|
ChemicalBook Optimization Suppliers |
| 名前: |
Sigma-Aldrich |
| 電話番号: |
021-61415566 800-8193336 |
| 電子メール: |
orderCN@merckgroup.com |
|
| 化学名: | ABS樹脂 | | 英語化学名: | ABS Resins | | 别名: | abscopolymer;absresin;absresins;acrylonitrile,polymerwith1,3-butadieneandstyrene;3DXMAX(TM) CFR-ABS carbon fiber reinforced ABS 3D printing filament black, diam. 1.75 mm;3DXMAX(TM) CFR-ABS carbon fiber reinforced ABS 3D printing filament black, diam. 2.85 mm;3DXNANO(TM) ESD CNT-ABS carbon nanotube reinforced ABS 3D printing filament black, diam. 1.75 mm;3DXNANO(TM) ESD CNT-ABS carbon nanotube reinforced ABS 3D printing filament black, diam. 2.85 mm | | CAS番号: | 9003-56-9 | | 分子式: | C45H51N3X2 | | 分子量: | 633.91 | | EINECS: | 618-371-8 | | カテゴリ情報: | Acrylonitrile Polymers and Copolymers;Acrylics;Hydrophobic Polymers;Polymers | | Mol File: | 9003-56-9.mol | 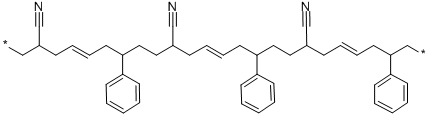 |
| 融点 | 58.54(±0.5)℃ | | 比重(密度) | 1.05 g/mL at 25 °C | | 溶解性 | acetone, MEK and DMF: soluble | | 外見 | powder | | 色 | natural | | SMILES | C(C/C=C/CC(C#N)CCC(C/C=C/CC(C*)C#N)C1=CC=CC=C1)(CCC(C#N)C/C=C/CC(C*)C1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 |$;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;*;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;*;;;;;;;;;;;;$| | | EPAの化学物質情報 | Acrylonitrile 1,3-butadiene styrene polymer (9003-56-9) |
| | ABS樹脂 Usage And Synthesis |
| 解説 | ABS樹脂,アクリロニトリル,ブタジエン,スチレンを重合させてつくられる樹脂で,それぞれのモノマーの頭文字をとってABS樹脂と呼ばれる。ポリスチレンの耐衝撃性を改善するために開発された樹脂であり,当初,アクリロニトリルとスチレンの共重合樹脂(AS樹脂)にアクリロニトリル・ブタジエンゴム(NBR)をブレンドしてつくられたが,最近では,NBRにアクリロニトリル,スチレンをグラフト重合したABS樹脂とか,そのグラフト樹脂とAS樹脂とのブレンド樹脂も製造されている。
株式会社平凡社 世界大百科事典 第2版について | | 用途 | ABS樹脂,金属に代わる耐衝撃性をもつ合成樹脂とされる、耐熱性、耐薬品性、耐低温性にも優れ、電気部品や自動車部品として用いられる. | | 化学的特性 | As has already been mentioned, the range of possible ABS polymers is very
large since both the ratio of the three monomers and the manner in which
they are assembled in the final product can be varied considerably. Thus
commercial ABS polymers are available with appreciable differences in
properties, but they are generally characterized by high impact strengths and
softening points as high as, or higher than, straight polystyrene.
The ABS polymers prepared by grafting contain varying amounts of
ungrafted polybutadiene (which has a low glass transition temperature) and
therefore have good low-temperature impact strength. Also, the ABS polymers prepared by grafting are superior to those obtained by blending in that
moulded specimens commonly have a better surface appearance.
In recent years, special grades of ABS polymers have been produced in
which a fourth monomer is present. For example, heat-resistant grades
contain a-methylstyrene and transparent grades incorporate
methyl methacrylate.
