| | Perfiuoroisobutylene Basic information |
| Product Name: | Perfiuoroisobutylene | | Synonyms: | Octafiuoroisobutylene;Perfiuoroisobutylene;Octafluoroisobutylene;PERFLUORISOBUTYLENE;Perfluor-2-methylprop-1-ene;2-(Trifluoromethyl)-1,1,3,3,3-pentafluoro-1-propene;2-Trifluoromethyl-1,1,3,3,3-pentafluoro-1-propene;Octafluoroisobutene, in Nitrogen | | CAS: | 382-21-8 | | MF: | C4F8 | | MW: | 200.03 | | EINECS: | | | Product Categories: | | | Mol File: | 382-21-8.mol | 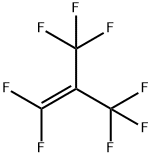 |
| | Perfiuoroisobutylene Chemical Properties |
| | Perfiuoroisobutylene Usage And Synthesis |
| Description | Perfluoroisobutylene (PFIB) is a schedule 2A substance under
the Chemical Weapons Convention, which means that while it
has significant ability to be used as a chemical weapon, it also
serves various other industrial uses. | | Uses | Perfluoroisobutylene or perfluoroisobutene is a monomer used
in synthesis of Teflon and other polymeric materials. It is also
used in etching for semiconductor fabrication, and is potentially
used as a chemical warfare agent. The US Food and Drug
Administration’s CFR 21 Section 173.360 allows for use of
octafluorocyclobutane as a propellant and also allows for PFIB
at a level of <.01% as an impurity in formulation. | | Synthesis Reference(s) | Journal of the American Chemical Society, 75, p. 2698, 1953 DOI: 10.1021/ja01107a044 | | Safety Profile | A deadly poison by inhalation. Askin, eye, and mucous membrane irritant. Human acuteexposure causes marked irritation of conjunctivae, throat,and lungs. When heated to decompos | | Environmental Fate | PFIB exists as a gas in the atmosphere, and is degraded by
reaction with hydroxyl radicals, with a reaction half-life
of ~5.7 days. PFIB is not susceptible to significant photolysis.
The Henry’s law constant of PFIB suggests volatization as
an important fate process. The half lives for volatization
calculated from a model lake and river were 5.6 days and
4.1 h, respectively, though a small portion will adsorb to
suspended solids and sediment. PFIB can also volatize
substantially from moist soils, and to a small degree from dry
soils. | | Toxicity evaluation | PFIB is a strong electrophile that reacts with nucleophiles. The
toxicity of PFIB may be correlated with its susceptibility to
nucleophilic attack and the generation of reactive
intermediates. |
| | Perfiuoroisobutylene Preparation Products And Raw materials |
| Raw materials | Propane, 1,1,1,2,3,3,3-heptafluoro-2-isocyanato--->Propane, 1,2-dichloro-1,1,3,3,3-pentafluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)--->Propane, 1,1,1,2,2,3,3-heptafluoro-3-isocyanato--->PERFLUORO-TERT-BUTYL IODIDE-->Octafluorocyclobutane-->DIBROMODIFLUOROMETHANE | | Preparation Products | Tetrafluoroethylene |
|