Synthesis of Thiophene
Jan 26,2022
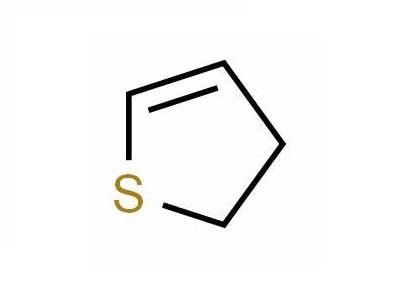
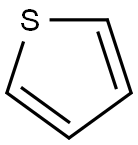
Thiophene is a five-membered, fully unsaturated, coplanar, sulfur heterocycle comprised of four carbon atoms and one sulfur atom, formed by replacement of the methylene group of 1,3-cyclopentadiene by sulfur. It was discovered by Victor Meyer in 1882 as a contaminant of commercial benzene. The development of the blue color from commercial benzene on heating with isatin and concentrated sulfuric acid was considered to be due to the formation of “indophenine,” a blue dye from thiophene present as an impurity. This mystery was resolved when pure benzene obtained by the decarboxylation of benzoic acid failed to give a blue-colored dye and also by isolation of a blue indophenine dye from commercial benzene.

Physical properties
The pKa of thiophene is (−4.5) lower than furan (−2.1) and pyrrole (+10.4). The smaller pKa value of thiophene indicates that it is least basic. The calculated π-electron density on the ring atoms is depicted in the following diagram. It is obvious from the π-electron density on the ring atom that C2 is in a more favorable and preferential position for electrophilic substitution compared to C3. The dipole moment of thiophene is (0.5 D) less than pyrrole (1.6 D) and furan (1.7 D). The higher the dipole moment of the compound, the stronger the electron withdrawal from C to heteroatom and vice versa. Thus in thiophene there is a weak electron withdrawal from C–S because its dipole moment is smaller.
Synthesis
This reaction is a cyclocondensation of α-methylene carbonyl compounds with alkyl cyanoacetate or malononitrile and sulfur in the presence of an organic base such as morpholine or piperidine in ethanol to deliver 2-aminothiophenes.

Under analogous conditions, cyclocondensation of cyclic ketones such as cyclohexanone or cyclopentanone with malononitrile or cyanoacetate and sulfur afforded bicyclic thiophene in high yields.

This is a widely used methodology for the construction of 2,5-disubstituted thiophene by cyclodehydration of 1,4-diketones in the presence of sulfurizing agents such as phosphorus pentasulfide or Lawesson’s reagent.

- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Why thiophene is commonly used in drugs? Nov 9, 2022
In medicinal chemistry, thiophene derivatives are extremely significant heterocycles exhibiting remarkable applications in different disciplines.
- Unique properties of thiophene May 5, 2022
Thiophene, systematic name 1-thia-2,4-cyclopentadiene, CAS number 110-02-1. From the structural point of view, thiophene is a heterocyclic compound and a thioether.
1,3-Dioxolane is a five-membered, nonplanar, fully saturated oxygen heterocycle with two oxygen atoms at the 1,3-positions of the cyclic system. It closely resembles THF because the methylene group at position 3 is replaced by an oxygen ato....
Jan 26,2022Organic Chemistry2,3-Dihydrothiophene, also known as 2-thiolene, is a five-membered, nonaromatic, partially saturated sulfur heterocycle comprised of four carbon atoms and one sulfur atom, derived by the partial reduction of one of the two double bonds of t....
Jan 26,2022Organic ChemistryThiophene
110-02-1You may like
- Thiophene
-

- $20.00 / 1kg
- 2025-03-31
- CAS:110-02-1
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 10 mt
- Thiophene
-

- $900.00 / 1T
- 2025-03-21
- CAS:110-02-1
- Min. Order: 25KG
- Purity: 99.99%
- Supply Ability: 200ton
- Thiophene
-

- $9.00 / 200Kg/Drum
- 2025-03-07
- CAS:110-02-1
- Min. Order: 16T
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 1000tons/month