|
|
| | Agropyrene Basic information |
| Product Name: | Agropyrene | | Synonyms: | Agropyrene;1-Phenyl-2,4-hexadiyne;6-Phenyl-2,4-hexadiyne;Capillen;Benzene, 2,4-hexadiyn-1-yl- | | CAS: | 520-74-1 | | MF: | C12H10 | | MW: | 154.21 | | EINECS: | | | Product Categories: | | | Mol File: | 520-74-1.mol | 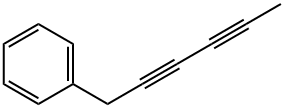 |
| | Agropyrene Chemical Properties |
| Melting point | 0-1 °C | | Boiling point | 140-143 °C(Press: 10 Torr) | | density | 0.9744 g/cm3 | | Odor | sweet anise methyl chavicol |
| | Agropyrene Usage And Synthesis |
| Chemical Properties | Almost colorless or pale yellowish crystals, or pale yellowish liquid. Poorly soluble in alcohol, miscible with essential oils and most perfume chemicals. Very unstable under UV-light or plain daylight. Oxidizes easily, and turns darker yellow. Peculiar sweet-medicinal odor, reminiscent of Anise, Estragon, etc. with a herbaceousminty note, quite tenacious. | | Uses | Could find some use in perfumes and flavors, if it were made commercially available. Agropyrene constitutes more than 9000 of the essential oil of Agropyrum repens (Couchgrass). | | Definition | ChEBI: Capillene is a member of benzenes. | | Synthesis | Agropyrene can be produced synthetically via the ketone Capillin made from Benzaldehyde plus Pentadiyne, followed by oxidation. Also from Phenylacetaldehyde plus Methyl�ethylketone followed by dehydration. |
| | Agropyrene Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|