロ葉酸FH4であり、炭素1分子を含むメチル基、メチレン基、ホルミル基、メテニル基などの転移酵素の補酵素として作用する。哺乳(ほにゅう)類は葉酸の構成成分であるプテリジンは合成できるが、これをほかの二つの構造(p-アミノ安息香酸、グルタミン酸)と結合できないので、テトラヒドロ葉酸を食物から摂取するか、腸管内の微生物から得る。
葉酸はビタミンB群に属する水溶性(水に溶けるタイプという意味)ビタミン。血をつくる働きに関係し、不足すると貧血になることもあります。また妊娠を望んでいる女性や妊娠中の女性は、妊娠前から妊娠初期にかけて1日0.4mgの葉酸を摂取することで胎児の神経管閉鎖障害の発症リスクを低下させるとされています。体内に蓄えることがなかなかできないので、毎日摂取することが大切。緑黄色野菜、果物などに多く含まれていますが、こうした野菜などから摂取できる葉酸の量は限られているので、サプリメント(栄養補助食品)の利用が勧められます。ただし、とりすぎは禁物で、1日の摂取目安量を守ることが大切です。サプリメントなどは表示をよく確認しましょう。
解説
化学式はC19H19N7O6。ビタミンB複合体の一つ。ビタミンM,ビタミンB(/c)とも呼ばれた。パラアミノ安息香酸にプテリンとグルタミン酸が結合したもので,水や多くの有機溶媒に難溶。酵母,糸状菌,肝臓,卵,アスパラガス,ホウレンソウなどに含まれる。核酸塩基の代謝に関係し,赤血球母細胞の成熟などに必要。また乳酸菌など微生物の増殖促進因子としても知られる。栄養失調症,悪性貧血などにビタミンB12,肝臓エキスと併用される。→関連項目悪性貧血|造血薬|ビタミン|プテリン
株式会社平凡社 百科事典マイペディアについて 情報
用途
薬理・生理作用研究用。
用途
核酸代謝に作用します。
生物学的性質
欠乏症:貧血,ヒトでは欠乏症ではまれ(腸内細菌により生成) 機能:テトラヒドロ葉酸として補酵素.プテロイルヘプタ(γ)グルタミン酸などとしても存在
生体との関係
肝臓から抗貧血因子、ホウレンソウから乳酸菌増殖因子として発見されたビタミンであることからもわかるように、ホウレンソウなどの緑黄色野菜、キノコ、肝臓、腎臓(じんぞう)に豊富で、その他の野菜や果実、食肉にもかなり含まれている。しかしながら調理加工、貯蔵中に失われる量が比較的多く、90%に達する例もある。所要量は1日成人0.2~0.4ミリグラム、乳児0.005~0.1ミリグラム、授乳婦0.6ミリグラムと推定されている。核酸やタンパク質の合成・分解に関与し、また骨髄での幼若細胞の成熟にも必要である。葉酸が欠乏すると赤血球の未熟などにより、たとえば巨赤芽球(きょせきがきゅう)貧血などがおこる。
葉酸は妊娠時に要求量が増大するので、アメリカなどでは受胎前のすべての女性に対して葉酸を強化した食事をとることを推奨している。これは葉酸摂取量が不足している場合、神経管異常neural tube defectの新生児が生まれる頻度が欧米で高くなっているからである。[木村修一]
化粧品の成分用途
皮膚コンディショニング剤
効能
貧血治療薬, 造血薬, 葉酸補充薬
商品名
フォリアミン (日本製薬); フォリアミン (日本製薬)
説明
Folic acid is an essential B vitamin. It is converted to folate
in vivo, which is a necessary cofactor for a variety of biological processes, including nucleotide synthesis and, thus, DNA synthesis and repair, among others. A deficiency in dietary folic acid can lead to a range of developmental and cognitive disorders, most prominently neural tube defects and congenital heart defects.
