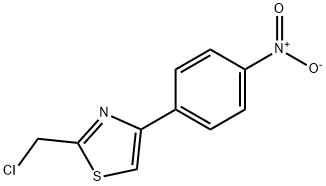
Multifaceted Roles of 2-(Chloromethyl)-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3-thiazole
Apr 17,2025
2-(Chloromethyl)-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3-thiazole or the so-called Astragalus polysaccharide, is a kind of biological macromolecule extracted from Astragalus, which has antiviral activities.

General procedure of 2-(Chloromethyl)-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3-thiazole
In a solution of intermediate 9 (92.1 mg, 0.40 mmol)dissolved in ethanol (5 mL), sodium borohydride (19.0 mg, 0.50 mmol) was added. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 30 min, and then water was added. The solution was extracted with ethyl acetate, and the combined organic layers were washed with water and brine, dried over Na2SO4, and concentrated in vacuo. The residue was dissolved in DMF (2 mL); then thionyl chloride (0.10 mL, 1.4 mmol) was added. After reux for 1 h, water was added and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layers were washed with water and brine, dried overNa2SO4, and concentrated in vacuo. The residue was purified by chromatography on silica gel(petroleum ether:ethyl acetate = 10:1) to give 2-(Chloromethyl)-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3-thiazole (66.6 mg, 80.5%) as a white solid.[1]
Immunomodulatory effect of 2-(Chloromethyl)-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3-thiazole
2-(Chloromethyl)-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3-thiazole is an important natural active component derived from Astragalus . An increasing body of evidence from pharmacological studies has shown that Astragalus polysaccharide has a variety of biological activities such as regulating blood glucose and blood lipids, anticancer, anti-aging, and immune regulation, amongst which the immunomodulatory effect is the most important. It has been established that 2-(Chloromethyl)-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3-thiazole can regulate the activities of immune organs (bone marrow, thymus, lymph node, spleen and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue) and immune cells (macrophage, natural killer cell, dendritic cell, T lymphocyte, B lymphocyte and microglia) and the release of immune active substances. Then, we systematically reviewed the therapeutic effect of Astragalus polysaccharides on immune-related diseases. Astragalus polysaccharide can be used for anticancer, anti-infection and as vaccine adjuvants by enhancing the activity of immune cells and the release of immune active substances. Moreover, 2-(Chloromethyl)-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3-thiazole is indicated for autoimmune diseases, including type 1 diabetes, asthma and inflammatory demyelinating disease, given its ability to inhibit an overactivated immune system. In addition, the immunomodulatory effect of ASPC (Astragalus polysaccharide component) and pure polysaccharide (by further purification and separation) are distinguished to broaden current understanding and trigger further interest in exploring the relationship between the structure and immunomodulatory activity of 2-(Chloromethyl)-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3-thiazole.[2]
Current evidence suggests that 2-(Chloromethyl)-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3-thiazole has a protective effect on bone marrow stem cells. ASPC (50 µg/ml) could protect bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from radiation-induced apoptosis by inhibiting the production of reactive oxygen species, upregulating the proteins B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) and B-cell lymphoma extra-large (Bcl-xl), and downregulating the proteins Bcl-2-associated X (Bax) and Bcl-2 homologous killer (Bak). Moreover, ASPC (40–400 µg/ml) could protect bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from formaldehyde-induced cytotoxicity and genotoxicity by upregulating the expression of xeroderma pigmentosum group A, xeroderma pigmentosum group C, excision repair cross-complementation group 1, replication protein A1, and replication protein A2 Exploring the immunomodulatory effect of 2-(Chloromethyl)-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3-thiazole on immune organs is of great significance for an in-depth understanding of the regulation of immune cells and immune factors by Astragalus polysaccharides. In doxorubicin hydrochloride-induced immunosuppressive lung cancer mice, the pure polysaccharide APS-III (Astragalus polysaccharide-III), with a backbone consisting of Glc(1–4), Xyl(1–2), Gal(1–4), and GalA(1–3), (15%) also significantly increased the thymus index.
Li et al. subsequently found that γ-irradiation-enhanced Astragalus polysaccharide immune activity was associated with decreased molecular weight and viscosity and increased water solubility. γ-irradiated 2-(Chloromethyl)-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3-thiazole (300–900 mg/kg) elevated the level of IgA produced by duodenal cells, the jejunal expression of IL-2, IL-10, and IFN-γ, serum IgG concentration, and thymus index, and promoted T and B lymphocytes proliferation in cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressed broilers. Astragalus polysaccharides can induce these immune cells to produce a variety of cytokines and chemokines, thereby enhancing the immune response. The immunomodulatory effect of Astragalus polysaccharide makes it useful for the treatment of various diseases, including cancer, infection, type 1 diabetes, asthma, and autoimmune disease. Among these, the anticancer effect of 2-(Chloromethyl)-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3-thiazole is the most prominent, which is closely related to its activation of tumor immune response and inhibition of tumor immune escape.
