How to synthesize Oxazosulfyl
Feb 23,2024
Description
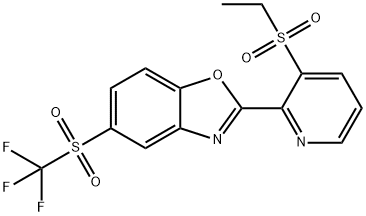
Sumitomo announced Oxazosulfyl as a new insecticide in 2017. Oxazosulfyl (2-[3-(ethylsulfonyl)-2-pyridyl]-5-(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)-1,3-benzoxazole), possessing insecticidal activity against rice pests belonging to Hemiptera, Lepidoptera, and Coleoptera was discovered[1]. The biological character of oxazosulfyl needs to be better understood because it is the first molecule in the new sulfyl class of insecticides.
Mode of action
Extracellular recordings revealed a depressed spontaneous nerve activity in the cockroaches injected with oxazosulfyl, which specifically affected the voltage-gated sodium channels (in German cockroaches (Blattella germanica) expressed in Xenopus oocytes) in the slow-inactivated state resulting in the inhibition of sodium currents. The potency of oxazosulfyl and other sodium channel blockers to block sodium channels was consistent with their insecticidal activity. Thus, the action mode of oxazosulfyl involves the state-dependent blockage of voltage-gated sodium channels[2].
Synthesis method
![Benzoxazole, 2-[3-(ethylsulfonyl)-2-pyridinyl]-5-[(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl]- Benzoxazole, 2-[3-(ethylsulfonyl)-2-pyridinyl]-5-[(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl]-](/NewsImg/2024-02-23/6384428337444034145539092.png)
The synthesis of oxazosulfyl starts from 3-chloro-2-cyanopyridine (173), which is converted by the replacement of the chloro substituent by an ethyl sulfide function and subsequent nitrile hydrolysis into the picolinic acid 175. This carboxylic acid reacts with 2-hydroxy-5-(tri- fluoromethylsulfanyl)aniline to the amide 176, cyclized by losing one equivalent water to the benzoxazole derivative 177. Finally, the oxidation of both sulfide groups in the benzoxazole and pyridine moieties to the corresponding sulfones delivers oxazosulfyl[3].
References
[1] Kamezaki, Masashi Junko Otsuki and Katsuya Natsuhara. “Insecticidal activity against rice pest of oxazosulfyl, a novel sulfyl insecticide.” Journal of Pesticide Science 43 1 (2024).
[2] Tatsuya Suzuki, Seiji Yamato. “Oxazosulfyl, a Novel Sulfyl Insecticide, Binds to and Stabilizes the Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels in the Slow-Inactivated State.” Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 69 14 (2021): 4048–4055.
[3] Stephane Jeanmart . “Synthetic approaches to the 2015–2018 new agrochemicals.” Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 39 (2021): Article 116162.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
Yes. The therapeutic fluoropyrimidines 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and 5-fluorocytosine (5-FC) have long been used to treat human cancer and severe invasive fungal infections, respectively.....
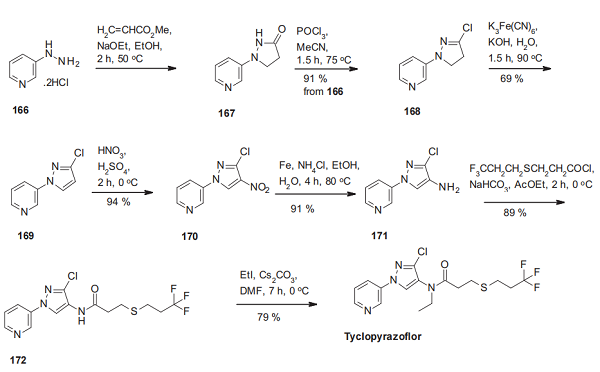
Nov 1,2024Biochemical EngineeringTyclopyrazoflor (GF-3242) is a pyridinyl–pyrazole insecticide with excellent activity against sap-feeding insects (especially against aphids), first disclosed by Dow (now Corteva) in 2013.....
Feb 23,2024Chemical pesticides ?Oxazosulfyl
1616678-32-0You may like