|
|
| | Einsteinium Chemical Properties |
| Melting point | 860 ±50° | | density | 8.84 | | form | metal | | color | metal; cubic | | CAS DataBase Reference | 7429-92-7 |
| | Einsteinium Usage And Synthesis |
| General Description | The first isotope of this element having mass number 253 and half-life 20 days was detected in 1952 in the Pacific in debris from the first thermonuclear explosion. The isotope was an alpha emitter of 6.6 MeV energy, chemically analogous to the rare earth element holmium. Isotope 246, having a half-life 7.3 minutes, was synthesized in the Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory cyclotron in 1954. The element was named Einsteinium in honor of Albert Einstein. Only microgram amounts have been synthesized. The element has high specific alpha activities. It may be used as a tracer in chemical studies. Commercial applications are few.
| | Production | The isotope Es-246 may be synthesized in a cyclotron by bombarding uranium238 with nitrogen ions:
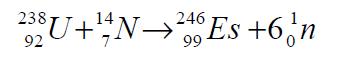
Isotopes of masses 248, 249, 250, 251 and 252 may be prepared from berkelium249 or californium-249 by bombardment with alpha particles or deuterium ions:
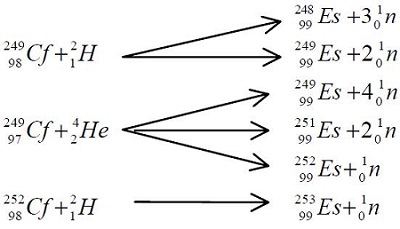
Heavier isotopes Es-253, Es-254 and Es-255 can be produced in a nuclear reactor by multiple neutron capture reactions that may occur when uranium, neptunium and plutonium isotopes are irradiated under intense neutron flux. These and other isotopes also are produced during thermonuclear explosions. | | Seperation | Einsteinium isotopes are separated on an ion exchange column and eluted with a solution of ammonium citrate. Radioactive isotopes are identified by an activity detector.
| | Chemical Properties | man-made radioisotope; identified by Ghiorso and colleagues at Berkeley in December 1952, as part of debris from first large thermonuclear explosion; chemical properties similar to those of holmium; ionic radius of Es+++ is 0.0925 nm; has lowest enthalpy of vaporization of any of the divalent elements; cub, a=0.575 nm; discovered in 1952; t1/2 of 253Es is 20.5 days, t1/2 of 254Es is 276 days, t1/2 of 255Es is 40 days [HAW93] [KIR78] | | History | The name of Es derives from “Albert Einstein”, the Geituan born physicist who proposed the theory of relativity. A collaboration of American scientists G. R. Choppin, S. G. Thompson, A. Ghiorso, and B. G. Harvey, from the Argonne National Laboratory near Chicago, Illinois, the Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory in Los Alamos, New Mexico and at the University of California lab in Berkeley, CA, first found 252Es in the radioactive debris from the first large thermonuclear bomb explosion, nicknamed “Mike,” which took place at Enewetak atoll, Marshall Islands in the Pacific on November 1, 1952. The longest halflife associated with this unstable element is 472 day 252Es. | | Definition | ChEBI: Einsteinium atom is an actinoid atom and a f-block element atom. |
| | Einsteinium Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|