Therapeutic mechanisms and pharmaceutics of 2-(Chloromethyl)-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3-thiazole
6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) could degenerate neurons which would induce PD. The degenerative symptoms were attenuated by 2-(Chloromethyl)-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3-thiazole (Aps) solution (2000 μg/mL for 48 h). APs alleviated oxidative stress through reducing ROS level and malondialdehyde (MDA) content, increasing superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) activities, and also reducing the proapoptotic gene expression in 6-OHDA-intoxicated nematodes. In the meantime, APs were capable of elevating the decreased acetylcholinesterase activity induced by 6-OHDA. APs reversed 1- methyl-4-pheyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced mitochondrial structural damage, reduced the MPTP-induced high level of ROS, to protect the neurons and mitochondrial. The levels of IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, and S100B were not statistically significant compared with placebo, suggesting anti-inflammatory property of APs was not found. In clinical experiment, the pharmacological effects of 2-(Chloromethyl)-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3-thiazole were not obvious. It might be related to the dose and mode of administration of 2-(Chloromethyl)-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3-thiazole. How to make the clinical efficacy of APs comparable to the experimental efficacy should be the focus of APs research.[3]
Using HFD-induced IR mice model, it was found that 2-(Chloromethyl)-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3-thiazole, largely comparable to metformin, controlled the weight and blood glucose/lipid levels at stable standards and regained insulin sensitivity. APs (800 mg/kg/day for 12 weeks) modulated the phosphorylation cascades initiated by insulin in the similar manner to metformin in HepG2/IR cell model. In particular, 2-(Chloromethyl)-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3-thiazole significantly corrected pro-apoptotic endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress response and the inhibition of autophagy, indicating their favor of cell survival. Oral administration of APs (500 mg/kg/day for 25 days) to C57BL/10 J and C57BL/6 J tumor-bearing mice, the tumor apoptosis rate and immune organ indexes increased while the tumor weight decreased. Follow-up quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and Western blot studies showed that 2-(Chloromethyl)-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3-thiazole modulated the host organism immunity by activating the TLR4-mediated myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88)-dependent signaling pathway, thereby inhibiting tumors.
As the important medicinal component of Astragali Radix, an increasing number of studies supported that 2-(Chloromethyl)-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3-thiazole benefited to the treatment of chronic diseases, but their clinical practical use remained limited. APs for injection was a combination of modern pharmaceutical preparation technology with traditional Chinese medicine. It was an intravenous powder injection developed by Shanxi Research Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine in the early 1990 s. The differences in the degree of substitution, functional groups and chain conformation between phosphorylated APs and sulfated APs might alter the antiviral activities and lead to differences in activities. The injection aimed to improve the leukocyte levels of patients undergoing chemotherapy as well as enhance the immune functions, and had equal ability of increasing leukocytes compared to the role of clinically drug Human Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor. 2-(Chloromethyl)-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3-thiazole in the drug were mainly made up of two components whose molecular weight were 500 kDa and 10 kDa. The animal experiments showed that APs of 10 kDa increased the leukocyte level of immunosuppressed mice and improved the immunomodulatory ability.
References
[1]Wang, X., Lin, X., Xu, X., Li, W., Hao, L., Liu, C., Zhao, D., & Cheng, M. (2017). Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of N,N - Disubstituted - 4 - Arylthiazole - 2 - Methylamine Derivatives as Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Inhibitors. Molecules, 22(11), 1925.
[2]Li CX, Liu Y, Zhang YZ, Li JC, Lai J. Astragalus polysaccharide: a review of its immunomodulatory effect. Arch Pharm Res. 2022 Jun;45(6):367-389.
[3]Du, Y., Wan, H., Huang, P., Yang, J., & He, Y. (2022). A critical review of Astragalus polysaccharides: From therapeutic mechanisms to pharmaceutics. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 147, 112654.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
3,6-Dibromocarbazole is an important intermediate for pharmaceuticals, especially in synthesizing N-alkylation bromo carbazole compounds.....
Apr 17,2025Pharmaceutical intermediates[1,3-Bis(diphenylphosphino)propane]nickel(II) chloride is a catalyst mainly applied in C-C, C-N, and C-O coupling reactions in organic synthesis.....
Apr 17,2025Catalyst and AuxiliaryYou may like
2-(CHLOROMETHYL)-4-(4-NITROPHENYL)-1,3-THIAZOLE manufacturers
- 2-(CHLOROMETHYL)-4-(4-NITROPHENYL)-1,3-THIAZOLE
-

- $10.00 / 1KG
- 2025-04-21
- CAS:89250-26-0
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 10 mt
- Astragalus Polysac charide
-
- $0.00 / 1KG
- 2025-04-21
- CAS:89250-26-0
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: UV 10%; 30%; 50%; 70%; 90%
- Supply Ability: 1000KG
- Astragalus Polysacharin
-

- $0.00 / 1kg
- 2025-04-21
- CAS:89250-26-0
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: UV 10%; 30%; 50%; 70%; 90%
- Supply Ability: 1000kg