化学的特性
orange to yellow crystalline powder
分布
広く存在.肝臓,酵母,緑葉に多い
物理的性質
The folates include a large number of chemically related species, each differing
with respect to the various substituents possible at three sites on the pteroylglutamic
acid basic structure. More than 170 different folates are theoretically possible. Not
all of these occur in nature; but it has been estimated that as many as 100 different
forms are found in animals. The folates from most natural sources usually have a
single carbon unit at N-5 and/or N-10; these forms participate in the metabolism of
the single-carbon pool.
Folic acid (pteroylmonoglutamic acid) is an orange-yellow crystalline substance
that is soluble in water but insoluble in ethanol or less polar organic solvents. It is
unstable to light, to acidic or alkaline conditions, to reducing agents, and, except in
dry form, to heat. It is reduced in vivo enzymatically (or in vitro with a reductant
such as dithionite) first to 7,8-dihydrofolic acid (FH2) and then to FH4; both of these
compounds are unstable in aerobic environments and must be protected by the pres ence of an antioxidant (e.g., ascorbic acid, 2-mer
Two derivatives of folic acid, each having an amino group in the place of the
hydroxyl at C-4, are folate antagonists of biomedical use: aminopterin (4-aminofolic
acid) and methotrexate (4-amino-N10-methylfolic acid). Aminopterin is used as a
rodenticide; methotrexate is an antineoplastic agent.
天然物の起源
Synthetic
使用
folic acid is generally used as an emollient. In vitro and in vivo skin studies now indicate its capacity to aid in DnA synthesis and repair, promote cellular turnover, reduce wrinkles, and promote skin firmness. There is some indication that folic acid may also protect DnA from uV-induced damage. Folic acid is a member of the vitamin B complex and is naturally occurring in leafy greens.
定義
ChEBI: An N-acyl-amino acid that is a form of the water-soluble vitamin B9. Its biologically active forms (tetrahydrofolate and others) are essential for nucleotide biosynthesis and homocysteine remethylation.
一般的な説明
Odorless orange-yellow needles or platelets. Darkens and chars from approximately 482°F.
空気と水の反応
Insoluble in water. Aqueous solutions have pHs of 4.0-4.8.
反応プロフィール
Acid solutions of Folic acid are sensitive to heat, but towards neutrality, stability progressively increases. Solutions are inactivated by ultraviolet light and alkaline solutions are sensitive to oxidation. Folic acid is also inactivated by light. Folic acid is incompatible with oxidizing agents, reducing agents and heavy metal ions.
火災危険
Flash point data for Folic acid are not available; however, Folic acid is probably combustible.
安全性プロファイル
Poison by
intraperitoneal and intravenous routes.
Experimental teratogenic effects. Mutation
data reported. When heated to
decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
純化方法
If paper chromatography indicates impurities, then recrystallise it from hot H2O or from dilute acid [Walker et al. J Am Chem Soc 70 19 1948]. Impurities may be removed by repeated extraction with n-BuOH of a neutral aqueous solution of folic acid (by suspending in H2O and adding N NaOH dropwise till the solid dissolves, then adjusting the pH to ~7.0-7.5) followed by precipitation with acid, filtration, or better collected by centrifugation and recrystallised form hot H2O. [Blakley Biochem J 65 331 1975, Kalifa et al. Helv Chim Acta 6 1 2739 1978.] Chromatography on cellulose followed by filtration through charcoal has also been used to obtain pure acid. [Sakami & Knowles Science 129 274 1959.] UV: max 247 and 296nm ( 12,800 and 18,700) in H2O pH 1.0; 282 and 346nm ( 27.600 and 7,200) in H2O pH 7.0; 256, 284 and 366nm ( 24600, 24,500 and 86,00) in H2O pH 13 [Rabinowitz in The Enzymes (Boyer et al. Eds), 2 185 1960]. [Beilstein 26 III/IV 3944.]
葉酸水和物 上流と下流の製品情報
原材料
準備製品