|
|
| | POLY(1,4-PHENYLENE SULFIDE) Basic information |
| Product Name: | POLY(1,4-PHENYLENE SULFIDE) | | Synonyms: | 3-[3-(1,1-BISHEXYLOXYETHYL)PYRIDIN-1-YL]PROPANE-1-SULFONATE;6-PPS;p-dichlorobenzene/ sodium sulfide copolymer;1,4-dichloro-benzenpolymerwithsodiumsulfide(na2s);Benzene,1,4-dichloro-,polymerwithsodiumsulfide;Poly(phenyleneaulgide);POLY(1,4-PHENYLENE SULFIDE);POLY(PHENYLENE SULPHIDE) | | CAS: | 26125-40-6 | | MF: | (C6H4Cl2.Na2S)x | | MW: | 225.05 | | EINECS: | 607-869-0 | | Product Categories: | Polymers | | Mol File: | 26125-40-6.mol | 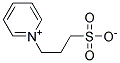 |
| | POLY(1,4-PHENYLENE SULFIDE) Chemical Properties |
| | POLY(1,4-PHENYLENE SULFIDE) Usage And Synthesis |
| Chemical Properties | Poly(phenylene sulphide) is a strong, stiff although somewhat brittle
material. Mouldings are generally processed so as to be crystalline; since the
glass-transition temperature is high (Tg = 90°C), heated moulds are used. The
outstanding characteristic of the polymer is its thermal stability, useful
mechanical properties being retained up to about 250°C. Electrical insulation
characteristics are also good. The polymer has excellent solvent resistance,
being unaffected by all common organic solvents. The polymer is resistant to most acids and alkalis, although it is attacked by concentrated sulphuric acid.
Poly(phenylene sulphide) is mostly processed by injection moulding and is
used in a variety of applications such as electrical components, automotive
parts and processing equipment exposed to corrosive environments. | | Uses | PPS can be sulfonated to form a proton exchange membrane with zeolite th at can be used as an electrolyte with higher thermal stability which facilitates in the fabrication of solar cells. It can also be used in the formation of organic- inorganic nanocomposite membranes using nanozeolites and carbon nanotubes as nanofillers which can be used as high performance gas separation membranes. PPS may be sulfonated and chloromethylated to form novel PPS fiber with higher dyeing ability in dispersive, anionic and cationic dyes. | | Preparation | Poly(p-phenylene sulphide) (commonly called poly(phenylene sulphide) or
PPS) is the sulphur analogue of poly(p-phenylene oxide) and is prepared from
p-dichloroben:lene and sodium sulphide:

|
| | POLY(1,4-PHENYLENE SULFIDE) Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|