| | Fluopyram Basic information |
| Product Name: | Fluopyram | | Synonyms: | fluopyraM;N-[2-[3-Chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridinyl]ethyl]-2-trifluoromethylbenzamide;BenzaMide, N-[2-[3-chloro-5-(trifluoroMethyl)-2-pyridinyl]ethyl]-2-(trifluoroMethyl)-;N-{2-[3-Chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]ethyl}-α,α,α-trifluoro-o-toluamide;N-[2-[3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-yl]ethyl]-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide;Fluopyram Solution, 1000ppm;Fluopyram 96%;Fluopyram Solution | | CAS: | 658066-35-4 | | MF: | C16H11ClF6N2O | | MW: | 396.71 | | EINECS: | | | Product Categories: | | | Mol File: | 658066-35-4.mol | 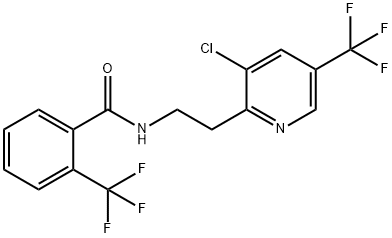 |
| | Fluopyram Chemical Properties |
| Hazard Codes | N | | Risk Statements | 50/53 | | RIDADR | UN 3077 9 / PGIII |
| | Fluopyram Usage And Synthesis |
| Uses | Fluopyram is a succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor (SDHI) used as a fungicide. It is also useful in cannabis testing kits as a component of pesticide mixes . | | Definition | ChEBI: A member of the class of benzamides, obtained by formal condensation of the carboxy group of 2-(trifluoromethyl)benzoic acid with the amino group of 2-[3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-yl]ethylamine. A fungicide used for foiliar application and as a s
ed treatment in order to control botrystis, powdery mildew and other diseases. | | Agricultural Uses | Initially, fluopyram was discovered by employing an “agrophore” chemical synthesis approach, which involves the combination of fragments present in already known active ingredients, the aim being to obtain molecules with an increased likelihood of biological activity. In the case of fungicides, this might mean targeting a log P of between 2.5 and 4.5 (C. Cornell, Aventis CropScience, unpublished results). the 3‐chloro‐5‐trifluoromethyl‐ 2‐pyridinyl residue was known to be present in a range of known agrochemicals that included fluopicolide (2; Infinito®), (3; Froncide®) (fungicides), haloxyfop‐P‐methyl (4; Eloge®) (herbicide), and the benzoyl phenyl urea, fluazuron (5; Acatak®, an insecticide used in animal health).
In the case of fluopyram, a second agrophoric element – an ortho‐substituted benzamide residue as found in benodanil (6, ortho‐I atom), mepronil (7, ortho‐CH3 group), or flutolanil (8, ortho‐CF3 group) – was incorporated from the classical SDH‐inhibitor structures.
It is remarkable that the relatively minor changes of lengthening the linker between the 3‐chloro‐5‐trifluoromethyl‐2‐pyridinyl residue and the carboxylic amide part of fluopicolide by one methylene unit (CH2 → CH2CH2), and changing the phenyl substitution pattern from ortho–ortho′ substitution (R1 and R2) to a single ortho substitution (R1), would result in a complete shift of the biological spectrum and mode of action (MoA).
Fluopicolide shows an excellent anti‐oomycete activity, whereas fluopyram has an outstanding activity against ascomycete pathogens, without demonstrating activity against oomycete diseases.
Thus, employing the agrophore approach led to the discovery of the pyridylethyl benzamides, the first nonaniline carboxamide derivatives. |
| | Fluopyram Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|