| | Bupropion Basic information |
| Product Name: | Bupropion | | Synonyms: | m-chloro-a-(tert-butylamino)propiophenone;Bupropion;BUPROPION/AMFEBUTAMONE;Wellbatrin:Wellbutrin;rac-(R*)-1-(3-Chlorophenyl)-2-(tert-butylamino)-1-propanone;Buproprion thioMorpholine carboxylic acid;Bupropion controlled release;1-Propanone,1-(3-chlorophenyl)-2-[(1,1-diMethylethyl)aMino]- | | CAS: | 34911-55-2 | | MF: | C13H18ClNO | | MW: | 239.74 | | EINECS: | | | Product Categories: | Isotope;APIs;BDO | | Mol File: | 34911-55-2.mol | 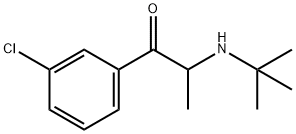 |
| | Bupropion Chemical Properties |
| | Bupropion Usage And Synthesis |
| Description | Bupropion hydrochloride, an aminoketone structurally unrelated to tricyclics or
tetracyclics, is a dopamine uptake blocker with antidepressant activity. Its clinical
efficacy is reportedly comparable to that of amitriptyline, yet unlike most conventional
antidepressants, bupropion hydrochloride is not associated with orthostatic hypotension or
other cardiovascular side-effects. | | Originator | Burroughs Wellcome (United Kingdom) | | Uses | vasoconstrictor;non-selective agonist of all adrenergic receptors | | Uses | Bupropion Hydrochloride used in methods of treating sleep disorders associated with pain. | | Definition | ChEBI: Bupropion is an aromatic ketone that is propiophenone carrying a tert-butylamino group at position 2 and a chloro substituent at position 3 on the phenyl ring. It has a role as an antidepressant, an environmental contaminant and a xenobiotic. It is a secondary amino compound, a member of monochlorobenzenes and an aromatic ketone. | | Manufacturing Process | To ethyl magnesium bromide (2 L, 3 M) was added over 45 min with stirring
and cooling m-chlorobenzonitrile (688.0 g, 5 mole) in ether (2.5 L). The
resultant solution was heated under gentle reflux for 5 h. The reaction mixture
was hydrolyzed with cold dilute hydrochloric acid, the ether was distilled off,
and the aqueous solution was heated at 90°C for 1 h. The flask was then
cooled. The solid ketone that separated was washed with cold water and
recrystallized from methanol. The recrystallized m-chloropropiophenone,
melting point 39°-40°C, weighed 750.0 g.
In methylene chloride (3 L) was dissolved m-chloropropiophenone (698.0 g;
4.15 mole). The solution was stirred with charcoal (Darco) and magnesium
sulfate for 2 h and filtered. To it was added with stirring (662.0 g) of bromine
in methylene chloride (1 L). When the bromine color had faded completely,
the solvent was evaporated in vacuum and m-chloro-α-bromopropiophenone
was obtained as oil.
The m-chloro-α-bromopropiophenone was dissolved in acetonitrile (1300 ml).
To this, t-butylamine (733.0 g) in acetonitrile (1300 ml) was added while
keeping the temperature below 32°C. The reaction mixture was allowed to
stand over night. It was then partitioned between water (4200 ml) and ether
(2700 ml). The aqueous layer was extracted with a further portion of ether
(1300 ml). The combined ethereal layers were then washed with water (4200
ml) to which hydrochloric acid was added until the pH of the aqueous layer
was 9. The aqueous layer was separated and washed with ether (500 ml) and
then discarded. The combined ethereal layers were then stirred with ice
(560.0 g) and concentrated hydrochloric acid (324 ml). The ethereal layer was
separated and again washed with water (200 ml) and concentrated
hydrochloric acid (50 ml). These last two acid layers were combined and
concentrated in vacuum until crystals appeared. The solution was then chilled
to 5°C and filtered. The product was sucked dry, washed with acetone and
recrystallized from a mixture of isopropanol (3 L) and absolute ethanol (800
ml). The DL-m-chloro-α-t-butylaminopropiophenone hydrochloride so was
obtained, melting point 233°-234°C.
The DL-m-chloro-α-t-butylaminopropiophenone was obtained by treatment of
DL-m-chloro-α-t-butylaminopropiophenone hydrochloride with sodium
hydroxide. | | Brand name | Wellbutrin (GlaxoSmithKline); Zyban
(GlaxoSmithKline). | | Therapeutic Function | Antidepressant; Smoking cessation aid | | Biological Functions | Bupropion (Wellbutrin) is a pharmacologically unique
antidepressant, since it is a weak inhibitor of both dopamine
and norepinephrine neuronal reuptake. However,
its actual antidepressant activity is not well understood.
Bupropion is generally well tolerated and does
not block muscarinic, histaminergic, or adrenergic receptors.
Unlike the SSRIs and venlafaxine, bupropion
does not cause sexual side effects. However, it can cause
CNS stimulation, including restlessness and insomnia.
High doses of bupropion, given as its original formulation,
were associated with a risk of seizures in 0.4% of
patients. However, this risk is lower with slow-release
bupropion (Wellbutrin SR). This formulation still requires
dosing twice a day, and bupropion is contraindicated
in patients with a history of seizures. Bupropion
inhibits the cytochrome P450 2D6 isoenzyme and may
elevate blood levels of drugs metabolized by this route. | | General Description | The mechanism of action of bupropion (Wellbutrin) is consideredcomplex and reportedly involves a block of DA reuptakevia the dopamine transporter (DAT), but the overallantidepressant action is noradrenergic. A metabolite thatcontributes to the overall action and its formation can beeasily rationalized. Oxidation of one of the methyl groupson the t-butyl substituent yields hydroxybupropion, an activemetabolite. Reduction of the keto group also occurs,yielding threohydrobupropion and erythrohydrobupropion.Both of these metabolites are also active.
Hydroxybupropion is half as potent as the parent bupropion,and the hydrobupropion isomers are five times less potent.The presence of these metabolites, especially hydroxybupropionwhich is formed by cytochrome P450 2D6(CYP2D6), suggests that there will be a myriad of drug interactionswith bupropion. | | Pharmacology | Bupropion is an α-aminoketone that is structurally related to amphetamines, and it exhibits
unique activity comparable to that of other antidepressants. It is believed that bupropion
restores the total amount of norepinephrine in the body. This compound is a poor reuptake
inhibitor of dopamine, and does not exhibit anticholinergic activity or inhibit MAO. Its
efficacy as an antidepressant is comparable to that of tricyclic antidepressants, and as a
serotonin uptake inhibitor it is comparable to fluoxetine. | | Synthesis | The synthesis of bupropion, 1-3(-chlorophenyl)-2-[(1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]-
1-propanone (7.3.5), begins with the reaction of 3-chlorobenzonitrile, with ethylmagnesium
bromide to give 3-chloropropiophenone (7.3.3). Brominating this with bromine gives
3-chloro-|á-bromopropiophenone (7.3.4), which on reaction with tert-butylamine gives bupro�pion (7.3.5) [54¨C58]. 
|
| | Bupropion Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|