| Company Name: |
Elabscience
|
| Tel: |
15608650971 |
| Email: |
13163253676@qq.com |
| Products Intro: |
Product Name:Rat IGF-1 (Insulin-like Growth Factor 1) ELISA Kit;Rat IGF-1;Insulin-like Growth Factor 1
Purity:99% Package:48T
|
| Company Name: |
SUPPLEMENT FITNESS
|
| Tel: |
08069023910Ext 773 |
| Email: |
|
| Products Intro: |
Product Name:Insulin Like Growth Factor 1
|
|
| | INSULIN-LIKEGROWTHFACTOR-1 Chemical Properties |
| | INSULIN-LIKEGROWTHFACTOR-1 Usage And Synthesis |
| Discovery | In 1957, a “sulfation factor” that mediates the action of
growth hormone (GH) on the incorporation of 35S sulfate
into a cartilage segment was discovered in rats, and
named somatomedin, now known as IGF-1. IGF-1 was
also identified in 1963 as nonsuppressible insulin-like
activity soluble in acid/ethanol (NSILA-S). In 1978,
IGF-1 was isolated from the Cohn fraction of plasma proteins together with IGF-2. | | Structure | IGF-1 is a single-chain polypeptide sharing high structural homology with proinsulin (about 50%) and IGF-2
(about 70%) .1 Three disulfide bonds that are
involved in the structural maintenance of the insulin family
peptides are conserved. PreproIGF-1 is composed of a signal peptide and five domains; B, C, A, D, and E.
The E domain is proteolytically cleaved before secretion. The aa sequence of IGF-1 is highly conserved in vertebrates. Mr ~7500, pI 8.5. Lyophilized peptide should be
reconstituted in 10mM HCl. Lyophilized peptide can
be stored at 2–4°C for at least 2 years.
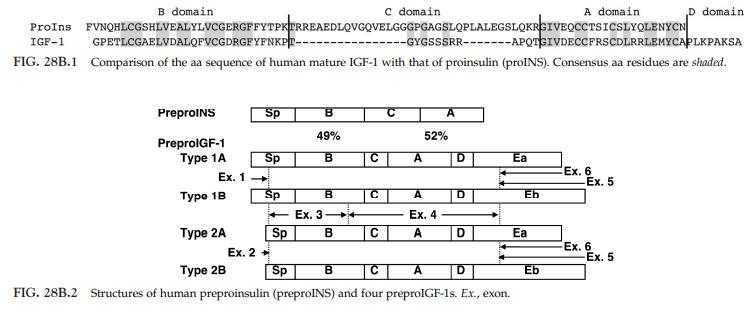 | | Gene, mRNA, and precursor | The human IGF-1 gene, IGF1, location 12q23.2, consists of six exons. There are six major transcript variants that differ in promoter use, RNA splicing, and
mRNA polyadenylation. These IGF-1
mRNAs are classified based on a combination of differential promoter use (Type 1 or 2) and alternative splicing of
exons encoding the E domain (Ea, Eb, and Ec). However,
all transcripts resulted in the same mature protein of 70 aa
residues. The organization of IGF-1 genes is substantially different among vertebrates; up to 11 exons are
found in Australian marsupials whereas 4–8 exons are
recognized in nonmammalian vertebrates. Two nonallelic genes for igf1 have been identified in the Xenopus,
zebrafish, and salmon. In the zebrafish and tilapia, a
gonad-specific igf3 (or igf1b) has been identified. Viruses
such as the family Iridoviridae express viral insulin/IGF-1-
like peptides (VILPs). VILPs are capable of activating
insulin and IGF-1 receptor signaling and may play a role
in disease. | | Synthesis and release | Mammalian IGF-1 genes have two promoters (P1 and
P2) that lack TATA and CAAT elements. P1 is the
potent major promoter, and is conserved widely in vertebrates. The proximate promoter region of the IGF-1 gene
contains binding sites for liver-enriched transcription
factors such as HNF-1α, C/EBPα, and C/EBPβ. GH is
the primary hormone regulating the synthesis and release
of IGF-1 in the liver after birth. The action of GH is mediated chiefly by the JAK2/Stat5b pathway. Several
GH-inducible Stat5b binding sites have been found in introns and distal regions of the Igf1 loci. However, such
GH-inducible Stat5b binding sites are absent in nonmammalian vertebrates and thus other regulatory pathways
by which GH stimulates the transcription of igf1 are