ABS polymers can be injection moulded and extruded and have been used
in a great variety of applications which require toughness, rigidity and good
appearance, e.g. automobile fascia panels and radiator grilles, household
appliances, business machines, telephones and pipe and pipe fittings. | | 化学的特性 |
white to off-white powder
| | 使用 | Typical Applications Include:
- Semi-con: HDD Components; Wafer Handling; Jigs;Casings; & Connectors
- Industiral: Converying;Metering; and Sensing applications
| | 調製方法 | acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene resins are commonly referred to as ABS resins. These materials are thermoplastic resins that are produced by grafting styrene and acrylonitrile onto a diene-rubber backbone. The usually preferred substrate is polybutadiene because of its low glasstransition temperature (just above ?80 °C). Where ABS resin is prepared by suspension or mass polymerization methods, stereospecific diene rubber made by solution polymerization is the preferred diene. Otherwise the diene used normally is a high-gel or cross-linked latex made by a “hot-emulsion” process. | | 製造方法 | Two basic processes are used commercially to prepare ABS polymers, namely
blending and grafting. These processes give rise to materials which are rather
different to each other. Of the two processes, grafting is now the more
important.
(a) Blending
The products obtained by this method are mechanical blends of styrene�acrylonitrile copolymers and acrylonitrile-butadiene rubbers. The preferred
method of preparation is by blending latices of the two copolymers and
coagulating the mixture. A wide range of products is possible, depending on
the composition of each copolymer and the relative amounts of each employed. A typical blend would consist of the following (solids):
70 parts of styrene-acrylonitrile copolymer (70: 30)
40 parts of acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber (35: 65)
It has been found that non-cross-linked acrylonitrile-butadiene rubbers are
compatible with styrene-acrylonitrile copolymers and the mixtures show
little improvement in impact strength and have low softening points. However, if the rubber is sufficiently cross-linked so as to be not completely
soluble in the copolymer then the mixtures have high impact strengths and
high softening points. A convenient method of preparing a suitably crosslinked acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber is to take an emulsion polymerization
to high conversion; alternatively, a small amount of divinylbenzene can be
added to the emulsion recipe. After the two latices have been mixed, coagulation is brought about by the addition of either an acid or a salt. The
resulting crumb is washed, filtered, dried, extruded and chopped into granules.
An alternative method of preparing a blend of the two copolymers is by
mixing the solids on a two-roll mill. In this case, a non-cross-linked acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber may be used as starting material. The rubber is
firstly cross-linked by milling with a peroxide and then the styrene-acrylonitrile copolymer is added.
The physical nature of these blends does not appear to be the same as that
of rubber-modified polystyrenes. When this type of ABS polymer is treated
with a solvent such as methyl ethyl ketone the sample swells and only
partially breaks up; this indicates that rubber networks permeate the styrene�acrylonitrile copolymer matrix. When rubber-modified polystyrenes are treated with a solvent such as toluene, complete disintegration into fine particles
occurs.
(b) Grafting
In this method of preparing ABS polymers, acrylonitrile and styrene are
polymerized in the presence of a polybutadiene latex. A wide range of
products is possible, depending on the relative quantities of reactants.
The reaction is carried out at about 50°C. The solid product is then isolated
from the latex.
ABS polymers prepared in this way consist of a continuous matrix of
styrene-acrylonitrile copolymer, dispersed particles of polybutadiene and a
boundary layer of poly butadiene grafted with acrylonitrile and styrene. | | 一般的な説明 | 3DXTech? ABS is made in the USA using 100% virgin resin and colorants - precision extruded onto 1kg reels (2.2 lbs.). The filament is then vacuum-sealed with desiccant to protect it from moisture. | | Advantages | ABS Resins is a strong and durable polymer. It is a chemically resistant resin. It gets easily attacked by polar solvents. It offers greater impact properties and slightly higher heat distortion temperature than HIPS.
It has a low melting temperature making it suitable for processing by 3D printing on an FDM machine.
ABS shows excellent mechanical properties. It is hard and tough in nature and thus delivers good impact strength. It offers a high degree of surface quality. Apart from these characteristics, Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene exhibits good electrical insulating properties.
It is an ideal material of choice for various structural applications. This is because of its several physical properties such as:
High rigidity, good weldability, and insulating properties; Good impact resistance, even at low temperatures; Good abrasion and strain resistance; High dimensional stability (Mechanically strong and stable over time); High surface brightness and excellent surface aspect |
|