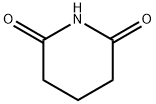
Glutarimide: Synthesis and derivatives
Aug 1,2024
Synthesis
Glutarimide has been prepared from glutaric acid and sulfamide or formamide by distillation of ammonium glutarate, by hydrolysis of pentanedinitrile with acetic acid, and by oxidation of piperidine with hydrogen peroxide.
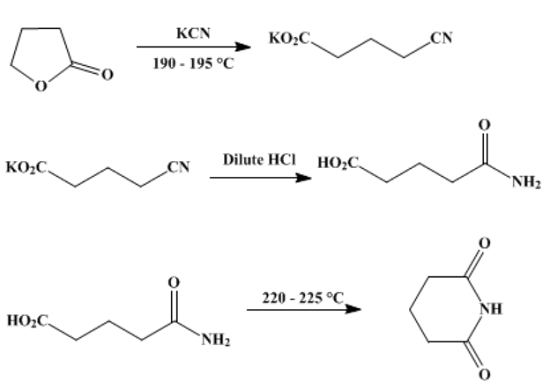
In a 500-ml three-necked flask fitted with a sealed mechanical stirrer and a reflux condenser are placed 86 g (1 mole) of γ-butyrolactone and 72 g (1.1 moles) of potassium cyanide. As the contents of the flask are stirred, the mixture is heated in an oil bath for 2 hours at a temperature of 190–195°. There is an initial vigorous reaction, which soon subsides. After the heating period, the mixture is cooled to about 100°, and the potassium salt of the cyano acid is dissolved in about 200 ml of hot water. The warm solution is cautiously acidified to Congo red by adding about 90 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid. The resultant solution, which contains glutaric acid monoamide and potassium chloride, prepares glutaric acid or glutarimide.
The solution containing the monoamide is extracted with six 50-ml portions of ether. The ether solution is dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate (or by filtering by gravity through a layer of the drying agent), and then the ether is evaporated by heating on a steam bath; the last portion is removed at reduced pressure. The oily residue of glutaric acid monoamide is placed in a 300-ml round-bottomed flask, fitted with a bent tube attached to a short condenser, and the flask is immersed in a bath held at 220–225°. Heating is continued until water no longer distils (3–4 hours). The cooled glutarimide is dissolved in about 200 ml of water, and the solution is boiled for about 30 minutes with about 2 g of charcoal. The charcoal is removed by filtration, water is removed by distillation at reduced pressure, and the dry residue is crystallized from about 125 ml of 95% ethanol, with final cooling in an ice bath. The yield of glittering white crystals of glutarimide, m.p. 152–154°, is 65.5–73.5 g (58–65%).
Glutarimide derivatives
Glutarimide antibiotics characterized by a glutarimide ring were derived mainly from Streptomyces in the past but were recently found in various strains, including Burkholderia, Pseudomonas, and other marine-derived strains. These compounds exhibit widespread pharmacological effects, such as antitumor, anti-inflammatory, and antifungal. The well-known members of this class of polyketides, iso-migrastatin (iso-MGS), lactimidomycin (LTM), cycloheximide (CHX), dorrigocins (DGN), and 9-methylstreptimidone, are best known as inhibitors of eukaryotic protein translation that have served as antitumor drug leads. The cysteine adducts of iso-MGS, NK30424A, and NK30424B could also inhibit the PLS-induced TNF-α production by suppressing the NF-kB signaling pathway. In contrast, 9-methylstreptimidone could inhibit NO production and iNOS expression in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
Sodium methyl mercaptide (Sodium thiomethoxide) is a kind of water white strong alkaline liquid that has an off-odour and can be used for the raw material of pesticides, medicine, Pigment Intermediates.....
Aug 1,2024Inorganic saltsEgrifta is the only FDA-approved prescription medication for reducing excess abdominal fat in HIV-infected and lipodystrophic patients, and is usually administered by injection.....
Aug 1,2024DrugsGlutarimide
1121-89-7You may like
- The synthesis method of neopentyl glycol
Sep 3, 2024
- Biphenyl: Chemical property and uses
Aug 13, 2024
- Putrescine and cadaverine
Aug 7, 2024
- Glutarimide
-

- $0.00 / 25KG
- 2023-10-16
- CAS:1121-89-7
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 50000KG/month
- Glutarimide
-

- $0.00 / 25KG
- 2023-09-06
- CAS:1121-89-7
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 500000kg
- Glutarimide
-

- $8.99 / 1KG
- 2022-02-25
- CAS:1121-89-7
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 100KG