|
ChemicalBook Optimization Suppliers |
|
| 化学名: | クロロブタノール | | 英語化学名: | Chlorobutanol | | 别名: | 2-TRICHLOROMETHYL-2-PROPANOL;2-METHYL-1,1,1-TRICHLORO-2-PROPANOL;BETA,BETA,BETA-TRICHLORO-TERT-BUTYL ALCOHOL;ACETONE CHLOROFORM;2-Trichhloromethyl-2-propanol;Acetone chloroform~Chloretone~Chlorobutanol~1-Methyl-1-(trichloromethyl)ethanol~1,1,1-Trichloro-2-methyl-2-propanol;ACETONE CHLOROFORM HEMIHYDRATE DAB, PH. EUR., B.P., N. F., PH. FRANC.;CHLORBUTOLANHYDROUS | | CAS番号: | 57-15-8 | | 分子式: | C4H7Cl3O | | 分子量: | 177.46 | | EINECS: | 200-317-6 | | カテゴリ情報: | CHLORETONE;Organics | | Mol File: | 57-15-8.mol | 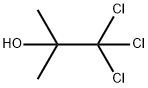 |
| | クロロブタノール Usage And Synthesis |
| 外観 | 本品は無色又は白色の結晶で,カンフルようのにおいが
ある.
本品はメタノール,エタノール(95)又はジエチルエーテル
に極めて溶けやすく,水に溶けにくい.
本品は空気中で徐々に揮散する. | | 定義 | 本品は、次の化学式で表されるハロゲン化アルコールである。 | | 化粧品の成分用途 | 防腐剤 | | 効能 | 局所麻酔薬, 催眠鎮静薬, 抗菌性保存剤 | | 確認試験 | (1) 本品の水溶液(1→200)5mLに水酸化ナトリウム試液
1mLを加え,ヨウ素試液3mLを徐々に加えるとき,黄色の
沈殿を生じ,ヨードホルムのにおいを発する.
(2) 本品0.1gに水酸化ナトリウム試液5mLを加えてよく
振り混ぜ,アニリン3~4滴を加え,穏やかに加温するとき,
フェニルイソシアニド(有毒)の不快なにおいを発する. | | 定量法 | 本品約0.1gを精密に量り,200mLの三角フラスコに
入れ,エタノール(95)10mLに溶かし,水酸化ナトリウム試
液10mLを加え,還流冷却器を付けて10分間煮沸する.冷後,
希硝酸40mL及び正確に0.1mol/L硝酸銀液25mLを加え,よ
く振り混ぜ,ニトロベンゼン3mLを加え,沈殿が固まるま
で激しく振り混ぜた後,過量の硝酸銀を0.1mol/Lチオシア
ン酸アンモニウム液で滴定〈2.50〉する(指示薬:硫酸アンモ
ニウム鉄(Ⅲ)試液2mL).同様の方法で空試験を行う. | | 純度試験 | (1) 酸 本品を粉末とし,その0.10gに水5mLを加えてよ
く振り混ぜるとき,液は中性である.
(2) 塩化物〈1.03〉 本品0.5gを希エタノール25mLに溶か
し,希硝酸6mL及び水を加えて50mLとする.これを検液と
し,試験を行う.比較液は0.01mol/L塩酸1.0mLに希エタノ
ール25mL , 希硝酸6mL 及び水を加えて50mL とする
(0.071%以下). | | 強熱残分 | 0.1%以下(1g). | | 化学的特性 | Volatile, colorless or white crystals with a musty, camphoraceous
odor. | | 化学的特性 | White or almost white, crystalline powder or colourless crystals, sublimes readily | | Originator | Chlorobutanol,Narchem | | 使用 | Chlorobutanol is used as a preservative and sedative. It has also been shown to exhibit antibacterial properties. | | 使用 | Plasticizer for cellulose esters and ethers,
preservative for biological fluids and solutions,
antimicrobial agent, anesthetic in dentistry. | | 定義 | ChEBI: Chlorobutanol is a tertiary alcohol. | | 調製方法 | Chlorobutanol is prepared by condensing acetone and chloroform
in the presence of solid potassium hydroxide. | | Manufacturing Process | 33 g (0.59 mol) of powdered potassium hydroxide was added in small
amounts to a solution of 50 g (0.86 mol) of acetone in 100 g (0.84 mol) of
chloroform to form a reaction mixture containing approximately 0.7 mol of
KOH per mol of chloroform. The mixture was chilled to a temperature below
0°C, thoroughly agitated, and than allowed to stand at temperature of about
0°C for 24 hours. The mixture was then filtered and the filtrate was distilled.
