| Company Name: |
Enzo Biochem Inc
|
| Tel: |
Enzo Biochem Inc. |
| Email: |
Enzoname@qq.com |
| Products Intro: |
Product Name:Nerve growth factor 7S (mouse)
|
| Company Name: |
Merck KGaA
|
| Tel: |
(+86) 21 2033 8288 |
| Email: |
sigmaname@qq.com |
| Products Intro: |
Product Name:ANTI-NGFB (CENTER) antibody produced in rabbit
|
|
| | 7S-NERVE GROWTH FACTOR, MOUSE Chemical Properties |
| storage temp. | −20°C | | form | lyophilized powder | | color | white to off-white | | biological source | rabbit |
| | 7S-NERVE GROWTH FACTOR, MOUSE Usage And Synthesis |
| Discovery | NGF is the first member of neurotrophins. In the first
half of the 20th century, it had been experimentally demonstrated in embryos that the nonneuronal “periphery” is
essential for the differentiation of the sensory and motor
centers of the central nervous system and the sensory
ganglia. By 1951, Rita Levi-Montalcini and Viktor
Hamburger discovered that certain mouse tumors release
a “substance” that induces nerve fibers to grow in a chick
embryo. With Stanley Cohen, they isolated “nerve
growth-stimulating factor,” a preparation containing
both protein and nucleic acid. Subsequently, “nerve
growth factor” was purified from snake venom and
mouse salivary glands, and identified as a protein. Its
complete amino acid sequence was determined in 1971. | | Structure | NGF consists of three types of subunits, α, β, and γ,
which specifically interact to form a 7S, 130-kDa complex.
The 7S complex contains two identical β-subunits.
Among the three types of subunits, β-subunit only has
bioactivity and therefore is referred to as NGF. The
human NGF gene (β-subunit, β-NGF) encodes a preproprotein of 241 aa residues (preproNGF) . After
cleavage by the protease activity of the γ-subunit, a 120-aa
peptide of NGF (β-subunit), which has biological activity,
is generated. The β-subunit dimerizes through noncovalent interaction, and presents as a 2.5S, 26-kDa protein. NGF has been identified in mammals, birds, reptiles,
amphibians, and teleosts. Six cysteines
involved in the intramolecular disulfide bond are conserved among all vertebrate NGFs.
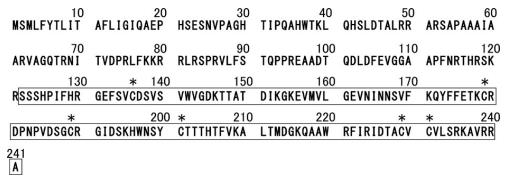 | | Properties | Mr. 26,518 (mouse preproNGF); 13,259 (mouse mature
NGF). pI 9.3. NGF is soluble in water. Disulfide bridges
are formed between Cys15 and Cys80, between Cys58
and Cys108, and between Cys68 and Cys110 (in mammalian mature NGFs). | | Gene, mRNA, and precursor | The human preproNGF (β-NGF) gene, NGF, location
1p13.2, consists of three exons. Human NGF mRNA
has 1061 bases that encode a preproNGF of 241 aa
residues. ProNGF shows broad expression in the ovary (RPKM
1.3), the heart (RPKM 0.5), and 18 other tissues, including
the brain. | | Synthesis and release | The expression of the NGF gene is regulated by the
developmental stage, neuronal innervation, and neuronal activity. NGF mRNA levels are increased during postnatal development in the rat hippocampus and basal
ganglia. Both continuous release and neuronal
activity-dependent release are reported. The release from
cultured hippocampal neurons is enhanced more than
three-fold within several minutes by a depolarizing
stimulus. | | Receptors | NGF binds to at least two classes of receptors: tropomyosin receptor kinase A (TrkA), the high-affinity receptor, and p75NTR, the low affinity receptor.
Both TrkA and p75NTR are single-transmembrane receptors. The human NTRK1 gene encodes TrkA (Trk1) of 790
aa residues. The human NGFR gene encodes p75NTR of
427 aa residues. TrkA has a tyrosine-kinase domain in the
cytoplasmic region. p75NTR has no tyrosine-kinase
domain. The binding activity of mature NGF:
Kd=10 pM (TrkA) and 1 nM (p75NTR). ProNGF also
binds to p75NTR (Kd: 100 pM) and TrkA (Kd: 1 nM). | | Biological functions | Both TrkA and p75NTR are expressed in sensory neurons, sympathetic neurons, and cholinergic neurons. The
activation of TrkA induces the survival of these neurons,
promotes outgrowth of the neurite, and stimulates the
synthesis of neurotransmitters. The involvement of
p75NTR in apoptosis is observed in the avian retina,
mouse basal forebrain, and rat cerebral cortex. p75NTR-mediated apoptosis of the rat oligodendrocytes
is induced specifically by NGF but not by other
neurotrophins. | | Description | NGF is the first member of the neurotrophin-family trophic
factors. NGF regulates the growth, maintenance, proliferation, and survival of certain target neurons through activation of the high affinity receptor, tropomyosin receptor
kinase A (TrkA). NGF is also involved in apoptosis through
binding to the low affinity receptor, p75NTR. NGF consists
of three types of subunits, α, β, and γ, and the β-subunit is
solely responsible for the nerve growth stimulating activity of
NGF. | | Clinical Use | NGF is now known to have therapeutic potential on
peripheral and central nervous system diseases but also
on the visual system, cutaneous wound healing, and
the regulation of immune system functions. NGF shows protective effects on cholinergic neurons
in the brains of Alzheimer’s disease model animals. NGF also shows promoting effects on neurite outgrowth
in the aged human and rat. |
| | 7S-NERVE GROWTH FACTOR, MOUSE Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|