Cabergoline: Pharmacology and Efficacy for Lactation Inhibition
Sep 23,2024
General Description
Cabergoline is an ergoline derivative primarily recognized for its role as a dopamine D2 agonist, effectively inhibiting prolactin secretion from lactotroph cells in the anterior pituitary gland. Its pharmacokinetics show rapid absorption, moderate plasma protein binding, and a long elimination half-life, facilitating less frequent dosing. Clinical studies demonstrate that cabergoline is effective for lactation inhibition, with comparative trials indicating its non-inferiority to bromocriptine. Real-world applications reveal its use among women facing specific medical circumstances. Overall, cabergoline offers a safe and effective option for managing lactation suppression in postpartum women across various clinical scenarios.

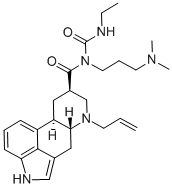
Figure 1. Cabergoline
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Cabergoline is primarily recognized as an ergoline derivative acting as a dopamine D2 agonist, specifically targeting lactotroph cells in the anterior pituitary gland. In the context of prolactin secretion, cabergoline works by binding to dopamine D2-type receptors, leading to a reduction in both the synthesis and release of prolactin. This mechanism is crucial because prolactin is integral to lactation and reproductive health. Unlike other dopaminergic medications, cabergoline boasts a higher affinity for dopamine D2 receptors compared to non-dopaminergic receptors. Clinical studies indicate that doses of cabergoline as low as 0.2 mg can effectively inhibit prolactin, while doses of 0.5 mg or higher typically deliver maximal suppression. The efficacy of cabergoline in reducing prolactin levels has made it a preferred choice for treating conditions linked to hyperprolactinemia, showcasing its importance in managing hormonal imbalances effectively. 1
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of cabergoline reveal several distinguishing features that impact its therapeutic use. When administered, cabergoline is rapidly absorbed, achieving peak plasma concentrations within two to three hours, and its absorption is not significantly affected by food intake. Plasma protein binding is moderate, with about 41% to 42% of the drug bound, while its long elimination half-life, estimated between 63 to 69 hours, allows for less frequent dosing compared to other dopamine agonists. Cabergoline is extensively metabolized in the liver, primarily through hydrolysis into inactive metabolites, minimizing the role of cytochrome P450 enzymes. Importantly, cabergoline's pharmacokinetics remain stable in patients with renal or mild to moderate hepatic insufficiency, although significant hepatic impairment can lead to increased plasma concentrations. Overall, the pharmacokinetic profile of cabergoline supports its effective and safe use in various clinical settings, particularly in controlling prolactin levels. 1
Efficacy for Lactation Inhibition
Cabergoline has been extensively studied for its efficacy in inhibiting lactation, particularly in women who choose not to breastfeed after delivery. Early investigations, including placebo-controlled dose-ranging trials, established that a single oral dose of cabergoline could effectively decrease serum prolactin levels, a hormone crucial for lactation. These studies indicated that cabergoline doses ranging from 0.4 mg to 1 mg produced significant results compared to placebo, demonstrating an increased efficacy at higher dosages. The data from these early trials was later supported by larger comparative studies, where cabergoline was evaluated against other lactation inhibitors, specifically bromocriptine. Notably, a prominent trial by Rolland et al. reinforced the effectiveness of cabergoline, highlighting its potential as a reliable option for lactation suppression in postpartum women. 2
Comparative Studies of Cabergoline vs. Bromocriptine
In comparative trials, cabergoline was rigorously tested against bromocriptine, with a focus on their respective efficiencies in promoting lactation inhibition. In the largest trial, involving 272 healthy postpartum women, participants were assigned to receive either a single oral dose of 1 mg cabergoline or bromocriptine dosed at 2.5 mg twice daily for 14 days. The results showed that cabergoline was non-inferior to bromocriptine in terms of complete success in preventing lactation, defined as the absence of breast symptoms within the first 15 days. The documented difference of −8.82% in complete lactation inhibition suggests that cabergoline holds its ground against established alternatives. Furthermore, the incidence of rebound breast symptoms and returning serum prolactin levels was notably lower in the cabergoline-treated group, reinforcing its position as a preferable choice for women experiencing various postpartum circumstances. 2
Clinical Application and Usage for Lactation Inhibition
Recent evaluations of cabergoline's real-world application in postpartum scenarios further underscore its utility. A study conducted in Qatar revealed that a significant proportion of women prescribed cabergoline received it due to specific medical circumstances, such as stillbirth or pregnancy termination, reflecting the drug’s application beyond typical breastfeeding decisions. Notably, the majority of women began their cabergoline treatment within 27 hours post-delivery, consistent with optimal timing for effectiveness. The preferred regimen emerged as a single oral 1 mg dose, which was administered to 72% of women in the sample. This study not only confirms the practical implications of cabergoline administration during critical postpartum periods but also highlights the versatility of cabergoline in addressing lactation inhibition amidst varied maternal health challenges. Overall, cabergoline serves as a potent option for lactation inhibition, offering safety and effectiveness that fulfill the needs of postpartum women in diverse scenarios. 2
Reference
1. Shimon I. Real-world value of cabergoline in the treatment of acromegaly. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2024; 38(4): 101887.
2. Tulloch KJ, Dodin P, Tremblay-Racine F, Elwood C, Money D, Boucoiran I. Cabergoline: a review of its use in the inhibition of lactation for women living with HIV. J Int AIDS Soc. 2019; 22(6): e25322.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
This review delves into the characteristics, synthesis, and applications of Fmoc-Trp(Boc)-OH, and its role in peptide synthesis and drug development.....
Sep 23,2024APISodium thiosulfate is a chemical compound with a diverse range of applications that highlight its importance in various industries.....
Sep 23,2024APICabergoline
81409-90-7You may like
- Cabergoline
-

- $1300.00 / 1g
- 2024-09-26
- CAS:81409-90-7
- Min. Order: 1g
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 1000kg
- Cabergoline
-

- $500.00/ gram
- 2024-09-25
- CAS:81409-90-7
- Min. Order: 1gram
- Purity: 99% HPLC
- Supply Ability: 100grams
- Cabergoline
-

- $25.00 / 1kg
- 2024-09-24
- CAS:81409-90-7
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 100kg