The fraction boiling within the range of 165-175°C was poured into an equal
amount of water to precipitate the 1,1,1-trichloro-tert-butyl alcohol. The
precipitated 1,1,1-trichloro-tert-butyl alcohol was filtered and recrystallized
from an ethanol-water mixture and air dried. The yield of 1,1,1-trichloro-tert�butyl alcohol was 6 g, that is, somewhat less than 4% of the theoretical yield
based on chloroform charged. When calculated on the basis of chloroform
consumed the yield was about 15%. | | Therapeutic Function | Hypnotic, Anesthetic, Antiseptic, Pharmaceutic aid,
Ophthalmologic | | Synthesis Reference(s) | Journal of the American Chemical Society, 70, p. 1189, 1948 DOI: 10.1021/ja01183a092 | | 危険性 | Action similar to chloral hydrate. Combustible. | | 応用例(製薬) | Chlorobutanol is primarily used in ophthalmic or parenteral dosage
forms as an antimicrobial preservative at concentrations up to 0.5%
w/v. It is commonly used as an antibacterial agent for
epinephrine solutions, posterior pituitary extract solutions, and
ophthalmic preparations intended for the treatment of miosis. It is
especially useful as an antibacterial agent in nonaqueous formulations.
Chlorobutanol is also used as a preservative in cosmetics ; as a plasticizer for cellulose esters and ethers; and has
been used therapeutically as a mild sedative and local analgesic in
dentistry. | | 生物活性 | In mammary epithelial cells, protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 6 (PTPN6) controls EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) signaling. It participates in the JAK/ST at (janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription) signaling pathway. PTPN6 regulates cytokine receptors like interleukin- 3 (IL-3) and erythropoietin. | | 安全性プロファイル | Poison by ingestion. A narcotic. A skin and eye irritant. Mutation data reported. See also CHLORAL HYDRATE, whch acts similarly. Dangerous; can react with oxidizing materials. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cl-. See also PHOSGENE. | | 安全性 | Chlorobutanol is widely used as a preservative in a number of
pharmaceutical formulations, particularly ophthalmic preparations.
Although animal studies have suggested that chlorobutanol
may be harmful to the eye, in practice the widespread use of
chlorobutanol as a preservative in ophthalmic preparations has
been associated with few reports of adverse reactions. A study of the
irritation potential of a local anesthetic on the murine cornea
indicated significant corneal surface damage in the presence of
0.5% w/v chlorobutanol, which may be related to the preservative’s
effective concentration. Reported adverse reactions to chlorobutanol
include: cardiovascular effects following intravenous
administration of heparin sodium injection preserved with chlorobutanol; neurological effects following administration of a
large dose of morphine infusion preserved with chlorobutanol;
and hypersensitivity reactions, although these are regarded as
rare.
The lethal human dose of chlorobutanol is estimated to be
50–500 mg/kg.
LD50 (dog, oral): 0.24 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, oral): 0.99 g/kg
LD50 (rabbit, oral): 0.21 g/kg | | 貯蔵 | Chlorobutanol is volatile and readily sublimes. In aqueous solution,
degradation to carbon monoxide, acetone and chloride ion is
catalyzed by hydroxide ions. Stability is good at pH 3 but becomes
progressively worse with increasing pH. The half-life at pH 7.5
for a chlorobutanol solution stored at 258℃ was determined to be
approximately 3 months. In a 0.5% w/v aqueous chlorobutanol
solution at room temperature, chlorobutanol is almost saturated
and may crystallize out of solution if the temperature is reduced.
Losses of chlorobutanol also occur owing to its volatility, with
appreciable amounts being lost during autoclaving; at pH 5 about
30% of chlorobutanol is lost. Porous containers result in losses
from solutions, and polyethylene containers result in rapid loss.
Losses of chlorobutanol during autoclaving in polyethylene
containers may be reduced by pre-autoclaving the containers in a
solution of chlorobutanol; the containers should then be used
immediately. There is also appreciable loss of chlorobutanol
through stoppers in parenteral vials.
The bulk material should be stored in an airtight container at a
temperature of 8–158℃. | | 不和合性 | Owing to problems associated with sorption, chlorobutanol is incompatible with plastic vials, rubber stoppers, bentonite, magnesium trisilicate, polyethylene, and polyhydroxyethylmethacrylate, which has been used in soft contact lenses. To a lesser extent, carboxymethylcellulose and polysorbate 80 reduce antimicrobial activity by sorption or complex formation. | | 毒物検査レベル | The ITSL for chlorobutanol has been changed from 0.04 μg/m3 to 0.1 μg/m3 based on an annual averaging time. | | 規制状況(Regulatory Status) | Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (IM, IV, and SC
injection; inhalations; nasal, otic, ophthalmic, and topical preparations).
Labeling must state ‘contains chlorobutanol up to 0.5%.’
Included in nonparenteral and parenteral medicines licensed in the
UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal
Ingredients.
In the UK, the maximum concentration of chlorobutanol
permitted for use in cosmetics, other than foams, is 0.5%. It is
not suitable for use in aerosols. |
|