assumed. IGF-1 gene expression is also regulated at
the transcription level by other hormones such as insulin,
cortisol, and sex steroids, and by the developmental stage
independently of GH action. Nutritional status regulates
IGF-1 mRNA at the posttranscriptional level by affecting
mRNA processing and stability. | | Receptors | The receptor of IGF-1 (type 1 IGF receptor, IGF-1R)
belongs to a family of the receptor tyrosine kinase
(RTK) containing a single transmembrane domain, and
shares high sequence homology (60%) with the insulin
receptor. The human IGF-1R gene, IGF1R, location15q26.3, consists of 21 exons encoding an extracellular α-subunit (706 aa residues), which contains a ligand
binding domain, and a transmembrane β-subunit (627
aa residues), which contains tyrosine kinase activity. The α- and β-subunits are synthesized as a single-chain prepropeptide and cleaved
after translation, then bridged by a disulfide bond to form
the IGF-1 half-receptor (αβ). Two half-receptors dimerize
to form a functional IGF-1R (α2β2). The IGF-1 half�receptor can also form a hybrid receptor with the insulin
half-receptor to bind mainly IGF-1. Teleosts have two paralogs of igf1r. | | Agonists and Antagonists | IGF-2, insulin, Des IGF-1, Long R3 IGF-1, LL-37,
hypoxia, and Akt-induced stem cell factor (HASF) are
agonists. IGFBPs, JB1, and JB3 (12-aa synthetic peptides), and
M1557 (D domain analog) are antagonists. | | Biological functions | IGF-1 acts on most tissues, but the liver is not a major
target. IGF-1 is involved in growth and metabolism at the
organismal level, and in cell proliferation, migration, differentiation, and survival at the cellular level. IGF-1
inhibits apoptosis. An important role of circulating
IGF-1 is to regulate GH synthesis/secretion at the pituitary and hypothalamus through a negative feedback
loop. | | Clinical implications | IGF-1 deficiency is related to Laron syndrome (short
stature due to GH resistance or insensitivity), liver cirrhosis, and age-related cardiovascular and neurological diseases. Epidemiologic studies suggest relationships
between IGF-1 and cancer risks such as prostate, colon,
and breast cancers. | | Description | IGF-1 is a multifunctional polypeptide structurally
related to proinsulin. IGF-1 promotes cell proliferation,
differentiation, growth, migration, and survival through
autocrine/paracrine and endocrine pathways. It mediates
part of growth hormone actions and is essential for normal
prenatal and postnatal growth. | | Clinical Use | IGF-1 levels are routinely used for diagnosis in
patients with suspected acromegaly or GH/IGF-1 deficiency. The US Food and Drug Administration approved
recombinant human IGF-1 for the treatment of patients
with severe primary IGF-1 deficiency. Due to its antiapoptotic and proliferative actions, the IGF-1 axis confers
tumor cell resistance to anticancer therapy. Thus, inhibition of the IGF-1 signaling using monoclonal antibodies
against IGF-1 and IGF-1R and tyrosine kinase inhibitors
is a potential therapy for cancers. However, the overexpression or dysregulation of the IGF-1 axis is not the
driver but rather secondary to another molecular event
in tumorigenesis. Combining IGF-targeted agents with
other agents may be a more effective therapeutic
approach. |
| | INSULIN-LIKEGROWTHFACTOR-1 Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|