| | 319460-85-0 Basic information More.. |
| Product Name: | Axitinib | | Synonyms: | N-METHYL-2-{[3-((E)-2-PYRIDIN-2-YLVINYL)-1H-INDAZOL-6-YL]SULFANYL}BENZAMIDE;AVERMECTINB;Axitinib for research;AG 013736;Benzamide, N-methyl-2-[[3-[(1E)-2-(2-pyridinyl)ethenyl]-1H-indazol-6-yl]thio]-;Axtinib;N-Methyl-2-({3-[(E)-2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethenyl]-1H-indazol-6-yl}sulfanyl)benzaMide;10MG/50MG/100G | | CAS: | 319460-85-0 | | MF: | C22H18N4OS | | MW: | 386.47 | | EINECS: | 638-771-6 | | Mol File: | 319460-85-0.mol | 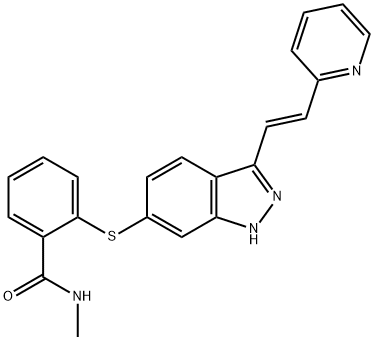 |
Use
In January 2012, the US FDA approved axitinib (also referred to as
AG-013736) for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC)
for patients who have not responded to prior therapy.
Axitinib is a pan VEGF inhibitor and functions by binding to
the intracellular tyrosine kinase catalytic domain of VEGF leading to blockade of signaling through this angiogenic pathway. Axitinib is�50–400 times more potent for VEGF (enzyme Ki and cellular IC50s for VEGF 1, 2, and 3 are ~0.1 nM) than first-generation inhibitors like sorafenib and sunitinib. Axitinib also inhibits c-Kit and PDGFR(α/β) with enzyme Ki's of
~2 nM and was selective when tested against a broad panel of other protein
kinases. Axitinib was discovered by a structure-based drug design approach
and binds to the kinase domain of VEGF in a DFG-out conformation.
Axitinib blocks VEGF-2 phosphorylation up to 7 h postdose in vivo and
inhibits endothelial cell proliferation in xenograft tumors implanted in
mice. Synthetic routes to axitinib employing a Migita coupling to form
the diaryl sulfide and a Heck reaction to install the 2-styrylpyridine moiety have been reported.
- Axitinib
-

- US $33.00-61.00 / mg
- 2024-11-16
- CAS:319460-85-0
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 99.81%
- Supply Ability: 10g
- Axitinib
-
- US $1.00-0.50 / kg
- 2024-11-15
- CAS:319460-85-0
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 200
- Axitinib
-

- US $33.00-61.00 / mg
- 2024-11-15
- CAS:319460-85-0
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 99.81%
- Supply Ability: 10g
|
|
319460-85-0
Recommend Suppliers |
|